Abstract
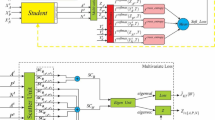
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) model has made remarkable achievements in many fields. Therefore, we have greater expectation for it, expecting it to have the same intelligence as human beings. However, ANNs still can’t perform continual learning like humans at present. The serious defect of ANNs model is called the catastrophic forgetting problem. For this problem, we put forward a novel method called neural mapping support vector machine based on Parameter Regularization and Knowledge Distillation or RD-NMSVM for short. Our model consists of three parts: firstly, the shared neural network module, which is used to extract common features of different tasks; Secondly, the specific task module, which employs multi-classification support vector machine as classifier, and it is equivalent to using neural networks as neural kernel mapping of support vector machine; Thirdly, the parameter regularization and knowledge distillation module, which inhibits the parameters of the shared network module from updating greatly and learns previous knowledge. Note that RD-NMSVM doesn’t utilize samples of previous tasks. From our experiments, we can see that RD-NMSVM has obvious advantages in eliminating catastrophic forgetting of ANNs model.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou T, Li Z, Zhang C (2019) Enhance the recognition ability to occlusions and small objects with Robust Faster R-CNN. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10:3155–3166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-01006-4
Chen H, Yao M, Gu Q (2020) Pothole detection using location-aware convolutional neural networks. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:899–911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01078-7
Lin Y, Li Q, Yang B et al (2021) Improving speech recognition models with small samples for air traffic control systems. Neurocomputing 445:287–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.08.092
Moritz N, Hori T, Roux J Le (2020) Streaming automatic speech recognition with the transformer model. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, IEEE Int Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process. 2020-May. pp 6074–6078. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054476
Bi JW, Liu Y, Fan ZP (2020) A deep neural networks based recommendation algorithm using user and item basic data. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:763–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-00981-y
Qian F, Huang Y, Li J et al (2021) DLSA: dual-learning based on self-attention for rating prediction. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12:1993–2005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01288-7
Zhao K, Jiang H, Li X, Wang R (2021) Ensemble adaptive convolutional neural networks with parameter transfer for rotating machinery fault diagnosis. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12:1483–1499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01249-6
Ye T, Zhang Z, Zhang X et al (2021) Fault detection of railway freight cars mechanical components based on multi-feature fusion convolutional neural network. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12:1789–1801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01274-z
Hsu M-F, Lin S-J (2021) A BSC-based network DEA model equipped with computational linguistics for performance assessment and improvement. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12:2479–2497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01331-7
Suri JS, Puvvula A, Majhail M et al (2020) Integration of cardiovascular risk assessment with COVID-19 using artificial intelligence. Rev Cardiovasc Med 21:541–560. https://doi.org/10.31083/j.rcm.2020.04.236
Sung I, Choi B, Nielsen P (2021) On the training of a neural network for online path planning with offline path planning algorithms. Int J Inf Manag 57:102142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102142
Yan C, Xiang X, Wang C (2020) Towards real-time path planning through deep reinforcement learning for a UAV in dynamic environments. J Intell Robot Syst 98:297–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-019-01073-3
Castrejón L, Kundu K, Urtasun R, Fidler S (2017) Annotating object instances with a polygon-RNN. In: Proceedings: 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017. pp 4485–4493
Zheng S, Jayasumana S, Romera-Paredes B et al (2015) Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis 2015 Inter. pp 1529–1537. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.179
Visin F, Romero A, Cho K et al (2016) ReSeg: a recurrent neural network-based model for semantic segmentation. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit Work. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2016.60
Luo J, Wu J, Zhao S et al (2019) Lossless compression for hyperspectral image using deep recurrent neural networks. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10:2619–2629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-00937-2
Chen J, Yang L, Zhang Y et al (2016) Combining fully convolutional and recurrent neural networks for 3d biomedical image segmentation. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 3036–3044
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N et al (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 5998–6008
Zheng S, Lu J, Zhao H et al (2021) Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 6881–6890
Dai Z, Cai B, Lin Y, Chen J (2021) Up-detr: Unsupervised pre-training for object detection with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 1601–1610
Tan F, Kong Y, Fan Y, et al (2021) SDNet: mutil-branch for single image deraining using swin. arXiv Prepr. http://arxiv.org/abs/2105.15077
Chen H, Wang Y, Guo T et al (2021) Pre-trained image processing transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 12299–12310
Guo S, Yan Z, Zhang K et al (2019) Toward convolutional blind denoising of real photographs. In: Proc IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2019-June. pp. 1712–1722. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00181
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells WM, Frangi AF (eds) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI 2015. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 234–241
Liu B, Zhou Y, Sun W (2020) Character-level text classification via convolutional neural network and gated recurrent unit. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:1939–1949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01084-9
Hajiabadi H, Molla-Aliod D, Monsefi R, Yazdi HS (2020) Combination of loss functions for deep text classification. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:751–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-00982-x
Gehring J, Auli M, Grangier D et al (2017) Convolutional sequence to sequence learning. In: International conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 1243–1252
Wang S, Wang B, Gong J et al (2020) Combining ResNet and transformer for Chinese grammatical error diagnosis. In: Proc 6th Work Nat Lang Process Tech Educ Appl, pp 36–43
Grossberg S (1982) Studies of mind and brain: neural principles of learning, perception, development, cognition, and motor control. Bost Stud Philos Sci xvii:662
Parisi GI, Kemker R, Part JL et al (2019) Continual lifelong learning with neural networks: a review. Neural Netw 113:54–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2019.01.012
Rannen A, Aljundi R, Blaschko MB, Tuytelaars T (2017) Encoder based lifelong learning. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). pp 1329–1337
Farajtabar M, Azizan N, Mott A, Li A (2020) Orthogonal Gradient Descent for Continual Learning. In: Chiappa S, Calandra R (eds) Proceedings of the twenty third international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics. PMLR, pp 3762–3773
Zenke F, Poole B, Ganguli S (2017) Continual Learning Through Synaptic Intelligence. In: Precup D, Teh YW (eds) Proceedings of the 34th international conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 3987–3995
Isele D, Cosgun A (2018) Selective experience replay for lifelong learning. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 32
Rebuffi S-A, Kolesnikov A, Sperl G, Lampert CH (2017) iCaRL: incremental classifier and representation learning. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). pp 5533–5542
Kirkpatrick J, Pascanu R, Rabinowitz N et al (2017) Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:3521–3526. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1611835114
Chaudhry A, Dokania PK, Ajanthan T, Torr PHS (2018) Riemannian walk for incremental learning: understanding forgetting and intransigence. Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 11215 LNCS. pp 556–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01252-6_33
Schwarz J, Czarnecki W, Luketina J, et al (2018) Progress and compress: a scalable framework for continual learning. In: Dy J, Krause A (eds) Proceedings of the 35th international conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 4528–4537
Aljundi R, Babiloni F, Elhoseiny M, et al (2018) Memory aware synapses: learning what (not) to forget. Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 11207 LNCS. pp 144–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_9
Li Z, Hoiem D (2018) Learning without forgetting. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40:2935–2947. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2773081
Castro FM, Marín-Jiménez MJ, Guil N, et al (2018) end-to-end incremental learning. Lect notes comput sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 11216 LNCS. pp 241–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01258-8_15
Dhar P, Singh RV, Peng KC, et al (2019) Learning without memorizing. Proc IEEE comput soc conf comput vis pattern recognit 2019-June. pp 5133–5141. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00528
Sun J, Wang S, Zhang J, Zong C (2020) Distill and replay for continual language learning. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on computational linguistics. pp 3569–3579
Monaikul N, Castellucci G, Filice S, Rokhlenko O (2021) Continual learning for named entity recognition. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 35:13570–13577
Roy D, Panda P, Roy K (2020) Tree-CNN: a hierarchical deep convolutional neural network for incremental learning. Neural Netw 121:148–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2019.09.010
Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y, Lipson H (2014) How transferable are features in deep neural networks? In: Ghahramani Z, Welling M, Cortes C et al (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems. Curran Associates Inc, New York
Wu C, Herranz L, Liu X et al (2018) Memory replay GANs: learning to generate images from new categories without forgetting. In: Proceedings of the 32nd international conference on neural information processing systems. Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook, NY, USA, pp 5966–5976
Hayes TL, Kafle K, Shrestha R et al (2020) REMIND your neural network to prevent catastrophic forgetting. Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 12353 LNCS. pp 466–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58598-3_28
Li Y, Zhang T (2017) Deep neural mapping support vector machines. Neural Netw 93:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2017.05.010
Xiao H, Rasul K, Vollgraf R (2017) Fashion-MNIST: a novel image dataset for benchmarking machine learning algorithms. arXiv Prepr 1–6. http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.07747
LeCun Y Cortes CORINNA BC MNIST handwritten digit database. http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
Clanuwat T, Bober-Irizar M, Kitamoto A, et al (2018) Deep learning for classical Japanese literature. arXiv Prepr 1–8. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.01718
Prabhu VU (2019) Kannada-MNIST: a new handwritten digits dataset for the Kannada language. arXiv Prepr 1–21. http://arxiv.org/abs/1908.01242
Bulatov Y (2011) notMNIST dataset. https://yaroslavvb.blogspot.com/2011/09/notmnist-dataset.html
Acknowledgements
Our paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61806013, 61876010, 61906005), General project of Science and Technology Plan of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (KM202110005028), Project of Interdisciplinary Research Institute of Beijing University of Technology (2021020101) and International Research Cooperation Seed Fund of Beijing University of Technology (2021A01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Zhang, T., Li, Y. et al. RD-NMSVM: neural mapping support vector machine based on parameter regularization and knowledge distillation. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 13, 2785–2798 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-022-01563-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-022-01563-1