Abstract
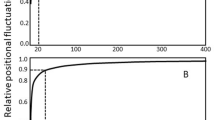
A method is described for the rapid and automatic analysis of flexible molecular alignments using multidimensional scaling and a normalized scoring scheme. A projection scheme was devised to separate orientational and conformational effects. It is shown that the approach can be utilized for the identification of common binding orientations or to the study of differences in partioning behavior. It is suggested that the method can be employed as a novel approach exploring molecular similarity as a dynamic property, so that it includes aspects of motion (by way of mutual orientations), conformations and molecular properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feher, M. and Schmidt, J., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 41 (2001) 346.
Lemmen, C. and Lengauer, T., J. Comput. Aid. Mol. Des., 14 (2000) 215.
Feher, M. and Schmidt, J., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 40 (2000) 495.
Labute, P., Williams, C., Feher, M., Sourial, E. and Schmidt, J., J. Med. Chem., 44 (2001) 1483.
Krzanowski, W.J., Principles of Multivariate Analysis, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1988.
Klebe, G., Mietzner, R. and Weber, F., J. Comput. Aid. Mol. Des., 8 (1994) 751.
Molecular Operating Environment, Version 2000.02, Chemical Computing Group Inc., Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
Halgren, T.A., J. Comp. Chem., 17 (1996) 490.
Still, W.C., Tempczyk, A., Hawley, R.C. and Hendrickson, T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 112 (1990) 6127.
Qiu, D., Shenkin, P.S., Hollinger, F.P. and Still, W.C., J. Phys. Chem. A., 101 (1997) 3005.
Ferguson, D.M. and Raber, D.J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 111 (1989) 4371.
ACD logD suite, version 4.56, Advanced Chemistry Development Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada.
NAG Statistical Add-Ins for Excel, Release 1.1, The Numerical Algorithm Group Ltd., Oxford, UK, 1999.
Girvan, R. and Grant, F., Scie. Comp. World 52 (2000) 31.
McCullough, B.D. and Wilson, B., Comp. Stat. Dat. Anal. 31 (1999) 27.
Testa, B., Carrupt, P.-A., Gaillard, P. and Billois, F., Pharm. Res, 13 (1996) 335.
Böhm, H.-J., Klebe, G. and Kubinyi, H., Wirkstoffdesign, Spektrum Verlag, 1996, pp. 345-346.
Böhm, H.-J., Klebe, G. and Kubinyi, H., Wirkstoffdesign, Spektrum Verlag, 1996, pp. 327-330.
Badger, J., Minor, I., Kremer, M.J., Oliveira, M.A., Smith, T.J., Griffith, J.P., Guerin, D.M.A., Krishnaswamy, S., Luo, M., Rossmann, M.G., McKinlay, M.A., Diana, G.T.D., Dutko, F.J. Fancher, M., Rueckert, R.R. and Heinz, B.A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 85 (1988) 3304.
Böhm, H.-J. and Klebe, G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 35 (1996) 2588.
Brzozowski, A.M., Pike, A.C., Dauter, Z., Hubbard, R.E., Bonn, T., Engstrom, O., Ohman, L., Greene, G.L., Gustafsson, J.A. and Carlquist, M., Nature, 389 (1997) 753.
Wurtz, J.-M., Egner, U., Heinrich, N., Moras, D. and Mueller-Fahrnow, A., J. Med. Chem. 41 (1998) 1803.
Arevalo, J.H., Hassig, C.A., Stura, E.A., Sims, M.J., Taussig, M.J. and Wilson, I.A., J. Mol. Biol., 241 (1994) 663.
Walliman, P., Marti, T., Fürer, A. and Diederich, F., Chem. Rev., 97 (1997) 1567.
Zhorov, B.S. and Lin, S.X., Proteins, 38 (2000) 414.
Schmidt, J., Mercure, J., Feher, M., Dunn-Dufault, R., Peter, M. and Redden P., De Novo Design i Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Non-Steroidal High Affinity Ligands for the Estrogen Receptor, to be published.
N'Goka, V., Schlewer, G., Linget, J.-M., Chambon, J.-P. and Wermuth, C.-G., J. Med. Chem. 34 (1991) 2547.
Carrupt, P.A., Gaillard, P., Billois, F., Weber, P., Testa, B., Meyer, C. and Perez, S., The Molecular Lipophilicity Potential: A New Tool for log P Calculations and Docking, and in Comparative Molecular Field Analysis, in Lipophilicity in Drug Action and Toxicology, VCH, Weinheim, 1996, pp. 195-217.
Carrupt, P.A., Testa, B., Bechalany, A., Tayar, N.E., Descas, P. and Perrissoud, D., J. Med. Chem. 34 (1991) 1272.
Avdeef, A., Assessment of Distribution-pH Profiles, in Lipophilicity in Drug Action and Toxicology, VCH, Weinheim, 1996, pp. 109-139.
Gaillard, P., Carrupt, P.A. and Testa, B., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 4 (1994) 737.
Kubinyi, H., Persp. Drug Disc. Des. 9/10/11 (1998) 225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feher, M., Schmidt, J.M. Identifying potential binding modes and explaining partitioning behavior using flexible alignments and multidimensional scaling. J Comput Aided Mol Des 15, 1065–1083 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015941316283
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015941316283