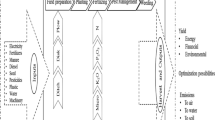
Abstract
Greenhouse cultivation has gained a lot of growers’ interest because of higher yield achieved by maintaining desired environment and provision for additional protective measures. Greenhouses degrade with time, which is caused by mechanical deterioration of construction elements and equipment, as well as by severe climate conditions. These factors are responsible for the gradual change of greenhouse parameter. Therefore, parameters are commonly re-tuned periodically to ensure desired model accuracy for realistic control action generation. The limitation of conventional parameter estimation is that while minimizing the deviation from sensors’ measurements, it ignores the fact that parameters change slowly, and hence, it can overfit to noisy measurements. This paper presents a re-tuning strategy , which utilizes the prior knowledge contained in the previously tuned parameters. For this, the strategy incorporates the deviation from the prior tuned parameters as an objective along with deviation from the sensor measurements, which may be beneficial in overcoming the overfitting of parameters. Multi-objective algorithms were considered for re-tuning , as objectives are of conflicting nature. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA)-II were used to obtain the Pareto fronts for multiple runs and different population sizes. The Pareto fronts obtained by NSGA-II were found favourable compared to MOPSO regarding the approximation quality of the Pareto front. The selection of the desired parameter set was made based on the balance amongst objectives.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, A., Lloyd, A.L.: An approach to periodic, time-varying parameter estimation using nonlinear filtering. Inverse Probl. 34(10), 105005 (2018)
Astrom, K.J., Wittenmark, B.: A survey of adaptive control applications. In: Decision and Control, 1995., Proceedings of the 34th IEEE Conference on, vol. 1, pp. 649–654. IEEE (1995)
Baytorun, A.N.: Bestimmung des luftwechsels bei gelufteten gewachshausern. Ph.D. thesis, Institute of Horticultural and Agricultural Engineering, University of Hannover. Hannover, Germany (1986)
Bekele, E.G., Nicklow, J.W.: Multi-objective automatic calibration of SWAT using NSGA-II. J. Hydrol. 341(3–4), 165–176 (2007)
Bitto, A., Frühwirth-Schnatter, S.: Achieving shrinkage in a time-varying parameter model framework. J. Econom. 210(1), 75–97 (2019)
Blasco, X., Martínez, M., Herrero, J.M., Ramos, C., Sanchis, J.: Model-based predictive control of greenhouse climate for reducing energy and water consumption. Comput. Electron. Agric. 55(1), 49–70 (2007)
Castaneda-Miranda, R., Ventura-Ramos Jr., E., Peniche-Vera, R.D.R., Herrera-Ruiz, G.: Analysis and simulation of a greenhouse physical model under weather conditions of the central region of mexico. Agrociencia 41(3), 317–335 (2007)
Chatterjee, S., Litt, J.: Online model parameter estimation of jet engine degradation for autonomous propulsion control. In: AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, p. 5425 (2003)
Chen, A.S., Na, J., Herrmann, G., Burke, R., Brace, C.: Adaptive air-fuel ratio control for spark ignition engines with time-varying parameter estimation. In: 2017 9th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC), pp. 1074–1079. IEEE (2017)
Cheng, C., Tourneret, J.Y.: A kernel density-based particle filter for state and time-varying parameter estimation in nonlinear state-space models. In: 2017 25th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), pp. 1664–1668. IEEE (2017)
Coello, C.A.C., Pulido, G.T., Lechuga, M.S.: Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 8(3), 256–279 (2004)
Cruz-Valeriano, E., Begovich, O., Ruiz-León, J.: Modeling of a greenhouse using particle swarm optimization. In: Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), 2013 10th International Conference on, pp. 268–273. IEEE (2013)
Cui, M., Khodayar, M., Chen, C., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Khodayar, M.E.: Deep learning-based time-varying parameter identification for system-wide load modeling. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 10(6), 6102–6114 (2019)
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., Meyarivan, T.: A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 6(2), 182–197 (2002)
Ding, F., Xu, L., Zhu, Q.: Performance analysis of the generalised projection identification for time-varying systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 10(18), 2506–2514 (2016)
Eberhart, R., Kennedy, J.: A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Micro Machine and Human Science, 1995. MHS’95., Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on, pp. 39–43. IEEE (1995)
Efstratiadis, A., Koutsoyiannis, D.: One decade of multi-objective calibration approaches in hydrological modelling: a review. Hydrol. Sci. J. J. Des Sci. Hydrol. 55(1), 58–78 (2010)
El Ghoumari, M., Tantau, H.J., Serrano, J.: Non-linear constrained MPC: real-time implementation of greenhouse air temperature control. Comput. Electron. Agric. 49(3), 345–356 (2005)
Gaudio, J.E., Annaswamy, A.M., Lavretsky, E., Bolender, M.A.: Parameter estimation in adaptive control of time-varying systems under a range of excitation conditions. arXiv:1911.03810 (2019)
Gill, M.K., Kaheil, Y.H., Khalil, A., McKee, M., Bastidas, L.: Multiobjective particle swarm optimization for parameter estimation in hydrology. Water Resour. Res., vol. 42(7), (2006) https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/action/showCitFormats?doi=10.1029%2F2005WR004528
Gupta, H.V., Bastidas, L., Sorooshian, S., Shuttleworth, W.J., Yang, Z.: Parameter estimation of a land surface scheme using multicriteria methods. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 104(D16), 19491–19503 (1999)
Hasni, A., Draoui, B., Bounaama, F., Tamali, M., Boulard, T.: Evolutionary algorithms in the optimization of natural ventilation parameters in a greenhouse with continuous roof vents. Int. Symp. Greenh. Cooling 719, 49–56 (2006)
Hasni, A., Taibi, R., Draoui, B., Boulard, T.: Optimization of greenhouse climate model parameters using particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithms. Energy Procedia 6, 371–380 (2011)
Herrero, J., Blasco, X., Martínez, M., Ramos, C., Sanchis, J.: Non-linear robust identification of a greenhouse model using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms. Biosyst. Eng. 98(3), 335–346 (2007)
Herrero, J., Blasco, X., Martínez, M., Ramos, C., Sanchis, J.: Robust identification of non-linear greenhouse model using evolutionary algorithms. Control Eng. Pract. 16(5), 515–530 (2008)
Jiang, S., Ong, Y., Zhang, J., Feng, L.: Consistencies and contradictions of performance metrics in multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44(12), 2391–2404 (2014)
Jong, T.d.: Natural ventilation of large multi-span greenhouses. Ph.D. thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University. Wageningen, Netherlands (1990)
Kulhavỳ, R., Kárnỳ, M.: Tracking of slowly varying parameters by directional forgetting. IFAC Proce. Vol. 17(2), 687–692 (1984)
Madsen, H.: Automatic calibration of a conceptual rainfall-runoff model using multiple objectives. J. Hydrol. 235(3–4), 276–288 (2000)
Madsen, H.: Parameter estimation in distributed hydrological catchment modelling using automatic calibration with multiple objectives. Adv. Water Resour. 26(2), 205–216 (2003)
Pérez-González, A., Begovich, O., Ruiz-León, J.: Modeling of a greenhouse prototype using PSO algorithm based on a labview tm application. In: Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), 2014 11th International Conference on, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2014)
Revathi, S., Sivakumaran, N.: Fuzzy based temperature control of greenhouse. IFAC-PapersOnLine 49(1), 549–554 (2016)
Ríos, H., Efimov, D., Moreno, J.A., Perruquetti, W., Rueda-Escobedo, J.G.: Time-varying parameter identification algorithms: finite and fixed-time convergence. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 62(7), 3671–3678 (2017)
Rohatgi, A.: Webplotdigitizer (version 4.2) (2019). https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer
Rudolph, G.: Evolutionary search under partially ordered sets. Department of Computer Science/LS11, University of Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany, Technical Report CI-67/99 (1999)
Sag, T., Cunkas, M.: Multiobjective genetic estimation to induction motor parameters. In: 2007 International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics, pp. 628–631. IEEE (2007)
Van Straten, G., van Willigenburg, G., van Henten, E., van Ooteghem, R.: Optimal Control of Greenhouse Cultivation. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2010)
Wang, C., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Zhao, D.: Robust time-varying parameter identification for composite load modeling. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 10(1), 967–979 (2017)
Zhang, Z.: Parameter estimation techniques: a tutorial with application to conic fitting. Image Vision Comput. 15(1), 59–76 (1997)
Zitzler, E., Deb, K., Thiele, L.: Comparison of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: empirical results. Evolut. Comput. 8(2), 173–195 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This publication is supported by Visvesvaraya Ph.D. Scheme, MeitY, Government of India, MEITY-PHD-1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singhal, R., Kumar, R. & Neeli, S. Multi-objective re-tuning of nonlinear model for degrading greenhouse. Prog Artif Intell 10, 37–48 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13748-020-00222-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13748-020-00222-2