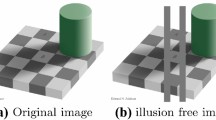
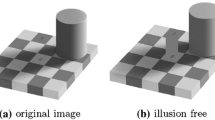
Abstract
Based on a variational optimization model, and by imposing physical constraints on the reflection value, and deriving deformation of the Retinex problem, we find that the Retinex problem is equivalent to a linear complementarity problem and its solution can be computed by solving an equivalent fixed-point equation. In light of the theoretical analysis of the special structure of the system matrix of the linear complementarity problem, we propose a variant of the two-step modulus-based matrix splitting iteration method, and then prove its unconditional convergence. We further give practically quasi-optimal values of the involved iteration parameters in this method. The numerical results show that the variant of the two-step modulus-based matrix splitting iteration method is effective in terms of iteration steps, computing time, and natural image quality evaluator.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Z-Z (1996) The convergence of parallel iteration algorithms for linear complementarity problems. Comput Math Appl 32:1–17
Bai Z-Z (1999) A class of modified block SSOR preconditioners for symmetric positive definite systems of linear equations. Adv Comput Math 10:169–186
Bai Z-Z (2009) Optimal parameters in the HSS-like methods for saddle-point problems. Numer Linear Algebra Appl 16:447–479
Bai Z-Z (2010) Modulus-based matrix splitting iteration methods for linear complementarity problems. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 17:917–933
Bai Z-Z (2012) Block alternating splitting implicit iteration methods for saddle-point problems from time-harmonic eddy current models. Numer Linear Algebra Appl. 19:914–936
Bai Z-Z (2013) Eigenvalue estimates for saddle point matrices of Hermitian and indefinite leading blocks. J Comput Appl Math. 237:295–306
Bai Z-Z, Golub GH, Ng MK (2003) Hermitian and skew-Hermitian splitting methods for non-Hermitian positive definite linear systems. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 24:603–626
Bai Z-Z, Pan J-Y (2021) Matrix Analysis and Computations. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA
Bai Z-Z, Wang C-L (2001) Sufficient conditions for the convergent splittings of non-Hermitian positive definite matrices. Linear Algebra Appl. 330:215–218
Bai Z-Z, Wu W-T (2018) On greedy randomized Kaczmarz method for solving large sparse linear systems. SIAM J Sci Comput 40:A592–A606
Cooper TJ, Baqai FA (2004) Analysis and extensions of the Frankle-McCann Retinex algorithm. J Electron Imag 13:85–92
Chen F (2015) On choices of iteration parameter in HSS method. Appl Math Comput 271:832–837
Chen F, Zhu Y, Muratova GV (2021) Two-step modulus-based matrix splitting iteration methods for Retinex problem. Numer Algor 88:1989–2005
Dong J-L, Jiang M-Q (2009) A modified modulus method for symmetric positive-definite linear complementarity problems. Numer Linear Algebra Appl 16:129–143
Dong J-L, Gao J-B, Ju F-J, Shen J-H (2016) Modulus methods for nonnegatively constrained image restoration. SIAM J Imaging Sci 9:1226–1246
Funt B, Ciurea F (2004) Retinex in MATLAB. J Electron Imag 13:48–57
Hurlbert A (1986) Formal connections between lightness algorithms. J Opt Soc Am A 3:1684–1693
Huang Y-M (2014) A practical formula for computing optimal parameters in the HSS iteration methods. J Comput Appl Math 255:142–149
Jobson DJ, Rahman Z (1997) Member, IEEE and G.A. Woodell, Properties and performance of a center/surround Retinex. IEEE Trans Image Process 6:451–462
Kimmel R, Elad M, Shaked D, Keshet R, Sobel I (2003) A variational framework for Retinex. Int J Comput Vis 52:7–23
Land EH, McCann JJ (1971) Lightness and Retinex theory. J Opt Soc Am A 61:1–11
Land EH (1977) The Retinex theory of color vision. Sci Amer 237:108–128
Land EH (1983) Recent advances in retinex theory and some implications for cortical computations: Color vision and the natural image. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:5163–5169
Land EH (1986) An alternative technique for the computation of the designator in the Retinex theory of color vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3078–3080
Li H-F, Zhang L-P, Shen H-F (2012) A perceptually inspired variational method for the uneven intensity correction of remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 50:3053–3065
Liang J-W, Zhang X-Q (2015) Retinex by higher order total variation \(L^1\) decomposition. J Math Imaging Vis 52:345–355
Morel JM, Petro AB, Sbert C (2010) A PDE formalization of Retinex theory. IEEE Trans Image Process 19:2825–2837
Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC (2013) Making a “Completely Blind’’ image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20:209–212
Ng MK, Wang W (2011) A total variation model for Retinex. SIAM J Imaging Sci 4:345–365
Rahman Z, Jobson DJ, Woodell GA (2004) Retinex processing for automatic image enhancement. J Electron Imag 13:100–110
Wang W, He C-J (2015) A variational model with barrier functionals for Retinex. SIAM J Imag Sci 8:1955–1980
Yang X, Huang Y-M, Sun L (2018) A modulus iteration method for Retinex problem. Numer Linear Algebra Appl 25:e2207
Zosso D, Tran G, Osher SJ (2015) Non-local Retinex-A unifying framework and beyond. SIAM J Imaging Sci 8:787–826
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Zhong-Zhi Bai.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supported by R &D Program of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (No. KM201911232010), P.R. China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Zhu, Y. A variant of two-step modulus-based matrix splitting iteration method for Retinex problem. Comp. Appl. Math. 41, 244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-022-01952-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-022-01952-w
Keywords
- Linear complementarity problem
- Two-step iteration method
- Modulus-based matrix splitting
- Retinex problem