Abstract
Purpose
The present study intends to provide a more established understanding of copper ammoniacal leaching and electrowinning in the presence of organic matter from WPCBs. Because the recirculation of the spent solutions is a matter of great importance from economic and environmental points of view in the hydrometallurgical processes, it was evaluated.
Methods
This work evaluates copper, zinc and nickel recoveries using ammonia–ammonium solutions to leach WPCBs samples; in samples free electronic components, namely electrolytic capacitors; and in samples after calcination at 550 °C. The electrowinning efficiency from pregnant solutions obtained was also evaluated and tests on successive leaching—electrowinning cycles were done to follow the recirculating potential of those solutions.
Results
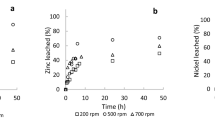
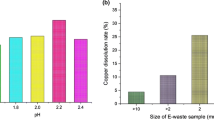
Pre-treatments to reduce organic compounds in WPCBs showed not significantly influence metals leaching efficiencies compared to WPCBs in all and apparently do not benefit copper electrowinning from the pregnant solutions. WPCBs shredding is crucial for obtaining high copper, zinc and nickel leaching recoveries. Electrowinning copper was carried out with extraction efficiencies above 98% in 5 to 6 h of electrolysis time; the copper deposits showed 89.2% copper and nearly 1% zinc and nickel. The recirculation of spent solutions was done with four leaching—electrowinning cycles, showing high copper recoveries up to reaching a pH below 7, which corresponded to a very low ammonia concentration of about 12 mg L−1.
Conclusion
Ammonia/ammonium leaching of WPCBs is attractive from the selective dissolution of copper, zinc and nickel. The pregnant solutions can be used directly for electrowinning and have high purity of copper products. Being the recirculation of solutions is a focal step in the hydrometallurgical processes.
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Arshadi, M., Yaghmaei, S., Esmaeili, A.: Evaluating the optimal digestion method and value distribution of precious metals from different waste printed circuit boards. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag 22, 1690–1698 (2020)
Koyama, K., Tanaka, M., Lee, J.: Copper leaching behavior from waste printed circuit board in ammoniacal alkaline solution. Mater. Trans. 47(7), 1788–1792 (2006)
Oishi, T., Koyama, K., Alam, S., Tanaka, M., Lee, J.C.: Recovery of high purity copper cathode from printed circuit boards using ammoniacal sulfate or chloride solutions. Hydrometallurgy (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2007.05.010
Rudnik, E., Pierzynka, M., Handzlik, P.: Ammoniacal leaching and recovery of copper from alloyed low-grade e-waste. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 18, 318–328 (2016)
Cui, J., Zhang, L.: Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.001
Dávila-Pulido, G.I., Salinas-Rodríguez, A., Carrillo-Pedroza, F.R., González-Ibarra, A.A., Méndez-Nonell, J., Garza-García, M.: Leaching kinetics of electronic waste for the recovery of copper: rate-controlling step and rate process in a multisize particle system. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 53(3), 379–389 (2021)
Oh, C.J., Lee, S.O., Yang, H.S., Ha, T.J., Kim, M.J.: Selective leaching of valuable metals from waste printed circuit boards. J. Air Waste Manag Assoc. 53(7), 897–902 (2003)
Choubey, P.K., Panda, R., Jha, M.K., Lee, J.C., Pathak, D.: Recovery of copper and recycling of acid from the leach liquor of discarded printed circuit boards (PCBs). Sep. Purif. Technol. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.10.012
Dutta, D., Panda, R., Kumari, A., Goel, S., Jha, M.K.: Sustainable recycling process for metals recovery from used printed circuit boards (PCBs). Sustain. Mater. Technol. 17, e00066 (2018)
Janyasuthiwong, S., Ugas, R., Rene, E.R., Alessandra, C., Esposito, G., Lens, P.N.L.: Effect of operational parameters on the leaching efficiency and recovery of heavy metals from computer printed circuit boards. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 91, 2038–2046 (2015)
Maguyon, M.C.C., Catalino, G., Alfafara, G., Migo, V.P., Movillon, J.L., Rebancos, C.M.: Recovery of copper from spent solid printed circuit board (PCB) wastes of a PCB manufacturing facility by two-step sequential acid extraction and electrochemical deposition.J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 15 (1), 17–27 (2012)
Yamane, L.H., Moraes, V.T., Espinosa, D.C.R., Tenório, J.A.S.: Recycling of WEEE: characterization of spent printed circuit boards from mobile phones and computers. Waste Manag. 31, 2553–2558 (2011)
Xiang, Y., Wu, P., Zhu, N., Zhang, T., Liu, W., Wu, P., Li, P.: Bioleaching of copper from waste printed circuit boards by bacterial consortium enriched from acid mine drainage. J. Hazard. Mater. 184(1), 812–818 (2010)
Fathima, A., Tang, J., Giannis, A., Ilankoon, I., Chong, M.: Catalysis electrowinning of copper from E-waste: a critical review. Chemosphere 298, 134340 (2022)
Li, H., Eksteen, J., Oraby, E.: Hydrometallurgical recovery of metals from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs): current status and perspectives—a review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl 139, 122–139 (2018)
Birloaga, I., Coman, V., Kopacek, B.: An advanced study on the hydrometallurgical processing of waste computer printed circuit boards to extract their valuable content of metals. Waste Manag. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.08.0028
Kumari, A., Jha, M.K., Lee, J., Singh, R.P.: Clean process for recovery of metals and recycling of acid from the leach liquor pf PCBs. J. Clean. Prod. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.08.018
Silvas, F.P.C., Correa, M.M.J., Caldas, M.P.K., Moraes, V.T., Espinosa, D.C.R., Tenório, J.A.S.: Printed circuit board recycling: physical processing and copper extractionby selective leaching. Waste Manag (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.08.030
Yang, H., Liu, J., Yang, J.: Leaching copper from shredded particles of waste printed circuit boards. J. Hazard. Mater. 187, 393–400 (2011)
Duan, H., Wang, Z., Yuan, X., Wang, S., Guo, H., Yang, X.: A novel sandwich supported liquid membrane system for simultaneous separation of copper, nickel and cobalt in ammoniacal solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 173, 323–329 (2017)
Liu, R., Shieh, R., Ruth, R.S., Yeh, Y.L., Lin, C.H.: The general utilization of scrapped PC board. Waste Manag. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.07.007
Sun, Z.H.I., Xiao, Y., Sietsma, J., Agterhuis, H., Visser, G., Yang, Y.: Selective copper recovery from complex mixtures of end-of-life electronic products with ammonia-based solution. Hidrometallurgy (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.12.013
Sun, Z.H.I., Xiao, Y., Sietsma, J., Agterhuis, H., Yang, Y.: Complex electronic waste treatment—an effective process to selectively recover copper with solutions containing different ammonium salts. Waste Manag. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.03.015
Xiao, Y., Yang, Y., Van den Berg, J., Sietsma, J., Agterhuis, H., Visser, G., Bol, D.: Hydrometallurgical recovery of copper from complex mixtures of end-of-life shredded ICT products. Hydrometallurgy (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.09.012
Liu, J.C., Kao, T.H.: Extraction of Cu and Pb from printed circuit board sludge using ammonia solutions. Water Sci. Technol. 47(1), 167–172 (2003)
Yang, J.-G., Wu, Y.-T., Li, J.: Recovery of ultrafine copper particles from metal components of waste printed circuit boards. Hydrometallurgy (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2012.04.015
Rania, S., Abdelbasir, S.M., Ayman, H.K., Saad, S.M.H.: Environmentally friendly synthesis of copper nanoparticles from waste printed circuit boards. Sep. Purif. Technol. 230, 115860 (2020)
Bello, W., Valenzuela, M., Bernardes, A., Cifuentes, G.: Removal of entrained organic matter in the copper electrolyte by ozonation. Metal. Mater. Int. Eng. J. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1590/0370-44672018720003
Ma, A., Sun, C., Li, G., Luo, Y., Zheng, X., Liu, C.: Kinetic studies for the absorption of organic matter from purified solution of zinc by coconut shell activated carbon characterization of minerals, metals, and materials. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48210-1_37
Park, J., Kim, E., Park, M., Lee, E.: Adsorption capacity of organic compounds using activated carbons in zinc electrowinning. Energies 12, 2169 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112169
Da Silva, T.R., Majuste, D., Bauer, J., Moats, M.S.: Effect of zinc ions on copper electrodeposition in the context of metal recovery from waste printed circuit boards. Hydrometallurgy 198, 105513 (2020)
Pinho, S.C., Ribeiro, C., Ferraz, C.A., Almeida, M.F.: Copper, zinc and nickel recovery from printed circuit boards using an ammonia–ammonium sulphate system. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01226-3
APHA–American Public Health Association,: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn. Public Office: American Public Health Association, Washington (1998)
EN 1484: : 1997 Water analysis. Guidelines for the determination of total organic carbon (TOC) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) ISO 11466:1995. Soil quality—extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia
Sun, Z., Xiao, Y., Sietsma, J., Agterhuis, H., Yang, Y.: A cleaner process for selective recovery of valuable metals from electronic waste of complex mixtures of end-of- life electronic products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 7981–7988 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by LA/P/0045/2020 (ALiCE), UIDB/00511/2020 and UIDP/00511/2020 (LEPABE), funded by national funds through FCT/MCTES (PIDDAC).
Funding
Funding was provided by Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pinho, S.C., Ferraz, C.A. & Almeida, M.F. Copper Recovery from Printed Circuit Boards Using Ammonia–Ammonium Sulphate System: A Sustainable Approach. Waste Biomass Valor 14, 1683–1691 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01953-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01953-0