Abstract
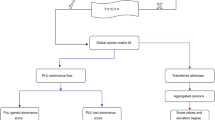
Probabilistic linguistic term sets (PLTSs) are an effective tool in keeping with the habits of decision makers (DMs). However, in multi-criteria group decision making (MCGDM) problems, it is necessary to deal with the information reliability problem because of the difference of the DMs’ knowledge backgrounds and knowledge structures. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel concept called probabilistic reliable linguistic term sets. Based on which, some basic operations, comparison laws, distance measures, similarity measures and aggregation operators are defined. After that, we propose the probabilistic reliable linguistic gained and lost dominance score method to cope with MCGDM problems, and we further apply the proposed method to solve an investment project selection problem about lucky bag machine. Finally, we make some comparative analyses to verify the effectiveness and highlight the strength of the proposed method compared with four methods, i.e., the aggregation-based method, the TOPSIS method under probabilistic reliable linguistic environment, the gained and lost dominance score (GLDS) method with probabilistic linguistic information and the GLDS method with hesitant linguistic information.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirsina J, Abbas NA (2018) Portfolio selection using Z-number theory: two solution methodologies. Int J Fuzzy Syst 20:2484–2496
Babanli MB, Huseynov VM (2016) Z-number-based alloy selection problem. Procedia Comput Sci 102:183–189
Bhanu MS, Velammal G (2015) Operations on Zadeh’s Z-numbers. Int Organ Sci Res J Math 11:8–94
Brusche L (2016) Gaps in academic literature on venture capitalists’ decision-making on funding for early-stage, high-tech ventures. Technol Transf Entrep 325(5939):379–379
Chatterjee K, Kar S (2018) A multi-criteria decision making for renewable energy selection using Z-numbers in uncertain environment. Technol Econ Dev Econ 24:739–764
Fu ZG, Wu XL, Liao HC, Herrera F (2018) Underground mining method selection with the hesitant fuzzy linguistic gained and lost dominance score method. IEEE Access 6(99):66442–66458
Gou XJ, Xu ZS (2016) Novel basic operational laws for linguistic terms, hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and probabilistic linguistic term sets. Inf Sci 372:407–427
Hadi-Vencheh A, Mirjaberi M (2014) Fuzzy inferior ratio method for multiple attribute decision making problems. Inf Sci 277:263–272
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E (1995) A sequential selection process in group decision making with a linguistic assessment approach. Inf Sci 85(4):223–239
Jin C, Wang H, Xu ZS (2019) Uncertain probabilistic linguistic term sets in group decision making. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(4):1241–1258
Kim SH, Ahn BS (1999) Interactive group decision making procedure under incomplete information. Eur J Oper Res 116(3):498–507
Kim SH, Choi SH, Kim JK (1999) An interactive procedure for multiple attribute group decision making with incomplete information: range-based approach. Eur J Oper Res 118(1):139–152
Lei F, Wu WG, Gao H, Jiang W (2020) TOPSIS method for developing supplier selection with probabilistic linguistic information. Int J Fuzzy Syst 22(3):749–759
Nuryakin C, Munro A (2019) Experiments on lotteries for shrouded and bundled goods: Investigating the economics of fukubukuro. Jpn Econ Rev 70:168–188
Pang Q, Wang H, Xu ZS (2016) Probabilistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inf Sci 369:128–143
Rahman A, Beg MMS (2019) Face sketch recognition: an application of Z-numbers. Int J Inf Technol 11:541–548
Rodriguez RM, Martinez L, Herrera F (2012) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 20(1):109–119
Song YM, Li GX (2019) A large-scale group decision-making with incomplete multi-granular probabilistic linguistic term sets and its application in sustainable supplier selection. J Oper Res Soc 70(5):827–841
Tang M, Long YL, Liao HC, Xu ZS (2019) Inclusion measures of probabilistic linguistic term sets and their application in classifying cites in the economic zone of Chengdu plain. Appl Soft Comput 82:1–16
Tindale RS, Hinsz VB (2003) Blackwell handbook of social psychology: group processes. Springer, Boston
Wang BL (2020) A novel preference measure for multi-granularity probabilistic linguistic term sets and its applications in large- scale group decision-making. Int J Fuzzy Syst 22(7):2350–2368
Wang YM (1997) Using the method of maximizing deviation to make decision for multi-indices. J Syst Eng Electron 8(3):21–26
Wu XL, Liao HC (2019) A consensus-based probabilistic linguistic gained and lost dominance score method. Eur J Oper Res 272:1017–1027
Wu XL, Liao HC, Xu ZS, Hafezalkotob A, Herrera F (2018) Probabilistic linguistic MULTIMOORA: a multi-criteria decision making method based on the probabilistic linguistic expectation function and the improved borda rule. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 26:3688–3702
Xia YQ, Wu QZ (2004) TOPSIS method for hybrid multi-attribute decision making problems. J Syst Eng 06:80–84
Xian SD, Chai JH, Yin YB (2019) A visual comparison method and similarity measure for probabilistic linguistic term sets and their applications in multi-criteria decision making. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(4):1154–1169
Xiao BY, Hong C, Zhong HJ (2019) Combination of probabilistic linguistic term sets and PROMETHEE to evaluate meteorological disaster risk: case study of southeastern China. Sustainability 11(5):1405–1450
Xu ZS (2005) Deviation measures of linguistic preference relations in group decision making. Omega 33(3):249–254
Xu ZS (2007) An interactive procedure for linguistic multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information. Fuzzy Optim Decis Mak 6(1):17–27
Xu ZS, He Y, Wang XZ (2019) An overview of probabilistic-based expressions for qualitative decision-making: techniques, comparisons and developments. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10(6):1513–1528
Zadeh LA (1974) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Springer, Boston
Zadeh LA (2011) A note on Z-numbers. Inf Sci 181(14):2923–2932
Zadeh LA (2011) The concept of a Z-number-a new direction in uncertain computation. In: IEEE international conference on information reuse & integration. California, USA, pp. xxii–xxiii
Zeshui Xu, Wang Hai (2017) On the syntax and semantics of virtual linguistic terms for information fusion in decision making. Inf Fusion 34:43–48
Zhang YX, Xu ZS, Liao HC (2019) Water security evaluation based on the TODIM method with probabilistic linguistic term sets. Soft Comput 23:6215–6230
Zhou JL, Jin AC (2020) A consensus model to manage minority opinions and non-cooperative behaviors in large group decision making with probabilistic linguistic term sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst PP(99):1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, N., Wang, X. & Xu, Z. Probabilistic reliable linguistic term sets applied to investment project selection with the gained and lost dominance score method. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 12, 2163–2183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01299-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01299-4