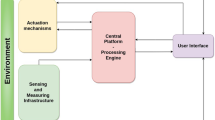
Abstract
The evolution and increasing commoditization of home and building automation systems (HBAS) is contributing to their widespread adoption. However, an effort must still be made to render them usable, intelligent, highly adaptive and able to fulfill users’ needs. When distinct users interact with such a system, their intentions are likely to be different, often resulting in conflicting situations, which the system ought to recognize and, if possible, resolve automatically. However, conflict detection and resolution in HBAS are not yet fully understood. This work aims at investigating conflict in Ambient Intelligence systems, namely those supported by HBAS. Our main contribution is a systematization and review of existing literature concerning conflict detection and resolution in these systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadi D, Madden S, Lindner W (2005) REED: robust, efficient filtering and event detection in sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 31st international conference on very large data bases, VLDB Endowment, VLDB ’05, pp 769–780
Abielmona R, Petriu E, Whalen T (2010) Distributed intelligent sensor agent system for environment mapping. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 1(2):95–110
Agarwal Y, Balaji B, Gupta R, Lyles J, Wei M, Weng T (2010) Occupancy-driven energy management for smart building automation. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM workshop on embedded sensing systems for energy-efficiency in buildings, ACM, BuildSys ’10, pp 1–6
Aipperspach R, Cohen E, Canny J (2006) Modeling human behavior from simple sensors in the home. Pervasive computing. In: Lecture notes in computer science, vol 3968, Springer, Berlin, pp 337–348
Alcañiz M, Rey B (2005) New technologies for ambient intelligence. Ambient Intell 6(1):3–15
Alshabi W, Ramaswamy S, Itmi M, Abdulrab H (2007) Coordination, cooperation and conflict resolution in multi-agent systems. In: Innovations and advanced techniques in computer and information sciences and engineering, Springer, Berlin, pp 495–500
Armac I, Kirchhof M, Manolescu L (2006) Modeling and analysis of functionality in eHome systems: dynamic rule-based conflict detection. In: 13th annual IEEE international symposium and workshop on engineering of computer based systems, 2006, ECBS 2006
Baldauf M, Dustdar S, Rosenberg F (2007) A survey on context-aware systems. Int J Ad Hoc Ubiquitous Comput (IJAHUC) 2(4):263–277
Ballagas R, Ringel M, Stone M, Borchers J (2003) iStuff: a physical user interface toolkit for ubiquitous computing environments. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems, ACM, CHI ’03, pp 537–544
Becker C, Handte M, Schiele G, Rothermel K (2004) PCOM—a component system for pervasive computing. In: Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE annual conference on pervasive computing and communications workshops, 2004, pp 67–76
Bell D, Grimson J (1992) Distributed Database Systems. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Bensaid N, Mathieu P (1997) A framework for cooperation in hierarchical multi-agent systems
Bottaro A, Gerodolle A (2008) Home SOA: facing protocol heterogeneity in pervasive applications. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE international conference on pervasive services, ACM, ICPS ’08, pp 73–80
Bucceri R (2006) Latest technology in automated home control: system design manual using X-10 & hardwired protocols. Silent Servant Inc.
Buchmayr M, Kurschl W (2011) A survey on situation-aware ambient intelligence systems. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 2(3):175–183
Capra L, Emmerich W, Mascolo C (2003) CARISMA: context-aware reflective middleware system for mobile applications. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 29(10):929–945
Casti J (1989) Alternate realities: mathematical models of nature and man. Wiley, New York
Chalmers D (2011) Sensing and systems in pervasive computing: engineering context aware systems. Springer, Berlin
Cialdini R (2001) Harnessing the science of persuasion. Harv Business Rev 79(9):72–81
Cook D, Das S (2004) Smart environments: technology, protocols and applications. In: Wiley Series on Parallel and Distributed Computing. Wiley, New York
Coombs C, Avrunin G (1988) The structure of conflict. L. Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale
Coutaz J, Fontaine E, Mandran N, Demeure A (2010) About composing our own smart home. In: Proceedings of the international conference on advanced visual interfaces, ACM, AVI ’10, pp 405–406
Cziker A, Chindris M, Miron A (2007) Implementation of fuzzy logic in daylighting control. In: 11th international conference on intelligent engineering systems, 2007, INES 2007., pp 195–200
Davidoff S, Lee M, Yiu C, Zimmerman J, Dey A (2006) Principles of smart home control. In: UbiComp 2006: ubiquitous computing. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4206. Springer, Berlin, pp 19–34
Deja R, Slezak D (2001) Rough set theory in conflict analysis. In: New frontiers in artificial intelligence. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 2253. Springer, Berlin, pp 349–353
Dey A (2001) Understanding and using context. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 5(1):4–7
de Ruyter B, Saini P, Markopoulos P, van Breemen A (2005) Assessing the effects of building social intelligence in a robotic interface for the home. Interact Comput 17(5):522–541
Doulos L, Tsangrassoulis A, Topalis F (2007) The impact of colored glazing and spectral response of photosensors in the estimation of daylighting energy savings. In: Proceedings of the 2nd PALENC Conference and the 28th AIVC Conference
Edwards W, Grinter R (2001) At home with ubiquitous computing: seven challenges. In: Ubicomp 2001: ubiquitous computing. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 2201. Springer, Berlin, pp 256–272
Endsley M (1988) Design and evaluation for situation awareness enhancement. In: Proceedings of the human Factors and Ergonomics Society 32nd Annual Meeting, Human Factors Society, pp 97–101
Epstein G, McCowan B, Birleanu D (2003) Integrating daylighting and electrical lighting for premium efficiency and performance. GreenBuild conference, US Green Building Council
Findlater L, Gajos K (2009) Design space and evaluation challenges of adaptive graphical user interfaces. AI Mag 30(4):68–73
Fisher R (2000) Sources of conflict and methods of resolution. The American University, Washington, DC
Floyd D, Parker D (1995) Field commissioning of a daylight-dimming lighting system. In: Right light 3: proceedings of the 3rd European conference on energy-efficient lighting
Fogg B (2003) Persuasive technology: using computers to change what we think and do. In: Morgan Kaufmann series in interactive technologies. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Burlington
Furey E, Curran K, Kevitt P (2012) Probabilistic indoor human movement modeling to aid first responders. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput pp 1–11
Furlong G (2005) The conflict resolution toolbox: models and maps for analyzing, diagnosing and resolving conflict. Wiley, Canada
Galasiu A, Atif M, MacDonald R (2004) Impact of window blinds on daylight-linked dimming and automatic on/off lighting controls. Solar Energy 76(5):523–544
García-Herranz M, Haya P, Alamán X, Martín P (2007) Easing the smart home: augmenting devices and defining scenario. In: 2nd international symposium on ubiquitous computing and ambient intelligence. Thomson editorial, pp 67–74
Garg V, Bansal N (2000) Smart occupancy sensors to reduce energy consumption. Energy Build 32(1):81–87
Ghanam Y, Shouman M, Greenberg S, Maurer F (2009) Object-specific interfaces in smart homes. Research report 2009-937-16, Department of Computer Science, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada
Granzer W, Kastner W, Neugschwandtner G, Praus F (2006) A modular architecture for building automation systems. In: IEEE international workshop on factory communication systems, 2006, pp 99–102
Gross T (2008) Cooperative ambient intelligence: towards autonomous and adaptive cooperative ubiquitous environments. Int J Auton Adapt Commun Syst 1(2):270–278
Ha T, Jung J, Oh S (2006) Method to analyze user behavior in home environment. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 10(2):110–121
Hasan M, Anh K, Mehedy L, Lee Y, Lee S (2006) Conflict resolution and preference learning in ubiquitous environment. In: Computational intelligence. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4114. Springer, Berlin, pp 355–366
Huerta-Canepa G, Lee D (2008) A multi-user ad-hoc resource manager for smart spaces. In: International symposium on a world of wireless, mobile and multimedia networks, 2008, pp 1–6
Jacak W, Proll K (2007) Heuristic approach to conflict problem solving in an intelligent multiagent system. In: Computer aided systems theory—EUROCAST 2007, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4739, Springer, Berlin, pp 772–779
Jiao S, Liu Y, Hu H, Wei D, Zhang Y (2008) Dynamic policy access model based on formal concept analysis. In: 4th international conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing, 2008, WiCOM ’08, pp 1–5
Jiao S, Liu Y, Qi X, Zhu Y, Wang J (2009) Detecting conflict policy rules with concept lattice. In: 5th international conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing, 2009, WiCom ’09, pp 1–4
Kaptein M, Markopoulos P, de Ruyter B, Aarts E (2009) Can you be persuaded? Individual differences in susceptibility to persuasion. In: Proceedings of the 12th IFIP TC 13 international conference on human–computer interaction: Part I, INTERACT ’09. Springer, Berlin, pp 115–118
Kawsar F, Nakajima T (2007) Persona: a portable tool for augmenting proactive applications with multimodal personalization support. In: Proceedings of the 6th international conference on mobile and ubiquitous multimedia, ACM, MUM ’07, pp 160–168
Kindberg T, Fox A (2002) System software for ubiquitous computing. IEEE Pervasive Comput 1(1):70–81
Korpipaa P, Mantyjarvi J, Kela J, Keranen H, Malm E (2003) Managing context information in mobile devices. IEEE Pervasive Comput 2(3):42–51
Kovach-Hebling A, Goller M, Herkel S, Wienold J (1997) Assessing the energy saving potential of daylighting technologies for non-residential buildings in Germany. In: Right light 4: proceedings of the 4th European conference on energy-efficient lighting
Kung H, Lin C (2006) Application-layer context-aware services for pervasive computing environments. In: First international conference on innovative computing, information and control, 2006, ICICIC ’06, vol 3, pp 229–232
Lah M, Zupancic B, Krainer A (2005) Fuzzy control for the illumination and temperature comfort in a test chamber. Build Environ 40(12):1626–1637
Lah M, Zupancic B, Peternelj J, Krainer A (2006) Daylight illuminance control with fuzzy logic. Solar Energy 80(3):307–321
Ledlie J, Ng C, Holland D (2005) Provenance-aware sensor data storage. In: 21st international conference on data engineering workshops, 2005
Lee E, DiBartolomeo D, Vine E, Selkowitz S (1998) Integrated performance of an automated Venetian Blind/electric lighting system in a full-scale private office. In: Proceedings of the ASHRAE/DOE/BTECC conference, thermal performance of the exterior envelopes of buildings VII
Li K (2012) Smart home technology for telemedicine and emergency management. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput, pp 1–12
LIFX (2012) Lifx: The light bulb re-invented. http://lifx.co Accessed on October 2012)
Littlefair P, Ortiz J, Bhaumik C (2010) A simulation of solar shading control on UK office energy use. Build Res Inf 38(6):638–646
Lupu E, Sloman M (1997) Conflict analysis for management policies. In: Proceedings of the 5th IFIP/IEEE international symposium on integrated network management V: integrated management in a virtual world. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 430–443
Maeda Y, Senoo K, Tanaka H (1999) Interval density functions in conflict analysis. In: New directions in rough sets, data mining, and granular-soft computing. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 1711. Springer, Berlin, pp 382–389
Markopoulos P (2005) Designing ubiquitous computer human interaction: the case of the connected family. In: Future interaction design. Springer, Berlin, pp 125–149
Markopoulos P, de Ruyter B, Privender S, van Breemen A (2005) Case study: bringing social intelligence into home dialogue systems. Interactions 12(4):37–44
Masoumzadeh A, Amini M, Jalili R (2007) Conflict detection and resolution in context-aware authorization. In: 21st international conference on advanced information networking and applications workshops, 2007, AINAW ’07. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, pp 505–511
Maybury M, Wahlster W (1998) Intelligent user interfaces: an introduction. In: Readings in intelligent user interfaces. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., Burlington, pp 1–13
Merz H, Hansemann T, Hübner C (2009) Building automation: communication systems with EIB/KNX, LON und BACnet. Signals and communication technology, Springer, Berlin
Miki M, Hiroyasu T, Imazato K (2004) Proposal for an intelligent lighting system, and verification of control method effectiveness. In: IEEE conference on cybernetics and intelligent systems, 2004, vol 1, pp 520–525
Moore C (2003) The mediation process: practical strategies for resolving conflict. Jossey-Bass Publishers, San Francisco
Nakashima H, Aghajan H, Augusto J (eds) (2010) Handbook of ambient intelligence and smart environments. Springer, Berlin
Neisse R, Wegdam M, van Sinderen M (2008) Trustworthiness and quality of context information. In: The 9th international conference for young computer scientists, 2008, ICYCS 2008, pp 1925–1931
Newsham G, Mancini S (2006) The Potential for demand responsive lighting in non-daylit offices. LEUKOS J Illum Eng Soc 3(2):105–120
Nichols J, Myers B, Higgins M, Hughes J, Harris T, Rosenfeld R, Pignol M (2002) Generating remote control interfaces for complex appliances. In: Proceedings of the 15th annual ACM symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, ACM, UIST ’02, pp 161–170
Park I, Lee D, Hyun S (2005) A Dynamic Context-Conflict Management Scheme for Group-Aware Ubiquitous Computing Environments. In: 29th annual international computer software and applications conference, 2005, COMPSAC 2005, vol 1. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, pp 359–364
Park T, Hong S (2006) Development of an experimental model of BACnet-based lighting control system. In: IEEE international conference on industrial informatics, 2006, pp 114–119
Pawlak Z (1984) On conflicts. Int J Man Mach Stud 21(2):127–134
Ramachandran V, Ramaswamy S, Rajan P (2001) Complex negotiation protocols for a distributed simulation environment. Summer computer simulation conference. Orlando, FL
Ranganathan A, Campbell R (2003) An infrastructure for context-awareness based on first order logic. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 7(6):353–364
Rashidi P, Cook D (2009) Keeping the resident in the loop: adapting the smart home to the user. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A Syst Humans 39(5):949–959
Reinisch C, Kofler M, Iglesias F, Kastner W (2011) Thinkhome energy efficiency in future smart homes. EURASIP J Embed Syst 2011(1):18
Remagnino P, Foresti G (2005) Ambient intelligence: a new multidisciplinary paradigm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A Syst Humans 35(1):1–6
Retkowitz D, Kulle S (2009) Dependency management in smart homes. Distributed applications and interoperable systems. In: Lecture notes in computer science, vol 5523. Springer, Berlin, pp 143–156
Richman E, Dittmer A, Keller J (1995) Field analysis of occupancy sensor operation: parameters affecting lighting energy savings. In: Proceedings of the illuminating engineering society of North America 1995 Annual Conference
Roberts F (1976) Discrete mathematical models, with applications to social, biological, and environmental problems. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Saini P, de Ruyter B, Markopoulos P, van Breemen A (2005) Benefits of Social intelligence in home dialogue systems. In: Human–computer interaction—INTERACT 2005. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 3585. Springer, Berlin, pp 510–521
Sandole D, Byrne S, Sandole-Staroste I, Senehi J (2009) Handbook of conflict analysis and resolution. Routledge, London
Santos A, Tarrataca L, Cardoso J, Ferreira D, Diniz P, Chainho P (2009) Context inference for mobile applications in the UPCASE Project. In: Mobilewireless middleware, operating systems, and applications. Lecture notes of the institute for computer sciences, social informatics and telecommunications engineering, vol 7. Springer, Berlin, pp 352–365
Satoh I (2007) Visual components for pervasive computing management. In: IEEE international conference on pervasive services, pp 19–28
Schaefer R, Muller W, Groppe J (2006) Profile processing and evolution for smart environments. In: Ubiquitous intelligence and computing. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4159. Springer, Berlin, pp 746–755
Silva T, Ruiz L, Loureiro A (2010) How to conciliate conflicting users’ interests for different collective, ubiquitous and context-aware applications? In: IEEE 35th conference on local computer networks (LCN), 2010, pp 288–291
Silva T, Ruiz L, Loureiro A (2011) Conflicts treatment for ubiquitous collective and context-aware applications. J Appl Comput Res 1(1):33–47
Skowron A, Deja R (2002) On some conflict models and conflict resolutions. Romanian J Inf Sci Technol 5(1–2):69–82
Skowron A, Ramanna S, Peters J (2006) Conflict analysis and information systems: a rough set approach. In: Rough sets and knowledge technology. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4062. Springer, Berlin, pp 233–240
Slezak D, Wang G, Szczuka M, Düntsch I, Yao Y (2005) Rough sets, fuzzy sets, data mining, and granular computing. In: 10th international conference, RSFDGrC 2005. Lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin
Smartthings (2012) Smarthings: make your world smarter. http://smartthings.com. Accessed on October 2012
Sorrentino F (2009) Ambient intelligence. In: Encyclopedia of information communication technology, IGI Global, pp 32–39
Spinellis D (2003) The information furnace: consolidated home control. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 7(1):53–69
Syukur E, Loke S, Stanski P (2005) Methods for policy conflict detection and resolution in pervasive computing environments. In: Policy management for web workshop in conjunction with WWW’05 conference, ACM, pp 10–14
Szewcyzk S, Dwan K, Minor B, Swedlove B, Cook D (2009) Annotating smart environment sensor data for activity learning. Technol Health Care 17(3):161–169
Tapia D, Abraham A, Corchado J, Alonso R (2010a) Agents and ambient intelligence: case studies. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 1(2):85–93
Tapia D, Rodríguez S, Corchado J (2010b) A distributed ambient intelligence based multi-agent system for Alzheimer health care. In: Pervasive computing, computer communications and networks. Springer, Berlin, pp 181–199
Thomas K (1992) Conflict and conflict management: reflections and update. J Organ Behav 13(3):265–274
Thomas K, Kilmann R (1978) Comparison of four instruments for measuring conflict behavior. Psychol Rep 42 (3):2
Tuttlies V, Schiele G, Becker C (2007) COMITY: conflict avoidance in pervasive computing environments. In: On the move to meaningful internet systems 2007: OTM 2007 workshops. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4806. Springer, Berlin, pp 763–772
Venkatesh V, Morris M, Davis G, Davis F (2003) User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS Q 27(3):425–478
Vernon P (1933) Some characteristics of the good judge of personality. J Soc Psychol 4(1):42–57
Wang W, Ting S (2011) Development of a computational simulation model for conflict management in team building. Int J Eng Business Manag 3(2):9–15
Weiser M (1991) The computer for the twenty-first century. Sci Am 265(3):94–104
Weiser M (1993) Hot topics: ubiquitous computing. IEEE Comput 26(10):71–72
Welbourne E, Lester J, LaMarca A, Borriello G (2005) Mobile context inference using low-cost sensors. In: Location- and context-awareness. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 3479. Springer, Berlin, pp 95–127
Yamazaki T (2007) The ubiquitous home. Int J Smart Home (IJSH) 1(1):17–22
Zhou H, Rao M, Chuang K (1993) Artificial intelligence approach to energy management and control in the HVAC process: an evaluation, development and discussion. Dev Chem Eng Mineral Process 1(1):42–51
Zimmer T (2004) Towards a better understanding of context attributes. In: Proceedings of the second IEEE annual conference on pervasive computing and communications workshops, 2004, pp 23–27
Acknowledgments
The work reported in this article was supported by national Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) funds under contract PEst-OE/EEI/LA0021/2011 and grant SFRH/BD/47409/2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Resendes, S., Carreira, P. & Santos, A.C. Conflict detection and resolution in home and building automation systems: a literature review. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 5, 699–715 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-013-0184-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-013-0184-9