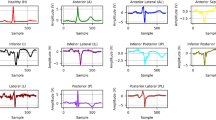
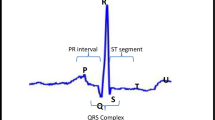
Abstract
Arrhythmia classification is crucial in electrocardiogram (ECG) based automatic cardiovascular disease diagnosis, e.g., to help prevent stroke or sudden cardiac death. However, the complex individual differences in ECG morphology make it challenging in accurately categorizing arrhythmia heartbeats. To promote robustness of the algorithm for individual differences, we propose a novel ECG arrhythmia classification method with stacked sparse auto-encoders (SSAEs) and a softmax regression (SF) model. The SSAEs is employed to hierarchically extract high-level features from huge amount of ECG data. Features are extracted automatically such that no individual difference in feature selection will bias extraction accuracy. Moreover, the input can be reconstructed completely by the features in each level of the auto-encoder. The SF is then trained to serve as a classifier for discriminating six different types of arrhythmia heartbeats. Computational experiments and comparative analyses are presented to validate the effectiveness of the theoretical models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afkhami RG, Azarnia G, Tinati MA (2016) Cardiac arrhythmia classification using statistical and mixture modeling features of ECG signals. Pattern Recognit Lett 70:45–51
Acir N (2005) Classification of ECG beats by using a fast least square support vector machines with a dynamic programming feature selection algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 14(4):299–309
Bengio Y (2009) Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and trends. Mach Learning 2(1):1–127
Braccini G, Edenbrandt L, Lagerholm M, Peterson C, Rauer O, Rittner R, Sornmo L (1997) Self-organizing maps and Hermite functions for classification of ECG complexes. Comp Cardiol. doi:10.1109/CIC.1997.647924
Chazal P, Reilly RB (2003) Automatic classification of ECG beats using waveform shape and heart beat interval features. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal (ICASSP), Hong Kong, China
Dilmac S, Korurek M (2015) ECG heart beat classification method based on modified ABC algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput 36:641–655
Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PC, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB, Peng C-K, Stanley HE (2000) PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23):e215–e220 
Hu YZ, Palreddy S, Tompkins WJ (1997) A patient-adaptable ECG beat classifier using a mixture of experts approach. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. doi:10.1109/10.623058
Javadi M, Arani SA, Sajedin A, Ebrahimpour R (2013) Classification of ECG arrhythmia by a modular neural network based on mixture of experts and negatively correlated learning. Biomed Signal Process Control 8(3):289–296
Kutlu Y, Kuntalp D (2012) Feature extraction for ECG heartbeats using higher order statistics of WPD coefficients. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 105(3):257–267
Khazaee A, Ebrahimzadeh A (2010) Classification of electrocardiogram signals with support vector machines and genetic algorithms using power spectral features. Biomed Signal Process Control 5(4):252–263
Kiranyaz S, Ince T, Gabbouj M (2016) Real-time patient-specific ECG classification by 1-D convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63(3):664–675
Linh TH, Osowski S, Stodolski M (2003) On-line heart beat recognition using Hermite polynomials and neuro-fuzzy network. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. doi:10.1109/TIM.2003.816841
Liu DC, Nocedal J (1989) On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale optimization. Math Program 45(1):503–528
Li TY, Min Z (2016) ECG classification using wavelet packet entropy and random forests. Entropy 18(285):1–16
Minami K, Nakajima H, Toyoshima T (1999) Real-time discrimination of ventricular tachyarrhythmia with Fourier-transform neural network. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 46(2):179–185
Moody GB, Mark RG (2001) The impact of the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database. IEEE Eng Med Biol 20(3):45–50
Melgani F, Bazi Y (2008) Classification of electrocardiogram signals with support vector machines and particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 12(5):667–677
Ozbay Y, Tezel G (2010) A new method for classification of ECG arrhythmias using neural network with adaptive activation function. Digit Signal Process 20(4):1040–1049
Osowski S, Linh TH (2001) ECG beat recognition using fuzzy hybrid neural network. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 48(11):1265–1271
Rahhal MM, Bazi Y, Alhichri H, Alajlan N, Melgani F, Yager RR (2016) Deep learning approach for active classification of electrocardiogram signal. Inf Sci 345:340–354
Sandoe E, Sigurd B (1992) Arrhythmia: a guide to clinical electrocardiology. Ann Emerg Med 21(10):1302
Ubeyli ED (2009) Statistics over features of ECG signals. Expert Syst Appl 36(5):8758–8767
Wang JS, Chiang WC, Hsu YL, Yang YT (2013) ECG arrhythmia classification using a probabilistic neural network with a feature reduction method. Neuro Comput 116:38–45
Xu J, Xiang L, Liu Q, Gilmore H, Wu J, Tang J, Madabhushi A (2015) Stacked sparse autoencoder (SSAE) for nuclei detection on breast cancer histopathology image. IEEE Trans Med Imaging PP 99:1
Yu SN, Chou KT (2008) Integration of independent component analysis and neural networks for ECG beat classification. Expert Syst Appl 34(4):2841–2846
Yu SN, Chen YH (2007) Electrocardiogram beat classification based on wavelet transformation and probabilistic neural network. Pattern Recogn Lett 28(10):1142–1150
Zidelmal Z, Amirou A, Ould-Abdeslam D, Merckle J (2013) ECG beat classification using a cost sensitive classifier. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 111(3):570–577
Zeng R, Wu JZ, Shao ZH, Senhadji L, Shu HZ (2014) Qunternion softmax classifier. Electron Lett 50(25):1929–1931
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by two grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61203160, 61673158) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (F2015201112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Bai, Y., Lin, F. et al. A novel electrocardiogram arrhythmia classification method based on stacked sparse auto-encoders and softmax regression. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 9, 1733–1740 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0677-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0677-5