Abstract
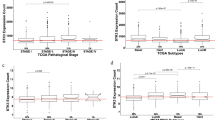
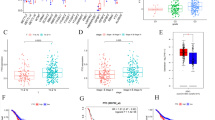
Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) gene family is an important cell cycle progression regulator, which may function as a tumor suppressor. We performed a systematic onco-informatics analysis to investigate the prognostic value of CDK6 in breast cancer. CDK6 expression was evaluated using the Oncomine and UALCAN database. The relevance between CDK6 level and clinical parameters and survival data in breast cancer was analyzed using the bc-GenExMiner, and Kaplan–meier plotter databases. The methylation status and heat map of CDK6 were analyzed by utilizing the UCSC Xena and UALCAN. It was identified that CDK6 was under-expressed in different subtypes of breast cancer. Estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) were negatively correlated with CDK6 expression. On the other hand, nottingham prognostic index (NPI), human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2) status, basal-like status, scarff–bloom–richardson (SBR) grade, and triple-negative status were positively correlated with CDK6 level in breast cancer samples with respect to normal tissues. Besides, a positive correlation between CDK6 and pronecroptosis E3 ubiquitin ligase (PELI1) gene expression was confirmed. Our study revealed that CDK6 might be used as a biomarker for breast cancer prognosis with PELI1. However, more comprehensive experimental data are needed to clarify the value of CDK6 in breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barman UD, Saha SK, Kader MA, Jamal MAHM, Sharma SP, Samad A et al (2020) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of GPC3 in human breast cancer and its 3D structure prediction. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinform 9:1–18
Butler MP, Hanly JA, Moynagh PN (2007) Kinase-active interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases promote polyubiquitination and degradation of the pellino family direct evidence for pellino proteins being ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligases. J Biol Chem 282(41):29729–29737
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BV et al (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19(8):649–658
Chen W-X, Cheng L, Xu L-Y, Qian Q, Zhu Y-L (2019) Bioinformatics analysis of prognostic value of TRIM13 gene in breast cancer. Biosci Rep 39(3):BSR20190285
Cui X, Yi Q, Jing X, Huang Y, Tian J, Long C et al (2018) Mining prognostic significance of MEG3 in human breast Cancer using bioinformatics analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem 50(1):41–51
Daura-Oller E, Cabre M, Montero MA, Paternain JL, Romeu A (2009) Specific gene hypomethylation and cancer: new insights into coding region feature trends. Bioinformation 3(8):340
Gao X, Wang X, Zhang S (2018) Bioinformatics identification of crucial genes and pathways associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep 38(6):BSR20181441
Geng B, Liang M, Qin L, Zhao W, Wang H, Wang L et al (2019) An TRIM 59-CDK 6 axis regulates growth and metastasis of lung cancer. J Cell Mol Med 23(2):1458–1469
Goldman MJ, Craft B, Hastie M, Repečka K, McDade F, Kamath A et al (2020) Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0546-8
Grossel MJ, Hinds PW (2006a) Beyond the cell cycle: a new role for Cdk6 in differentiation. J Cell Biochem 97(3):485–493. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.20712
Grossel MJ, Hinds PW (2006b) From cell cycle to differentiation: an expanding role for cdk6. Cell Cycle 5(3):266–270
Györffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert C, Budczies J, Li Q et al (2010) An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123(3):725–731
Hossain MS, Ferdous S, Karim-Kos HE (2014) Breast cancer in South Asia: a Bangladeshi perspective. Cancer Epidemiol 38(5):465–470
Hussain MS, Baig SM, Neumann S, Peche VS, Szczepanski S, Nürnberg G et al (2013) CDK6 associates with the centrosome during mitosis and is mutated in a large Pakistani family with primary microcephaly. Hum Mol Genet 22(25):5199–5214
Ikeda Y, Oda K, Ishihara H, Wada-Hiraike O, Miyasaka A, Kashiyama T et al (2015) Prognostic importance of CDK4/6-specific activity as a predictive marker for recurrence in patients with endometrial cancer, with or without adjuvant chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 113(10):1477
Jézéquel P, Campone M, Gouraud W, Guérin-Charbonnel C, Leux C, Ricolleau G et al (2012) bc-GenExMiner: an easy-to-use online platform for gene prognostic analyses in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131(3):765–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1457-7
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC (2017) Robbins basic pathology e-book. Elsevier Health Sciences, Amsterdam
Landis MW, Pawlyk BS, Li T, Sicinski P, Hinds PW (2006) Cyclin D1-dependent kinase activity in murine development and mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 9(1):13–22
Li B, He H, Tao B-B, Zhao Z-Y, Hu G-H, Luo C et al (2012) Knockdown of CDK6 enhances glioma sensitivity to chemotherapy. Oncol Rep 28(3):909–914
Lim S, Kaldis P (2013) Cdks, cyclins and CKIs: roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development 140(15):3079–3093
Lin X, Liu J, Hu SF, Hu X (2019) Increased expression of TMED2 is an unfavorable prognostic factor in patients with breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res 11:2203
Lisany NF, Jamal MAHM, Chung H-J, Hong S-T, Rahman MS (2020) Prognostic significance of the Cdk5 gene in breast cancer: an in silico study. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinform 9(1):1–10
Lou W, Ding B, Fan W (2019) High expression of pseudogene PTTG3P indicates a poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Mol Ther-Oncolytics 14:15–26
Meyerson M, Harlow E (1994) Identification of G1 kinase activity for cdk6, a novel cyclin D partner. Mol Cell Biol 14(3):2077–2086
Nagasawa M, Gelfand EW, Lucas JJ (2001) Accumulation of high levels of the p53 and p130 growth-suppressing proteins in cell lines stably over-expressing cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (cdk6). Oncogene 20(23):2889
Nagel S, Leich E, Quentmeier H, Meyer C, Kaufmann M, Drexler HG et al (2008) Amplification at 7q22 targets cyclin-dependent kinase 6 in T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 22(2):387–392. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2405028
Nagy Á, Lánczky A, Menyhárt O, Győrffy B (2018) Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma using expression data of independent datasets. Sci Rep 8(1):9227. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27521-y
Radpour R, Barekati Z, Kohler C, Lv Q, Bürki N, Diesch C et al (2011) Hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes involved in critical regulatory pathways for developing a blood-based test in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 6(1):e16080. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016080
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N, Varambally R, Ghosh D et al (2004) ONCOMINE: a cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining platform. Neoplasia 6(1):1–6
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB et al (2007) Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia 9(2):166–180
Saha SK, Biswas PK, Gil M, Cho S-G (2019a) High expression of TTYH3 is related to poor clinical outcomes in human gastric cancer. J Clin Med 8(11):1762
Saha SK, Islam SR, Kwak K-S, Rahman MS, Cho S-G (2019b) PROM1 and PROM2 expression differentially modulates clinical prognosis of cancer: a multiomics analysis. Cancer Gene Ther. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-019-0109-7
Saha SK, Kader MA, Samad KA, Biswas KC, Rahman MA, Parvez MAK et al (2020) Prognostic and clinico-pathological significance of BIN1 in breast cancer. Inform Med Unlocked 19:100327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100327
Silber J, Hashizume R, Felix T, Hariono S, Yu M, Berger MS et al (2012) Expression of miR-124 inhibits growth of medulloblastoma cells. Neuro-Oncol 15(1):83–90
Tadesse S, Yu M, Kumarasiri M, Le BT, Wang S (2015) Targeting CDK6 in cancer: State of the art and new insights. Cell Cycle 14(20):3220–3230
Wang H, Meng H, Li X, Zhu K, Dong K, Mookhtiar AK et al (2017) PELI1 functions as a dual modulator of necroptosis and apoptosis by regulating ubiquitination of RIPK1 and mRNA levels of c-FLIP. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(45):11944–11949
Zanuy M, Ramos-Montoya A, Villacañas O, Canela N, Miranda A, Aguilar E et al (2012) Cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 control tumor progression and direct glucose oxidation in the pentose cycle. Metabolomics 8(3):454–464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13721_2020_250_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
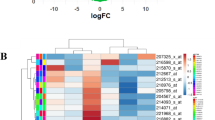
Supplementary file1 A heat map of CDK6 expression and DNA methylation status; B CDK6 expression in different DNA methylation clusters. (PPTX 179 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zinia, J.A., Rahman, M.S. Evaluation of the prognostic significance of CDK6 in breast cancer. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma 9, 40 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-020-00250-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-020-00250-x