Abstract
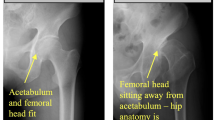
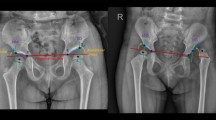
Radiography is the primary modality for diagnosing canine hip dysplasia (CHD), with visual assessment of radiographic features sometimes used for accurate diagnosis. However, these features typically constitute small regions of interest (ROI) within the overall image, yet they hold vital diagnostic information and are crucial for pathological analysis. Consequently, automated detection of ROIs becomes a critical preprocessing step in classification or segmentation systems. By correctly extracting the ROIs, the efficiency of retrieval and identification of pathological signs can be significantly improved. In this research study, we employed the most recent iteration of the YOLO (version 8) model to detect hip joints in a dataset of 133 pelvic radiographs. The best-performing model achieved a mean average precision (mAP50:95) of 0.81, indicating highly accurate detection of hip regions. Importantly, this model displayed feasibility for training on a relatively small dataset and exhibited promising potential for various medical applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaur, M., Wasson, V.: ROI Based medical image compression for telemedicine application. Procedia Comput. Sci. (2015)
Alexander, J.W.: The pathogenesis of canine hip dysplasia. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50051-1
Pinna, S., Tassani, C., Antonino, A., Vezzoni, A.: Prevalence of Primary Radiographic Signs of Hip Dysplasia in Dogs. Animals (Basel). (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202788
Allan, G., Davies, S.: Chapter 21 - Radiographic Signs of Joint Disease in Dogs and Cats, Textbook Vet. Diagn. Radiol. (Seventh Edition), pp. 403–433 (2018)
Wang, S., et al.: (2021). Review and Prospect: artificial intelligence in advanced medical imaging. Frontiers Radiol. (2021)
Sun, S., Zhang, R.: Region of interest extraction of medical image based on improved region growing algorithm. (2017). https://doi.org/10.2991/mseee-17.2017.87
Joshi, A., Charan, V., Prince, S.: A novel methodology for brain tumor detection based on two stage segmentation of MRI images, In: 2015 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems, Coimbatore, India, (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCS.2015.7324127
Xie, L., et al.: Automatic lung segmentation in dynamic thoracic MRI using two-stage deep convolutional neural networks. Proc. SPIE- Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2612558
Pawar, P., Talbar, S.: Two-Stage hybrid approach of deep learning networks for interstitial lung disease classification. Biomed. Res. Int. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7340902
Liu, F-Y., et al.: Automatic hip detection in anteroposterior pelvic radiographs-A labelless practical framework. J. Personalized Med. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060522
Mcevoy, F., et al.: Deep transfer learning can be used for the detection of hip joints in pelvis radiographs and the classification of their hip dysplasia status. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. (2021)
Gomes, D.A., Alves-Pimenta, M.S., Ginja, M., Filipe, V.: Predicting Canine Hip Dysplasia in X-Ray Images Using Deep Learning. In: Pereira, A.I., Fernandes, F.P., Coelho, J.P., Teixeira, J.P., Pacheco, M.F., Alves, P., Lopes, R.P. (eds.) OL2A 2021. CCIS, vol. 1488, pp. 393–400. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-91885-9_29
Terven, J., Cordova-Esparza, D-M.: A Comprehensive Review of YOLO: From YOLOv1 to YOLOv8 and Beyond (2023)
Jocher, G., Chaurasia, A., Qiu, J.: YOLO by Ultralytics. https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics. Accessed 1 Jun 2023
Ultralytics YOLOv5. Ultralytics YOLOv5 - Ultralytics YOLOv8 Docs. https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5. Accessed 31 May 2023
Wang, C-Y., Bochkovskiy, A., Liao, H.: YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. (2022). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2207.02696
Solawetz, J., Francesco.: What is YOLOv8? The Ultimate Guide. https://blog.roboflow.com/whats-new-in-yolov8. Accessed 1 Jun 2023
Zand, M., Etemad, A., Greenspan, M.: ObjectBox: From Centers to Boxes for Anchor-Free Object Detection (2022)
Wang, D., Li, C., Wen, S., Nepal, S., Xiang, Y.: Daedalus: Breaking Non-Maximum Suppression in Object Detection via Adversarial Examples (2019)
Li, Y., Fan, Q., Huang, H., Han, Z., Gu, Q.: A modified YOLOv8 detection network for UAV aerial image recognition (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7050304
Lou, H., et al.: DC-YOLOv8: Small-Size object detection algorithm based on camera sensor. Electronics (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12102323
Tzutalin. LabelImg. (2015). https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg
Ruder, S.: An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms. (2016)
Lin, T-Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. (2014)
Horvat, M., Jelečević, L., Gledec, G.: A comparative study of YOLOv5 models performance for image localization and classification (2022)
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by project Dys4Vet (POCI-01–0247-FEDER-046914), co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through COMPETE2020 - the Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation (OPCI). The authors are also grateful for all the conditions made available by FCT- Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, under the projects UIDP/00772/2020, LA/P/0059/2020, and Scientific Employment Stimulus Institutional Call-CEECINST/00127/2018 UTAD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Loureiro, C. et al. (2024). Deep Learning-Based Hip Detection in Pelvic Radiographs. In: Pereira, A.I., Mendes, A., Fernandes, F.P., Pacheco, M.F., Coelho, J.P., Lima, J. (eds) Optimization, Learning Algorithms and Applications. OL2A 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1982 . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53036-4_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53036-4_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-53035-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-53036-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)