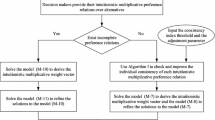
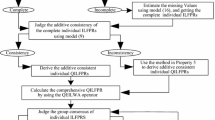
Abstract
Pairwise comparison is a useful tool to express decision makers’ (DMs’) preferences in the group decision-making (GDM) problems. However, the preferences provided by pairwise comparisons could be self-contradictory, i.e., ordinal inconsistencies exist. Therefore, before reaching consensus, the first thing is to assure the DM’s judgments that are not contradictory. As the purpose of the GDM is to choose most preferred alternative, the consensus degree for each alternative of all the DMs should be measured. In the present paper, an alternative consensus model for additive preference relations (APRs) based on ordinal consistency (OC) is developed. An algorithm is applied to detect and adjust the ordinally inconsistent elements for APRs. Then the alternative rankings for each ordinally consistent APR and the aggregated APR is obtained, respectively. A model is designed to change the DMs’ importance, which increases the alternative consensus degree. The proposed model does not change the DMs’ preferences, aiming to make full use of the DMs’ judgements. Finally, an illustrative example and comparisons with the current approaches are furnished to demonstrate the effectiveness of the developed method.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bordogna, G., Fedrizzi, M., Pasi, G.: A linguistic modeling of consensus in group decision making based on OWA operators. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 27, 126–132 (1997)
Davey, A., Olson, D.: Multiple criteria decision making models in group decision support. Group Decis. Negot. 7, 55–75 (1998)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Herrera, F., Chiclana, F.: A consensus model for multiperson decision making with different preference structures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 32, 394–402 (2002)
Ben-Arieh, D., Chen, Z.F.: Linguistic-labels aggregation and consensus measure for autocratic decision making using group recommendations. IEEE Tran. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 36, 558–568 (2006)
Cabrerizo, F.J., Herrera-Viedma, E., Pedrycz, W.: A method based on PSO and granular computing of linguistic information to solve group decision making problems defined in heterogeneous contexts. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 230, 624–633 (2013)
Liu, X., Xu, Y.J., Montes, R., Dong, Y.C., Herrera, F.: Analysis of self-confidence indecies-based additive consistency for fuzzy preference relations with self-confidence and its application in group decision making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 34, 920–946 (2019)
Cabrerizo, F.J., Chiclana, F., Al-Hmouz, R., Morfeq, A., Balamash, A.S., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Fuzzy decision making and consensus: challenges. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 29, 1109–1118 (2015)
del Moral, M.J., Chiclana, F., Tapia, J.M., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A comparative study on consensus measures in group decision making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 33, 1624–1638 (2018)
Xu, Z.S., Cai, X.Q.: Group consensus algorithms based on preference relations. Inf. Sci. 181, 150–162 (2011)
Wu, Z.B., Xu, J.P.: A concise consensus support model for group decision making with reciprocal preference relations based on deviation measures. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 206, 58–73 (2012)
Xu, Y.J., Li, K.W., Wang, H.M.: Distance-based consensus models for fuzzy and multiplicative preference relations. Inf. Sci. 253, 56–73 (2013)
Palomares, I., Estrella, F.J., Martínez, L., Herrera, F.: Consensus under a fuzzy context: taxonomy, analysis framework AFRYCA and experimental case of study. Inf. Fusion 20, 252–271 (2014)
Liu, X., Xu, Y.J., Herrera, F.: Consensus model for large-scale group decision making based on fuzzy preference relation with self-confidence: detecting and managing overconfidence behaviors. Inf. Fusion 52, 245–256 (2019)
Dong, Y.C., Zhang, G.Q., Hong, W.C., Xu, Y.F.: Consensus models for AHP group decision making under row geometric mean prioritization method. Decis. Support Syst. 49, 281–289 (2010)
Wu, Z.B., Xu, J.P.: A consistency and consensus based decision support model for group decision making with multiplicative preference relations. Decis. Support Syst. 52, 757–767 (2012)
Dong, Y.C., Fan, Z.P., Yu, S.: Consensus building in a local context for the AHP-GDM with the individual numerical scale and prioritization method. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23, 354–368 (2015)
Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F., Li, H.Y., Feng, B.: The OWA-based consensus operator under linguistic representation models using position indexes. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 203, 455–463 (2010)
Gong, Z.W., Forrest, J., Yang, Y.J.: The optimal group consensus models for 2-tuple linguistic preference relations. Knowl. Based Syst. 37, 427–437 (2013)
Zhang, G.Q., Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F.: Consistency and consensus measures for linguistic preference relations based on distribution assessments. Inf. Fusion 17, 46–55 (2014)
Cabrerizo, F.J., Al-Hmouz, R., Morfeq, A., Balamash, A.S., Martínez, M.A., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Soft consensus measures in group decision making using unbalanced fuzzy linguistic information. Soft. Comput. 21, 3037–3050 (2017)
Wu, J., Chiclana, F.: Multiplicative consistency of intuitionistic reciprocal preference relations and its application to missing values estimation and consensus building. Knowl. Based Syst. 71, 187–200 (2014)
Zhang, Z.M., Wang, C., Tian, X.D.: A decision support model for group decision making with hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Knowl. Based Syst. 86, 77–101 (2015)
Wu, Z.B., Xu, J.P.: Managing consistency and consensus in group decision making with hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Omega 65, 28–40 (2016)
Xu, Y.J., Cabrerizo, F.J., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A consensus model for hesitant fuzzy preference relations and itsapplication in water allocation management. Appl. Soft Comput. 58, 265–284 (2017)
Xu, Y.J., Rui, D., Wang, H.M.: A dynamically weight adjustment in the consensus reaching process for group decision-making with hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 48, 1311–1321 (2017)
Xu, Y.J., Li, C.Y., Wen, X.W.: Missing values estimation and consensus building for incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations with multiplicative consistency. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 11, 101–119 (2018)
Xu, Y.J., Wen, X.W., Sun, H., Wang, H.M.: Consistency and consensus models with local adjustment strategy for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 2216–2233 (2018)
Liu, W.Q., Dong, Y.C., Chiclana, F., Cabrerizo, F.J., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Group decision-making based on heterogeneous preference relations with self-confidence. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Making 16, 429–447 (2017)
Liu, Y.T., Dong, Y.C., Liang, H.M., Chiclana, F., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Multiple attribute strategic weight manipulation with minimum cost in a group decision making context with interval attribute weights information. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2018.2874942
Kacprzyk, J., Fedrizzi, M.: A ‘soft’ measure of consensus in the setting of partial (fuzzy) preferences. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 34, 316–325 (1988)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Cabrerizo, F.J., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W.: A review of soft consensus models in fuzzy environment. Inf. Fusion 17, 4–13 (2014)
Dong, Y.C., Zhao, S., Zhang, H.J., Chiclana, F., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A self-management mechanism for non-cooperative behaviors in large-scale group consensus reaching processes. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26, 3276–3288 (2018)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Alonso, S., Chiclana, F., Herrera, F.: A consensus model for group decision making with incomplete fuzzy preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 15, 863–877 (2007)
Cabrerizo, F.J., Ureña, M.R., Pedrycz, W., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Building consensus in group decision making with an allocation of information granularity. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 255, 115–127 (2014)
Xu, Y.J., Zhang, W.C., Wang, H.M.: A conflict-eliminating approach for emergency group decision of unconventional incidents. Knowl. Based Syst. 83, 90–104 (2015)
Xu, Y.J., Wen, X.W., Zhang, W.C.: A two-stage consensus method for large-scale multi-attribute group decision making with an application to earthquake shelter selection. Comput. Ind. Eng. 116, 113–129 (2018)
Xu, Y.J., Patnayakuni, R., Wang, H.M.: The ordinal consistency of a fuzzy preference relation. Inf. Sci. 224, 152–164 (2013)
Xu, Y.J., Gupta, J.N.D., Wang, H.M.: The ordinal consistency of an incomplete reciprocal preference relation. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 246, 62–77 (2014)
Chen, S.M., Lee, L.W.: Autocratic decision making using group recommendations based on the ILLOWA operator and likelyhood-based comparison relations. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 42, 115–129 (2012)
Orlovsky, S.A.: Decision-making with a fuzzy preference relation. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1, 155–167 (1978)
Tanino, T.: Fuzzy preference orderings in group decision making. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 12, 117–131 (1984)
Fodor, J., Roubens, M.: Fuzzy Preference Modelling and Multicriteria Decision Support. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1994)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Herrera, F., Chiclana, F., Luque, M.: Some issues on consistency of fuzzy preference relations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 154, 98–109 (2004)
Ma, J., Fan, Z.P., Jiang, Y.P., Mao, J.Y., Ma, L.: A method for repairing the inconsistency of fuzzy preference relations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 157, 20–33 (2006)
Xu, Y.J., Da, Q.L., Liu, L.H.: Normalizing rank aggregation method for priority of a fuzzy preference relation and its effectiveness. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 50, 1287–1297 (2009)
Basile, L.: Ranking Alternatives by Weak Transitivity Relations. Springer, Netherlands (1990)
Baets, B.D., Meyer, H.D.: Transitivity frameworks for reciprocal relations: cycle-transitivity versus FG-transitivity. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 152, 249–270 (2005)
Xu, Y.J., Wang, Q.Q., Cabrerizo, F.J., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Methods to improve the ordinal and multiplicative consistency for reciprocal preference relations. Appl. Soft Comput. 67, 479–493 (2018)
Chiclana, F., Mata, F., Martinez, L., Herrera-Viedma, E., Alonso, S.: Integration of a consistency control module within a consensus model. Int. J. Uncertainty Fuzziness Knowl. Based Syst. 16, 35–53 (2008)
Palomares, I., Martínez, L., Herrera, F.: A consensus model to detect and manage noncooperative behaviors in large-scale group decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 516–530 (2014)
Zhang, Z., Guo, C.H., Martínez, L.: Managing multigranular linguistic distribution assessments in large-scale multiattribute group decision making. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 47, 3063–3076 (2017)
Liu, X., Xu, Y.J., Montes, R., Ding, R.X., Herrera, F.: Alternative ranking-based clustering and reliability index-based consensus reaching process for hesitant fuzzy large scale group decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 27, 159–171 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grants (No. 71871085, 71471056), and the project TIN2016-75850-R financed by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Xi, Y., Cabrerizo, F.J. et al. An Alternative Consensus Model of Additive Preference Relations for Group Decision Making Based on the Ordinal Consistency. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1818–1830 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00696-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00696-w