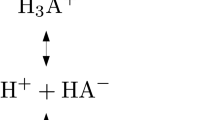Abstract
Both, dielectric continuum solvation models as well as surface or group based methods using polarity and lipophilicity parameters have been proven to be useful tools for the analysis of solvation and partition questions. For the first time, COSMO-RS provides an integrated theory, which combines the aspects of continuum solvation and surface interactions, and which ends up with chemical potentials of molecules in almost arbitrary solvents and mixtures. Due to its sound theoretical basis, COSMO-RS does not only provide a new quantitative access to solvation and partition properties in well defined solvents, but it also opens a novel view and gives a better understanding of the general problem of solvation. Finally, this allows for a generalisation of COSMO-RS to sophisticated
physiological partition problems involving as complex phases as blood, brain, or cell membranes. The use of COSMO-RS for drug discovery and design is demonstrated by applications to blood-brain partition coefficients, and water solubility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben Naim, A., Solvation Thermodynamics, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1987.
Jorgensen, W.L., In Schleyer, P. V.R. and Allinger, L., (Eds), Computation of Free Energy Changes in Solution, Encyclopedia of Computational Chemistry, Vol. 2, Wiley, New York, NY, 1998, pp. 1061-1070.
Schäfer, H., van Gunsteren, W.F. and Mark, A.E, J. Comp. Chem., 20 (1999) 1604.
Duffy, E.M. and Jorgensen, W.L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 122 (2000) 2878.
Jorgensen, W.L. and Duffy, E.M., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 10 (2000) in press.
Hansch, C. and Leo, A.J., Substituent Parameters for Correlation Analysis in Chemistry and Biology, Wiley, New York, NY, 1979.
CLOGP program, BioByte Corporation, Claremont, CA.
Duban, M.E., Bures, M.G., DeLazzer, J. and Martin, Y.C., Helv. Chem. Acta (2000) in press.
Abraham, M.H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 22 (1993) 72.
Gmehling, J., Fluid Phase Equilibria, 144 (1998) 37.
Cramer, C.J. and Truhlar, D.G., in Lipkowitz, K.B. and Boyd, D.B. (Eds), Reviews in Computational Chemistry, Vol. 6, VCH Publishers, New York, NY, 1995.
Tomasi, J. and Persico, M., Chem. Rev., 94 (1994) 2027.
Klamt, A. and Schüürmann, G., J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans., 2 (1993) 799.
Giesen, D.J., Gu.M.Z., Cramer, C.J. and Truhlar, D.G., J. Org. Chem., 61 (1996) 8720.
Klamt, A., COSMO and COSMO-RS, in Schleyer, P. v.R. and Allinger, L. (Eds.) Encyclopedia of Computational Chemistry, Vol. 2, Wiley, New York, NY, 1998, pp. 604-615.
Klamt, A., J. Phys. Chem., 99 (1995) 2224.
Klamt, A., Jonas, V., Buerger, T. and Lohrenz, J.C.W., J. Phys. Chem., 102 (1998) 5074.
Klamt, A. and Eckert, F., Fluid Phase Equilibria, 172 (2000) 43.
Bondi, A., Phys. Chem., 68 (1964) 441.
Mehler, K., Thesis, TU Münich (to be published).
Busalla, T., Diploma Thesis, Univ. Cologne, 1996.
Klamt, A., Eckert, F., Hornig, M. and Blake, J.F. (to be published).
Klamt, A., Eckert, F. and Hornig, M. (to be published).
Ahlrichs, R., Bär, M., Häser, M., Horn, H., and Kölmel, C., Chem. Phys. Letters, 162 (1989) 165.
Schäfer, A., Klamt, A., Sattel, D., Lohrenz, J.C.W. and Eckert, F., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2 (2000) 2187.
MOPAC2000 program, Fujitsu, Japan, 1999.
COSMOtherm program, COSMOlogic GmbH & CoKG, Leverkusen, Germany, 1999.
Cerius2 program, Molecular Simulations, San Diego, CA.
DMol3 program, Molecular Simulations, San Diego, CA.
Andzelm, J., Kölmel, C. and Klamt, A., J. Chem. Phys., 103 (1995) 9312.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klamt, A., Eckert, F. & Hornig, M. COSMO-RS: A novel view to physiological solvation and partition questions. J Comput Aided Mol Des 15, 355–365 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011111506388
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011111506388