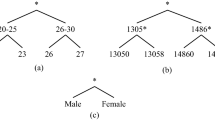
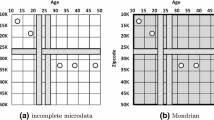
Abstract
Privacy violation issues must be taken into consideration when datasets are released for public use. To address these issues, there are various anonymization models to be proposed, e.g., k-anonymity, l-diversity, and t-closeness. However, these anonymization models generally propose to address privacy violation issues in datasets which are assumed that all attributes of them must be completed. Thus, these anonymization models could be insufficient to address privacy violation issues in such a dataset which is allowed to collect missing-values, e.g., rating datasets and trajectory datasets. Therefore, a new appropriate privacy preservation model for missing-value datasets is proposed by this work. With the proposed model, aside from privacy preservation, the data utility is also maintained as much as possible. Moreover, a suitable data utility metric for missing-value datasets is also presented by this work. Furthermore, the proposed model is shown that it is an NP-Complete problem by reduction from the X3C problem.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal G, Feder T, Kenthapadi K, Motwani R, Panigrahy R, Thomas D, Zhu A. Approximation algorithms for k-anonymity. J Priv Technol. 2005. http://ilpubs.stanford.edu:8090/645/
Bayardo RJ, Rakesh A. Data privacy through optimal k-anonymization. In: 21st international conference on data engineering (ICDE’05). 2005. p. 217–28. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2005.42
Bredereck R, Froese V, Hartung S, Nichterlein A, Niedermeier R, Talmon N. The complexity of degree anonymization by vertex addition. In: Gu Q, Hell P, Yang B, editors. Algorithmic aspects in information and management. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2014. p. 44–55.
Burke R. Knowledge-Based Recommender Systems. In: Encyclopedia of library and information systems; 2000
Byun JW, Kamra A, Bertino E, Li N. Efficient k-anonymization using clustering techniques. In: Kotagiri R, Krishna PR, Mohania M, Nantajeewarawat E, editors. Advances in databases: concepts, systems and applications. Berlin: Springer; 2007. p. 188–200.
Chen W, Niu Z, Zhao X, Li Y. A hybrid recommendation algorithm adapted in e-learning environments. World Wide Web. 2014;17(2):271–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-012-0187-z.
Chi Y, Hong J, Jurek A, Liu W, O’Reilly D. Privacy preserving record linkage in the presence of missing values. Inf Syst. 2017;71:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2017.07.001.
De Vimercati SDC, Foresti S, Livraga G, Samarati P. Data privacy: deinitions and techniques. Int J Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowl Based Syst. 2012;20(6):793–817. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218488512400247
Fung, BCM, Cao M, Desai BC, Xu H. Privacy protection for rfid data. In: Proceedings of the 2009 ACM symposium on applied computing, SAC ’09. New York: ACM; 2009. p. 1528–35. https://doi.org/10.1145/1529282.1529626
Fung BCM, Wang K, Chen R, Yu PS. Privacy-preserving data publishing: a survey of recent developments. ACM Comput Surv. 2010;42(4):14:1–53. https://doi.org/10.1145/1749603.1749605.
Fung BCM, Wang K, Yu PS. Top-down specialization for information and privacy preservation. In: 21st international conference on data engineering (ICDE’05). 2005. p. 205–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2005.143
Garey MR, Johnson DS. Computers and Intractability: a guide to the theory of NP-completeness. New York: W. H. Freeman & Co.; 1979.
Ghinita G, Karras P, Kalnis P, Mamoulis N. A framework for efficient data anonymization under privacy and accuracy constraints. ACM Trans Database Syst. 2009;34(2):9:1–47. https://doi.org/10.1145/1538909.1538911.
Gionis A, Tassa T. k-anonymization with minimal loss of information. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. 2009;21(2):206–19.
Jagannathan G, Wright RN. Privacy-preserving imputation of missing data. Data Knowl Eng. 2008;65(1):40–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.datak.2007.06.013.
Kordelas GA, Alexiadis DS, Daras P, Izquierdo E. Content-based guided image filtering, weighted semi-global optimization, and efficient disparity refinement for fast and accurate disparity estimation. IEEE Trans Multimed. 2016;18(2):155–70. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2015.2505905.
LeFevre K, DeWitt DJ, Ramakrishnan R. Incognito: efficient full-domain k-anonymity. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, SIGMOD ’05. ACM. 2005. p. 49–60. https://doi.org/10.1145/1066157.1066164
LeFevre K, DeWitt DJ, Ramakrishnan R. Mondrian multidimensional k-anonymity. In: 22nd international conference on data engineering (ICDE’06). 2006. p. 25. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2006.101
Li N, Li T, Venkatasubramanian S. t-closeness: privacy beyond k-anonymity and l-diversity. In: 2007 IEEE 23rd international conference on data engineering. 2007. p. 106–15. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2007.367856
Liu J, Tang M, Zheng Z, Liu X, Lyu S. Location-aware and personalized collaborative filtering for web service recommendation. IEEE Trans Serv Comput. 2016;9(5):686–99. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2015.2433251.
Machanavajjhala A, Kifer D, Gehrke J, Venkitasubramaniam M. L-diversity: privacy beyond k-anonymity. ACM Trans Knowl Discov Data. 2007;. https://doi.org/10.1145/1217299.1217302.
Meyerson A, Williams R. On the complexity of optimal k-anonymity. In: Proceedings of the twenty-third ACM SIGMOD-SIGACT-SIGART symposium on principles of database systems, PODS ’04. New York: Association for Computing Machinery; 2004. p. 223–28. https://doi.org/10.1145/1055558.1055591.
Nergiz ME, Clifton C. Thoughts on k-anonymization. In: 22nd international conference on data engineering workshops (ICDEW’06). 2006. p. 96. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDEW.2006.147
Ramakrishnan N, Keller BJ, Mirza BJ, Grama AY, Karypis G. Privacy risks in recommender systems. IEEE Internet Comput. 2001;5(6):54–62. https://doi.org/10.1109/4236.968832.
Riyana S, Harnsamut N, Soontornphand T, Natwichai J. (k, e)-anonymous for ordinal data. In: 2015 18th international conference on network-based information systems. 2015. p. 489–93. https://doi.org/10.1109/NBiS.2015.118
Riyana S, Natwichai J. Privacy preservation for recommendation databases. Serv Oriented Comput Appl. 2018;12(3–4):259–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11761-018-0248-y.
Riyana S, Riyana N, Nanthachumphu S. Enhanced (k,e)-anonymous for categorical data. In: Proceedings of the 6th international conference on software and computer applications, ICSCA ’17. New York: ACM; 2017. p. 62–7. https://doi.org/10.1145/3056662.3056668
Schnell R, Bachteler T, Reiher J. Privacy-preserving record linkage using bloom filters. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2009;9:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6947-9-41.
Sitti S, Riyana S, Riyana N. Scenario of privacy violation within the recommendation databases. In: 2017 international conference on digital arts, media and technology (ICDAMT). 2017. p. 383–88. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDAMT.2017.7904997
Sweeney L. Achieving k-anonymity privacy protection using generalization and suppression. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst. 2002;10(5):571–88. https://doi.org/10.1142/S021848850200165X.
Sweeney L. K-anonymity: a model for protecting privacy. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst. 2002;10(5):557–70. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218488502001648.
Xu J, Wang W, Pei J, Wang X, Shi B, Fu AWC. Utility-based anonymization using local recoding. In: Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD ’06. New York, ACM; 2006. p. 785–90, 383–88. https://doi.org/10.1145/1150402.1150504
Zhang Q, Koudas N, Srivastava D, Yu T. Aggregate query answering on anonymized tables. In: 2007 IEEE 23rd international conference on data engineering. 2007. p. 116–25. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2007.367857
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This paper does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the topical collection “Privacy, Data Protection and Digital Identity” guest edited by Fernando Boavida, Andrea Praitano and Georgios V. Lioudakis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riyana, S., Nanthachumphu, S. & Riyana, N. Achieving Privacy Preservation Constraints in Missing-Value Datasets. SN COMPUT. SCI. 1, 227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-020-00241-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-020-00241-9