Abstract
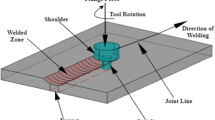
This paper investigates neutrosophic optimization (NSO) approach to optimize the cost of welding of a welded steel beam, while the maximum shear stress in the weld group, maximum bending stress in the beam, maximum deflection at the tip and buckling load of the beam have been considered as flexible constraints. The problem of designing an optimal welded beam consists of dimensioning a welded steel beam such as height, length, depth, width of welded beam, so as to minimize its cost, subject to the constraints as stated above. The purpose of the present study firstly is to investigate the effect of truth, indeterminacy and falsity membership function in NSO in perspective of welded beam design in imprecise environment and secondly is to analyze the results obtained by different optimization methods like fuzzy, intuitionistic fuzzy and several deterministic methods so that the welding cost of the welded steel beam become most cost-effective. Specifically based on truth, indeterminacy and falsity membership function, a single-objective NSO algorithm has been developed to optimize the welding cost, subjected to a set of flexible constraints. It has been shown that NSO is an efficient method in finding out the optimum value in comparison with other iterative methods for nonlinear welded beam design in precise and imprecise environment. Numerical example is also given to demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed NSO approach.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy set. Inf. Control 8, 338–353 (1965)
Atanassov, K.T.: Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20, 87–96 (1986)
Angelov, P.P.: Optimization in intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 86, 299–306 (1997)
Smarandache, F.:Neutrosophic logic and set,mss. http://fs.gallup.unm.edu/neutrosophy.htm (1995). Accessed 8 Mar 2017
Wang, H., Smarandache, F., Zhang, Y.Q., Raman, R.: Single valued neutrosophic sets. Multispace Multistruct. 4, 410–413 (2010)
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Karimi, H.R., Wang, M.: H∞ ← model reduction for continuous-time Markovian jump systems with incomplete statistics of mode information. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 45, 1496–1507 (2014)
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Karimi, H.R., Wang, M.: New results on H1 dynamic output feedback control for Markovian jump systems with time-varying delay and defective mode information. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 35, 656–675 (2014)
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Karimi, H.R., Wang, M.: Filtering design for two-dimensional Markovian jump systems with state-delays and deficient mode information’’. Inf. Sci. 269, 316–331 (2014)
Zimmermann, H.J.: Fuzzy linear programming with several objective function. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1, 45–55 (1978)
Ragsdell, K.M., Phillips, D.T.: Optimal design of a class of welded structures using geometric programming. ASME J. Eng. Ind. 98, 1021–1025 (1976)
Lee, K.S., Geem, Z.W.: A new meta-heuristic algorithm for continuous engineering optimization: harmony search theory and practice. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 194, 3902–3933 (2005)
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Moitra, S.: Mechanical component design for multiple objectives using elitist non-dominated sorting GA. In: Proceedings of the Parallel Problem Solving from Nature VI Conference, Paris, Vol 16–20, pp. 859–868 (2000). -->
Coello, C.A.C.: Use of a self-adaptive penalty approach for engineering optimization problems. Comput. Ind. 41, 113–127 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0166-3615(99)00046-9
Mahdavi, M., Fesanghary, M., Damangir, E.: An improved harmony search algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 188, 1567–1579 (2007)
Coello Coello, C.A.: Solving engineering optimization problems with the simple constrained particle swarm optimizer. Informatica 32, 319–326 (2008)
Coello, C.A.C., Montes, E.M.: Useful infeasible solutions in engineering optimization with evolutionary algorithms. In: Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. (2005). DOI: 10.1007/11579427_66
Aguirre, A.H., Zavala, A.M., Diharce, E.V., Rionda, S.B.: COPSO: Constrained Optimization via PSO Algorithm. Centre for Research in Mathematics (CIMAT). Technical report No.I-07-04/22-02-2007, (2007)
Coello Coello, C.A., Montes, M.: Contraint-handling techniques in genetic algorithms through dominance based tournament selection. Adv. Eng. Inform. 16, 193–203 (2002)
Coello Coello, C.A., Becerra, R.L.: Efficient evolutionary optimization through the use of a cultural algorithm. Eng. Optim. 36, 219–236 (2004)
He, Q., Wang, L.: An effective co-evolutionary particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 20, 89–99 (2007)
He, Q., Wang, L.: Ahybrid particle swarm optimization with a feasibility based rule for constrained optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 186, 1407–1422 (2007)
Zahara, E., Kao, Y.T.: Hybrid Nelder-mead simplex search and particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 36, 3880–3886 (2009)
David, D.C.N., Stephen, S.E.A., Ajoy, J.A.: Cost minimization of welded beam design problem using PSO, SA, PS, GOLDLIKE, CUCKOO, FF, FP, ALO, GSA and MVO. Int. J. Appl. Math. 5, 1–14 (2016)
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Karimi, H.R.: Reliable output feedback control of discrete-time fuzzy affine systems with actuator faults. pp. 1–12 (2016). Doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2605685
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Lam, H.K., Wu, L.: Approaches to T-S Fuzzy-affine-model-based reliable output feedback control for nonlinear itˆo stochastic systems. IEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2016). doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2566810
Das, P., Roy, T.K.: Multi-objective non-linear programming problem based on neutrosophic optimization technique and its application in Riser Design Problem. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 9, 88–95 (2015)
Singh, B., Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K.: Intuitionistic fuzzy optimization of truss design: a comperative study. Int. J. Comput. Organ. Trends (IJCOT) 3, 25–33 (2016)
Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K.: Intuitionistic fuzzy optimization on structural design:a comparative study. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 5, 18471–18482 (2016)
Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K.: Truss design optimization with imprecise load and stress in intuitionistic fuzzy environment. J. Ultra Sci. Phys. Sci. 29, 12–23 (2017)
Sarkar, M., Dey, S., Roy, T.K.: Truss Design optimization using neutrosophic optimization technique. Neutrosphic Sets Syst. 13, 62–69 (2016)
Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K.: Truss design optimization using neutrosophic optimization technique: a comparative study. Adv. Fuzzy Math. 12, 411–438 (2017)
Sarkar, M., Dey, S., Roy, T.K.: Neutrosophic optimization technique and its application on structural design. J. Ultra Sci. Phys. Sci. 28, 309–321 (2016)
Sarkar, M., Dey, S., Roy, T.K.: Multi-objective neutrosophic optimization technique and its application to structural design. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 148, 31–37 (2016)
Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K.: Multi-objective welded beam optimization using neutrosophic goal programming technique. Adv. Fuzzy Math. 12, 515–538 (2017)
Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K.: Truss design optimization with imprecise load and stress in neutrosophic environment. Adv. Fuzzy Math. 12, 439–474 (2017)
Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K.: Optimization of welded beam with imprecise load and stress by parameterized intuitionistic fuzzy optimization technique. Adv. Fuzzy Math. 12, 577–608 (2017)
Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K.: Multi-objective welded beam design optimization using T-norm and T-conorm based intuitionistic Fuzzy optimization technique. Adv. Fuzzy Math. 12, 549–575 (2017)
Werner, B.: Interactive fuzzy programming systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 23, 133–178 (1987)
Acknowledgements
The research work of Mridula Sarkar is financed by Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship [F1-17.1/2013-14-SC-wes-42549/(SA-III/Website)], Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, M., Roy, T.K. Optimization of Welded Beam Structure Using Neutrosophic Optimization Technique: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 847–860 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0362-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0362-6