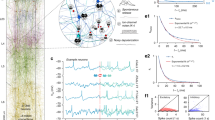
Abstract
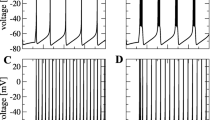
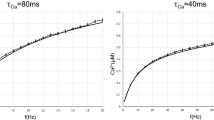
Neocortical pyramidal neurons in vivo are subject to an intense synaptic background activity that has a significant impact on various electrophysiological properties and dendritic integration. Using detailed biophysical models of a morphologically reconstructed neocortical pyramidal neuron, in which synaptic background activity was simulated according to recent measurements in cat parietal cortex in vivo, we show that the responsiveness of the cell to additional periodic subthreshold stimuli can be significantly enhanced through mechanisms similar to stochastic resonance. We compare several paradigms leading to stochastic resonance-like behavior, such as varying the strength or the correlation in the background activity. A new type of resonance-like behavior was obtained when the correlation was varied, in which case the responsiveness is sensitive to the statistics rather than the strength of the noise. We suggest that this type of resonance may be relevant to information processing in the cerebral cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azouz R, Gray C (1999) Cellular mechanisms contributing to response variability of cortical neurons in vivo. J. Neurosci. 19:2209-2223.
Benzi R, Suter A, Vulpiani A (1981) The mechanism of stochastic resonance. J. Phys. A14:L453-L457.
Bezrukov SM, Vodyanoy I (1997) Stochastic resonance in nondynamical systems without response thresholds. Nature 385:319-321.
Bulsara A, Jacobs EW, Zhou T, Moss F, Kiss L (1991) Stochastic resonance in a single neuron model: Theory and analog simulation. J. Theor. Biol. 152:531-555.
Capurro A, Pakdaman K, Nomura T, Sato S (1998) Aperiodic stochastic resonance with correlated noise. Phys. Rev. E 58:4820-4827.
Chialvo DR, Apkarian AV (1993) Modulated noisy biological dynamics: Three examples. J. Stat. Phys. 70:375-391.
Chow CC, Imhoff TT, Collins JJ (1998) Enhancing aperiodic stochastic resonance through noise modulation. Chaos 8:616-620.
Collins JJ, Chow CC, Imhoff TT (1995) Stochastic resonance without tuning. Nature 376:236-238.
Collins JJ, Imhoff TT, Grigg P (1996) Noise enhanced information transmission in rat SA1 cutaneous mechanoreceptors via a periodic stochastic resonance. J. Neurophysiol. 76:642-645.
Contreras D, Destexhe A, Steriade M (1997) Intracellular and computational characterization of the intracortical inhibitory control of synchronized thalamic inputs in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 78:335-350.
Contreras D, Timofeev I, Steriade M (1996) Mechanisms of long lasting hyperpolarizations underlying slow sleep oscillations in cat corticothalamic networks. J. Physiol. 494:251-264.
Cook EP, Johnston D (1997) Active dendrites reduce location-dependent variability of synaptic input trains. J. Neurophysiol. 78:2116-2128.
Cragg BG (1967) The density of synapses and neurons in the motor and visual areas of the cerebral cortex. J. Anat. 101:639-654.
DeFelipe J, Fariñ as I (1992) The pyramidal neuron of the cerebral cortex: Morphological and chemical characteristics of the synaptic inputs. Prog. Neurobiol. 39:563-607.
Denk W, Webb WW (1989) Thermal-noise-limited transduction observed in mechanosensory receptors of the inner ear. Phys. Rev. Lett. 63:207-210.
Destexhe A, Mainen ZF, Sejnowski TJ (1998) Kinetic models of synaptic transmission. In: Koch C, Segev I, eds. Methods in Neuronal Modeling (2nd ed.). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp. 1-26.
Destexhe A (2001) Simplified models of neocortical pyramidal cells preserving somatodendritic voltage attenuation. Neurocomputing. 38:167-173.
Destexhe A, Paré D (1999) Impact of network activity on the integrative properties of neocortical pyramidal neurons in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 81:1531-1547.
Douglas RJ, Wilkens L, Pantazelou E, Moss F (1993) Noise enhancement of information transfer in crayfish mechanoreceptors by stochastic resonance. Nature 365:337-340.
Evarts EV (1964) Temporal patterns of discharge of pyramidal tract neurons during sleep and waking in the monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 27:152-171.
Fauve S, Heslot FJ (1993) Stochastic resonance in a bistable system. Phys. Lett. A97:5-7.
French CR, Sah P, Buckett KJ, Gage PW (1990) Avoltage-dependent persistent sodium current in mammalian hippocampal neurons. J. Gen. Physiol. 95:1139-1157.
Gammaitoni L, Hänggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F (1998) Stochastic resonance. Rev. Mod. Phys. 70:223-287.
Gerstein GL, Bedenbaugh P, Aertsen AJ (1989) Neuronal assemblies. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 36:4-14.
Gruner JE, Hirsch JC, Sotelo C (1974) Ultrastructural features of the isolated suprasylvian gyrus. J. Comp. Neurol. 154:1-27.
Hines ML, Carnevale NT (1997) The NEURON simulation environment. Neural Computation 9:1179-1209.
Hô N, Destexhe A (2000) Synaptic background activity enhances the responsiveness of neocortical pyramidal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 84:1488-1496.
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117:500-544.
Hubel D (1959) Single-unit activity in striate cortex of unrestrained cats. J. Physiol. 147:226-238.
Huber MT, Krieg JC, Dewald M, Voigt K, Braun HA (1998) Stimulus sensitivity and neuromodulatory properties of noise intrinsic neuronal oscillators. BioSystems 48:95-104.
Huguenard JR, Hamill OP, Prince DA (1988) Developmental changes in Na+ conductances in rat neocortical neurons: Appearance of a slow inactivating component. J. Neurophysiol. 59:778-795.
Huguenard JR, McCormick DA (1992) Simulation of the currents involved in rhythmic oscillations in thalamic relay neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 68:1373-1383.
Ivey C, Apkarian AV, Chivalvo DR (1998) Noise-induced tuning curve changes in mechanoreceptors. J. Neurophysiol. 79:1879-1890.
Jaramillo F, Wiesenfeld K (1998) Mechanoelectrical transduction assisted by Brownian motion: A role for noise in the auditory system. Nature Neuroscience 1:384-388.
Johnston D, Magee JC, Colbert CM, Cristie BR (1996) Active properties of neuronal dendrites. Annual Rev. Neurosci. 19:165-186.
Lampl I, Reichova I, Ferster D (1999) Synchronous membrane potential fluctuations in neurons of the cat visual cortex. Neuron 22:361-374.
Larkman AU (1991) Dendritic morphology of pyramidal neurons of the visual cortex of the rat. III. Spine distributions. J. Comp. Neurol. 306:332-343.
Lee SG, Kim S (1999) Parameter dependence of stochastic resonance in the stochastic Hodgkin-Huxley neuron. Phys. Rev. E 60:826-830.
Lee SG, Neiman A, Kim S (1998) Coherence resonance in a Hodgkin-Huxley neuron. Phys. Rev. E 57:3292-3297.
Levin JE, Miller JP (1996) Broadband neural coding in the cricket sensory system enhanced by stochastic resonance. Nature 380:165-168.
Longtin A (1993) Stochastic resonance in neuron models. J. Stat. Phys. 70:309-327.
Longtin A, Bulsara A, Moss F (1991) Time-interval sequences in bistable systems and the noise-induced transmission of information by sensory neurons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67:656-659.
Longtin A, Chialvo DR (1998) Stochastic and deterministic resonance for excitable systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81:4012-4015.
Lytton WW (1996) Optimizing synaptic conductance calculation for network simulations. Neural Computation 8:501-509.
Magee JC, Johnston D (1995a) Characterization of single voltagegated sodium and calcium channels in the apical dendrites of rat CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Physiol. 487:67-90.
Magee JC, Johnston D (1995b) Synaptic activation of voltage-gated channels in the dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Science 268:301-304.
Mar DJ, Chow CC, Gerstner W, Adams RW, Collins JJ (1999) Noise shaping in populations of coupled model neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:10450-10455.
Mato G (1998) Stochastic resonance in neural systems: Effects of temporal correlation in the spike trains. Phys. Rev. E 58:876-880.
Matsumura M, Cope T, Fetz EE (1988) Sustained excitatory synaptic input to motor cortex neurons in awake animals revealed by intracellular recording of membrane potentials. Exp. Brain Res. 70:463-469.
McCormick DA, Huguenard JR (1992) A model of the electrophysiological properties of thalamocortical relay neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 68:1384-1400.
Migliore M, Hoffman DA, Magee JC, Johnston D (1999) Role of an A-type K+ conductance in the back-propagation of action potentials in the dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Comp. Neurosci. 7:5-15.
Neiman A, Pei X, Russell D, Wojtenek W, Wilkens L, Moss F, Braun HA, Huber MT, Voigt K (1999a) Synchronization of the noisy electrosensitive cells in the paddlefish. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82:660-663.
Neiman A, Schimansky-Geier L, Moss F, Shulgin B, Collins JJ (1999b) Synchronization of noisy systems by stochastic signals. Phys. Rev. E 60:284-292.
Nicolis C (1982) Stochastic aspects of climatic transitions: Response to a periodic forcing. Tellus 34:1.
Nowak LG, Sanchez-Vives MV, McCormick DA (1997) Influence of low and high frequency inputs on spike timing in visual cortical neurons. Cereb. Cortex 7:487-501.
Paré D, Shink E, Gaudreau H, Destexhe A, Lang EJ (1998) Impact of spontaneous synaptic activity on the resting properties of cat neocortical neurons in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 79:1450-1460.
Pei X, Wilkens AL, Moss F (1996) Light enhances hydrodynamic signaling in the multimodal caudal photoreceptor interneurons of the crayfish. J. Neurophysiol. 76:3002-3011.
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (1993) Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing. (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Richardson KA, Imhoff TT, Grigg P, Collins JJ (1998) Using electrical noise to enhance the ability of humans to detect subthreshold mechanical cutaneous stimuli. Chaos 8:599-603.
Rudolph M, Destexhe A (2000) Models of neocortical pyramidal neurons in the presence of correlated synaptic background activity: High discharge variability, enhanced responsiveness and independence of input location. Soc. Neurosci. Abstracts 26:1623.
Segev I, Rall W (1998) Excitable dendrites and spines: Earlier theoretical insights elucidate recent direct observations. Trends Neurosci. 21:453-460.
Shimokawa T, Rogel A, Pakdaman K, Sato S (1999) Stochastic resonance and spike-timing precision in an ensemble of leaky integrate and fire neuron models. Phys. Rev. E 59:3461-3470.
Simonotto E, Riani M, Seife C, Roberts M, Twitty J, Moss F (1997) Visual perception of stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78:1186-1189.
Srebo R, Malladi P (1999) Stochastic resonance of the visually evoked potential. Phys. Rev. E 59:2566-2570.
Stacey WC, Durand DM (2000) Stochastic resonance improves signal detection in hippocampal CA1 neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 83:1394-1402.
Steriade M (1978) Cortical long-axoned cells and putative interneurons during the sleep-waking cycle. Behav. Brain Sci. 3:465-514.
Steriade M, Timofeev I, Grenier F (2001) Natural waking and sleep states: A view from inside neocortical neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 85:1969-1985.
Stuart GJ, Sakmann B (1994) Active propagation of somatic action potentials into neocortical pyramidal cell dendrites. Nature 367:69-72.
Szentagothai J (1965) The use of degeneration in the investigation of short neuronal connections. In: Singer M, Shade JP, eds. Progress in Brain Research 14. Elsevier, Amsterdam. pp. 1-32.
Traub RD, Miles R (1991) Neuronal Networks of the Hippocampus. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Wang W, Wang Y, Wang ZD (1998) Firing and signal transduction associated with an intrinsic oscillation in neuronal systems. Phys. Rev. E 57:R2527-R2530.
White EL (1989) Cortical Circuits. Birkhauser, Boston.
Wiesenfeld K, Moss F (1995) Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: From ice ages to crayfish and SQUIDS. Nature 373:33-36.
Yamada WM, Koch C, Adams PR (1989) Multiple channels and calcium dynamics. In: Koch C, Segev I, eds. Methods in Neuronal Modeling. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Zhou T, Moss F (1990) Analog simulations of stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. A41:4255-4264.
Zohary E, Shadlen MN, Newsome WT (1994) Correlated neuronal discharge rate and its implications for psychophysical performance. Nature 370:140-143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rudolph, M., Destexhe, A. Do Neocortical Pyramidal Neurons Display Stochastic Resonance?. J Comput Neurosci 11, 19–42 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011200713411
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011200713411