Abstract
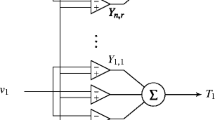
A hybrid correlator architecture is described which combines the serial structure of an active correlator with the parallel structure of a matched filter correlator. The mean PN code acquisition time performance of this hybrid serial-parallel correlator structure is analysed. Results are shown which compare the acquisition performance of the serial, parallel, and serial-parallel structures. The results are for a PN code length of 64 code chips and assumes a Gaussian channel with the receiver detection threshold set to obtain a constant false alarm rate. An enhancement to the serial-parallel acquisition algorithm is also described which can increase the acquisition time performance by about 15% for typical operating conditions. Overall the results demonstrate that the hybrid correlator can provide rapid code acquisition with a limited receiver complexity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.K. Holmes and C.C. Chen, “Acquisition Time Performance of PN Spread-Spectrum Systems”, IEEE Trans. on Comms., Vol. COM-25, No.8, pp. 778–783, 1977.
M. Pandit, “Mean Acquisition Time of Active and Passive Correlation Systems for Spread-Spectrum Communications”, IEE Proceedings, Vol. 128, Part, No. 4, pp. 100–109, 1981.
R.F. Ormondroyd, “PN Code Synchronisation for Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum Systems - a Comparative Evaluation”, IEE Colloquium on New Synchronisation Techniques for Radio Systems, London, pp. 9/1–9/7, 1995.
G.J.R. Povey and P.M. Grant, “Simplified Matched Filter Receiver Designs for Spread Spectrum Communications Applications”, Electronics & Communication Engineering Journal, pp. 59–64, 1993.
M.K. Simon, J.K. Omura, R.A. Scholtz and B.K. Levitt, Spread Spectrum Communications Handbook: Revised Edition, McGrawHill Inc., 1994.
G.J.R. Povey & J. Talvitie, “Doppler Compensation and Code Acquisition Techniques for LEO Satellite Mobile Radio Communications”, International Conference on Satellite Systems for Mobile Communications and Navigation, SSMCN '96, London, pp. 16–19, 1996.
J.G. Proakis, Digital Communications: 2nd Edition, McGrawHill Inc., 1989.
D.A. Shnidman, “Evaluation of the Q Function”, IEEE Trans. on Comms., pp. 342–346, 1974.
A.P. Hulbert, “Comprehensive Rake - A Novel and Practical Receiver Architecture Offering Improved Performance”, Proc. IEEE ISSSTA '94, Oulu, Finland, pp. 470–474.
M.K. Sust, R.F. Kaufmann, F. Molitor and G.A. Bjornstrom, “Rapid Acquisition Concept for Voice Activated CDMA Communication”, IEEE Globecom '90, pp. 1820–1826.
“The Spread Spectrum Handbook: 3rd Edition”, Stanford Telecom, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Povey, G.J. Spread Spectrum PN Code Acquisition Using Hybrid Correlator Architectures. Wireless Personal Communications 8, 151–164 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008855326327
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008855326327