Abstract
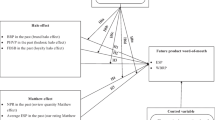
Logistics service as an important key link between online take-out platform and offline users. Its quality directly affects customer service perception and experience, but also lead to the heart of the willingness of consumers to re-use. So a framework constructed for understanding logistics service quality on consumers’ behavioral psychology is focused on, suitable service encounter points (function encounter, the distributor encounter, service results encounter, word-of-mouth encounter have been identified from the literature and the connotation of service encounter in logistics service. In view of the limitations of traditional statistical analysis methods in dealing with Likert scale data and the fuzziness of scale evaluation grade, a combination of statistical analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation is used to analyze the scale. Then combined with the logical connection between perceived value, customer satisfaction and behavioral psychology in the classic American Customer Satisfaction Index Model model, emotional attachment of platform as the adjustment variable. The findings indicate that the four encounter points of online take-out logistics service are positively related to customer purchase satisfaction and perceived value. Additionally, the most significant impact on the perceived value is the functional encounter and the distributor encounter, and the most significant impact on the customer satisfaction is the service results encounter and word-of-mouth encounter; platform emotional attachment positively regulates the positive correlation between perceived value/customer satisfaction and behavioral psychology. So this research extends the theory of service encounter to online delivery logistics service quality evaluation, which is a further expansion of the connotation of service encounter and provides the platform with suggestions to pay attention to the flaw of logistics service and improve service.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhishek D, Johnson LW, Charles WD et al (2018) Consumer emotional brand attachment with social media brands and social media brand equity. Eur J Mark 43(3):276–292
Ali F, Amin M, Cobanoglu C (2016) An integrated model of service experience, emotions, satisfaction, and price acceptance: an empirical analysis in the Chinese hospitality industry. J Hosp Market Manag 25(4):449–475
Angelova B, Zekiri J (2011) Measuring customer satisfaction with service quality using American Customer Satisfaction Model (ACSI Model). Int J Acad Res Bus Soc Sci 1(3):232
Bhattacharjya J, Ellison A, Tripathi S (2016) An exploration of logistics-related customer service provision on Twitter: the case of e-retailers. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 46(6/7):659–680
Chang CS, Chen SY, Lan YT (2013) Service quality, trust, and patient satisfaction in interpersonal-based medical service encounters. BMC Health Serv Res 13(1):22–32
Curaković D, Šikora I, Garača V et al (2013) The degree of consumer satisfaction with hotel services. Revista de turism-studii si cercetari in turism 15:6–11
Delcourt C, Gremler DD, De Zanet F, van Riel AC (2017) An analysis of the interaction effect between employee technical and emotional competencies in emotionally charged service encounters. J Serv Manag 28(1):85–106
Demong NAR, Othman AK, Bawasa S (2016) Influencing factors on customer satisfaction towards American Brands in the Food and Beverage Industry in Malaysia. Adv Bus Res Int J 12(3):69–76
Fornell C (1992) A national customer satisfaction barometer: the Swedish experience. J Manag 56(1):6–21
Hsieh PL (2013) Perceived opportunism (PO) in e-return service encounters. Manag Serv Qual Int J 23(2):96–110
Hwang SY, Kim S (2018) Does mIM experience affect satisfaction with and loyalty toward O2O services? Comput Hum Behav 82:70–80
Hyun S, Kim I (2014) Identifying optimal rapport-building behaviors in inducing patrons’ emotional attachment in luxury restaurants. J Hosp Tour Res 38(2):162–198
Jang YJ, Kim WG, Lee HY (2015) Coffee shop consumers’ emotional attachment and loyalty to green stores: the moderating role of green consciousness. Int J Hosp Manag 44(2):146–156
Jiao Z (2016) Service mode and development trend of the “last-mile delivery” of e-commerce logistics. In: Wang L, Lee S, Chen P, Jiang X, Liu B (eds) Contemporary logistics in China. Springer, Singapore, pp 239–261
Jiménez FR, Voss KE (2014) An alternative approach to the measurement of emotional attachment. Psychol Mark 31(5):360–370
Larivière B et al (2017) “Service Encounter 2.0”: an investigation into the roles of technology, employees and customers. J Bus Res 79(2):238–246
Lin IY, Mattila AS (2010) Restaurant service scape, service encounter, and perceived congruency on customers’ emotions and satisfaction. J Hosp Mark Manag 19(8):819–841
Liu W, Xu P (2014) A study on influencing factors of the helpfulness of online reviews in O2O of restaurant industry-based on tobit model. Chin J Manag Sci 5(24):168–176
Oliver RL (1999) Whence consumer loyalty? J Mark 34(63):33–44
Paddeu D, Fancello G, Fadda P (2017) An experimental Customer Satisfaction Index to evaluate the performance of city logistics services. Transport 32(3):262–271
Raji MNA, Zainal A (2017) The effect of customer perceived value on customer satisfaction: a case study of Malay upscale restaurants. Geogr Malays J Soc Space 12(3):593–598
Rao S, Goldsby TJ, Griffis SE et al (2011) Electronic logistics service quality (e-LSQ): its impact on the customer’s purchase satisfaction and retention. J Bus Logist 32(2):167–179
Singh S (2013) Positive service encounter: a tool for customer loyalty in retail. J Bus Theory Pract 1(2):244–246
Soh KL, Chin SH, Wong WP (2017) A theoretical model to investigate customer loyalty on logistics service providers for sustainable business performance. Int J Bus Perform Supply Chain Model 7(3):212–223
Vlachos PA (2012) Corporate social performance and consumer-retailer emotional attachment: the moderating role of individual traits. Eur J Mark 46(11/12):1559–1580
Voxman W (2001) Canonical representations of discrete fuzzy numbers. Fuzzy Sets Syst 118(3):457–466
Wang L, Bo Y (2018) Research on o2o take-away restaurant recommendation system: taking ele.me app as an example. Clust Comput 7(4):1–9
Wei F (2013) Study on E-commerce logistics evaluation system optimization strategy from the perspective of ser-vice encounter. J Converg Inf Technol 8(6):59–66
Wu TJ, Zhao RH, Tzeng SY (2015) An empirical research of consumer adoption behavior on catering transformation to mobile O2O. J Interdiscip Math 18(6):769–788
Zehir C, Narcıkara E (2016) E-service quality and e-recovery service quality: effects on value perceptions and loyalty intentions. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 229:427–443
Acknowledgements
This research was financially support by the China National Nature Science Found (71401090, 71531009) and the project of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (no. 2018M643214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Zhang, W., He, W. et al. Research on customer purchase behaviors in online take-out platforms based on semantic fuzziness and deep web crawler. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 11, 3371–3385 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01533-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01533-6