Abstract
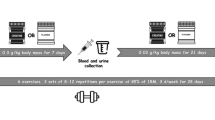
The nutritional supplement of athletes before and after exercise determines their performance in the competitive process. This study aims to explore the effect of protein supplementation on athletes’ physical fitness. This article takes 48 male and female athletes as experimental subjects and randomly divides them into 6 groups. The experiment period was 8 days, and each group was supplemented with protein every day. During the experiment, the athlete collected 10 ml of elbow venous blood for the first time in a quiet fasting state in the laboratory at 8 am. Two hours after the main class (after relaxing), go to the laboratory to draw 10 ml of venous blood from the elbow twice until the 8th day. Then, the chemical immunoassay method is used to measure the blood insulin content, and then the analysis device is used to measure the composition of various compounds in the blood before and after exercise. After 1 week of nutritional supplement intervention, the H2O2 content of each experimental group was significantly reduced after acute high-intensity exercise stimulation compared with the non-intervention situation, and the reduction in the intervention group (A) was more significant (P < 0.01). The research results show that scientific sports nutrition supplements can effectively improve the body’s endurance to high-intensity sports training. Sports nutrition and health products can improve the physiological function of athletes, accelerate the metabolism of lactic acid, promote heart and lung function, and accelerate the recovery after physical training.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Al-Kirshi R, Alimon AR, Zulkifli I et al (2016) Utilization of mulberry leaf meal (Morus alba) as protein supplement in diets for laying hens. Ital J Anim Sci 9(3):265–267
Gutman JBL, Kongshavn PAL (2019) Cysteine/cystine-rich undenatured whey protein supplement in patients’ pressure ulcers outcomes: an open label study. J Wound Care 28(Sup7):S16–S23
Harthan LB, Cherney DJR (2017) Okara as a protein supplement affects feed intake and milk composition of ewes and growth performance of lambs. Anim Nutr 3(2):171–174
Julius OO, Quinn GP (2019) Nutritional evaluation of defatted groundnut cake meal with amino acid as protein supplement in African Catfish (Clarias Gariepinus Burchell, 1822) Juveniles diet. J Fish Aquat Ence 14(1):7–14
Kazuto S, Ayaka S, Yukio Y, Yoichi K, Kumiko K, Yuri Y et al (2018a) Validity of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire based on food groups and cooking with a protein supplement in Japanese collegiate athletes. J Phys Fit Sports Med 7(2):131–142
Kazuto S, Ayaka S, Yukio Y et al (2018b) Validity of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire based on food groups and cooking with a protein supplement in Japanese collegiate athletes. J Phys Fit Sports Med 7(2):131–142
Kurien A, Sharma N, Marathe M, Joshi N, Sambashivaiah S (2020) Acute effect of a protein supplement on targeted plasma amino acid profile among healthy asian indians: a randomized controlled trial. J Nutr Metab 2020(18):1–9
Larsen A, Bibby B, Hansen M (2018) Effect of a whey protein supplement on preservation of fat free mass in overweight and obese individuals on an energy restricted very low caloric diet. Nutrients 10(12):1918
Leyh SM, Willingham BD, Baur DA, Panton LB, Ormsbee MJ (2018) Pre-sleep protein in casein supplement or whole-food form has no impact on resting energy expenditure or hunger in women. Br J Nutr 120(9):988–994
Metochis C, Crampton VO, Ruohonen K, Bell JG, Adams A, Thompson KD (2016) the Effects of Increasing Dietary Levels of Amino Acid-Supplemented Soy Protein Concentrate and Constant Dietary Supplementation of Phosphorus on Growth, Composition and Immune Responses of Juvenile Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar l.). Fish Physiol Biochem 42(3):807–829
Pineda A, Ballou MA, Campbell JM, Cardoso FC, Drackley JK (2016) Evaluation of serum protein-based arrival formula and serum protein supplement (Gammulin) on growth, morbidity, and mortality of stressed (transport and cold) male dairy calves. J Dairy Ence 99(11):9027–9039
Pomerantz A, Blachman-Braun R, Vital-Flores S, Berebichez-Fridman R, Lara-Villalón D (2016) Protein supplement consumption and its possible association with kidney damage in Mexican Elite Athletes. Rev Med Del Inst Mex Del Seguro Soc 54(1):42
Vieira-Brock PDL, Vaughan BM, Vollmer DL (2018) Thermogenic blend alone or in combination with whey protein supplement stimulates fat metabolism and improves body composition in mice. Pharmacogn Res 10(1):37–43
Walrand S, Gryson C, Salles J, Giraudet C, Boirie Y (2016a) Fast-digestive protein supplement for ten days overcomes muscle anabolic resistance in healthy elderly men. Clin Nutr 35(3):660–668
Walrand S, Gryson C, Salles J et al (2016b) Fast-digestive protein supplement for ten days overcomes muscle anabolic resistance in healthy elderly men. Clin Nutr 35(3):660–668
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
There was no moral or ethical violation in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D. Factors affecting the difference of protein supplements on physical fitness. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma 11, 4 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-021-00335-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-021-00335-1