Abstract
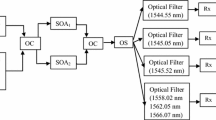
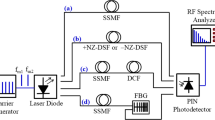
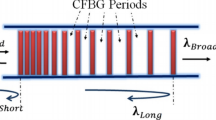
All-optical wavelength conversion based on multi-section semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs) in a symmetrical Mach-Zehnder interferometer (SMZI) is modeled for use in optical networks. It incorporates an enhanced SOA model that is implemented using the time domain transfer matrix approach and hence the overall numerical model determines simultaneously the wavelength and gain parameters for the wavelength converter. The overall model accurately predicts the optimal conditions for the SMZI arrangement in order to achieve the best results for the chirp, the phase inversion and the converted probe signal power. It is also demonstrated that large chirp and mismatch of the phase inversion reduces the eye opening ratio (EOR) which can seriously affect the performance of the wavelength converter to be used as a sub-system component in all-optical networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. E. Olsson, et al., WDM to OTDM multiplexing using an Ultrafast all-optical wavelength converter, IEEE Photonics Technol. Letters, vol. 13,no. 9, (2001), pp. 1005-1007.
X. Hou, et al., Design of wavelength-convertible optical switches for the all-optical next-generation Internet, Conf. Proc. IEEE Workshop on High Performance Switching and Routing (Dallas, USA, 2001), pp. 97-101.
R. Sato, et al., Polarization insensitive SOA-PLC hybrid integrated Michelson interferometeric wavelength converter and its application to DWDM networks, IEICE Transaction on Electron, vol. E84-C,no. 5, (2001), pp. 571-578.
M. Listanti, R. Sabella, Wavelength conversion in WDM optical networks: Strategies and algorithms for limiting the number of converters in the optical cross-connects, Photonic Network Communications, vol. 2,no. 4, (2000), pp. 335-348.
B. Mukherjee, WDM Optical communication networks: Progress and challenges, IEEE Journal on Selected areas in Communications, vol. 18,no. 10, (Nov. 2000), pp. 1810-1824.
P. Polishuk, DWDM system components, Fiber and Integrated Optics, vol. 18,no. 3, (1999), pp. 149-153.
C. Joergensen, et al., Optical wavelength converters-techniques and systems aspects, Proc of SPIE, vol. 2692, (1996), pp. 1-11.
R. Sato, et al., Demonstration of packet-by-packet wavelength conversion from FP-LD light to ITU-T grid wavelengths, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, vol. 13,no. 6, (June 2001), pp. 612-614.
T. K. Nayak, K. N. Sivarajan, A new approach to dimensioning optical networks, IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 20,no. 1, (Jan. 2002), pp. 134-148.
H. Ishikawa, et al., Wavelength conversion technologies for photonic network systems, FUJITSU Scientific Technology Journal, vol. 35,no. 1, (1999), pp. 126-138.
S. J. B. Yoo, Wavelength conversion technologies for WDM applications, Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 14,no. 6, (Sept. 1996), pp. 955-966.
J. M. H. Elmirghani, All-optical wavelength conversion: Technologies and applications in DWDM networks, IEEE Communication Magazine, vol. 38,no. 3, (March 2001), pp. 86-92.
H. Lee, et al., Theoretical study of frequency chirping and extinction ratio of wavelength-converted optical signals by XGM and XPM using SOAs, IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, vol. 35,no. 8, (Aug. 1999), pp. 1213-1219.
T. Durhuus, et al., All-optical wavelength conversion by semiconductor optical amplifiers, Journal of Lightwave Technology, IEEE/OSA Journal, vol. 14,no. 6, (June 1996), pp. 942-953.
S. Nakamura, et al., 168-Gb/s All-optical wavelength conversion with a symmetric-Mach-Zehnder-type switch, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, vol. 13,no. 10, (2001), pp. 1091-1093.
M. Asghari, et al., Wavelength conversion using semiconductor optical amplifiers, Journal of Lightwave Technology, IEEE/OSA Journal, vol. 15,no. 7, (July 1997), pp. 1181-1190.
M.-H. Lee, et al., All optical signal regeneration in cascaded Mach-Zehnder interferometer wavelength converter, IEE Proceedings on Optoelectronics, vol. 148,no. 4, (2001), pp. 189-194.
K. Obermann, et al., Performance analysis of wavelength converters based on cross-gain modulation in semiconductor-optical amplifiers, Journal of Lightwave Technology, IEEE/OSA Journal, vol. 16,no. 1, (Jan. 1998), pp. 78-85.
C. Gosset, G. H. Duan, Extinction ratio improvement and wavelength conversion based on four-wave mixing in a semiconductor optical amplifier, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, vol. 13,no. 2, (2001), pp. 139-141.
S.-C. Cao, et al., Detailed excremental characterization of chirp properties of an SOA-MZI wavelength converter, Conf. Proc. OFC'01 (Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exhibit, March 2001), vol. 2,no. WDD68, pp. 1-3.
S. Shin, S. K. Han, Probe signal dependence of XPM wavelength converters, Conf. Proc. CLEO (Pacific Rim, 1999), pp. 1034-1035.
M. G. Davis, R. F O'Dowd, A transfer matrix method based large-signal dynamic model for multielectrode DFB lasers, IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, vol. 30,no. 11, (Nov. 1994), pp. 2258-2466.
W. Shieh, A. E. Willner, Optimal conditions for high-speed all-optical SOA-based wavelength converter, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, vol. 7,no. 11, (Nov. 1995), pp. 1273-1275.
S. Shimada, H. Ishio, Optical amplifiers and their applications, (John Wiley & Sons, NY, 1998).
A. E. Willner, W. Shieh, Optimal spectral and power parameters for all-optical wavelength shifting: Single stage, fanout, and cascadability, Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 13,no. 5, (May 1995), pp. 771-781.
T. Durhuus, et al., Detailed dynamic model for semiconductor optical amplifiers and their crosstalk and intermodulation distortion, Journal of Lightwave Technology, IEEE/OSA Journal, vol. 10,no. 8, (Aug. 1992), pp. 1056-1065.
G. P. Agrawal, N. K. Dutta, Semiconductor Lasers, (Van Nostrand, New York, 1993).
J. Carrol, J. Whiteaway, D. Plumb, Distributed feedback Semiconductor lasers, (IEE SPIE Optical Engineering Press, London, 1998).
J. S. Perino, et al., fiber transmission of 10Gbit/s signals following wavelength conversion using a travelling-wave semiconductor optical amplifier, IEE Electronics Letters, vol. 30,no. 3, (1994), pp. 256-257.
V. A. Djalali, et al., Theoretical and excremental chirp measurement in a semiconductor optical amplifier, Conf. Proc. CLEO'99 (Optical Society America, Washington, DC, USA, 1999), pp. 310-311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamro, M.Y., Senior, J.M., Leeson, M.S. et al. Modeling Chirp and Phase Inversion in Wavelength Converters based on Symmetrical MZI-SOAs for use in All-Optical Networks. Photonic Network Communications 5, 289–300 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023096304572
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023096304572