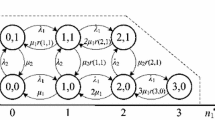
Abstract
In this work we address the problem of statistically multiplexing a variable number of telephone calls via a limited number of channels. Terminals operate with voice activity and silence detectors, and the speech is encoded to a bit rate which is system state dependent. Growing from zero, calls in the system are admitted with a maximum bit rate (maximum quality) until the cutoff fraction of talkspurt (a front end clipping) reaches a certain threshold. At this point the voice bit rate of all transmitting terminals is reduced. If due to traffic fluctuations, the number of calls in progress decreases, then all voice terminals are allowed to operate at the maximum bit rate again. In order to avoid annoying effects to listeners, both the percentage of voice information that is lost and the mean number of changes in the bit rate per mean call holding time are constrained. The first constraint is strongly dependent on the encoding bit rate, and the second one is controlled by using a hysteresis threshold when switching from one bit rate to another. In this work we have used three encoding bit rates, high, medium and low. A birth–death Markov process is used to model the system, which provided exact numerical evaluations for the percentage of time the system operates in each encoding bit rate and for the mean number of changes in the bit rate. Metrics are defined to measure the percentage of both types of voice information that are lost (not transmitted), cutoff or front end clipping and uniform dropping. Finally, an illustrative example is reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Babich, Contention resolution multiple access techniques for handling speech and data traffic on wireless networks, in: Proc. of the Internat. Zurich Seminar on Digital Communications, Zurich, Switzerland (8–11 March 1994) pp. 476-487.
T. Bially, B. Gold and S. Seneff, A technique for adaptive voice flow control in integrated packet networks, IEEE Transactions on Communications 28(3) (1980) 325-333.
V. Casares-Giner and J. Alcober-Segura, Sub-rating scheme for handover. A performance analysis, in: Proc. of WIRELESS '96, Calgary, Canada (8–11 July 1996) pp. 372-379.
V. Casares-Giner and J. Paradells-Aspas, An integrated voice/data traffic model with variable voice service rate, in: Proc. of the IEEE ICC '89, Internat. Conf. on Communications, Boston, USA (11–14 June 1989) pp. 971-976.
V. Casares-Giner and J. Paradells-Aspas, A priority queueing system for integrated voice/data traffic, in: Proc. of the ICCT '90, Internat. Conf. on Communication Technology, Beijing, China (18–20 June 1990) pp. 663-666.
V. Casares-Giner and J. Paradells-Aspas, The busy period of a queue with state dependent service, in: Proc. of the BILKENT '90 Internat. Conf. on New Trends in Communications, Control, and Signal Processing, Ankara, Turkey (2–5 July 1990) pp. 1650-1656.
V. Casares-Giner and J. Paradells-Aspas, Variable voice service rate in wireless access packet networks, in: Proc. of WIRELESS '93, Calgary, Canada (12–14 July 1993) pp. 609-623.
R.B. Cooper, Introduction to Queueing Theory (MacMillan, New York, 1972).
L.E.N. Delbrouck, A unified approximate evaluation of congestion functions for smooth and peaky traffics, IEEE Transactions on Communications 29(1) (1981) 85-91.
J. Filipiak, Real Time Network Management (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1991).
D.J. Goodman, Embedded DPCM for variable bit rate transmission, IEEE Transactions on Communications 28(7) (1980) 1040-1046.
D. Hong and S.S. Rappaport, Traffic model and performance analysis for cellular mobile radio telephone systems with prioritized and nonprioritized handoff procedures, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 35(3) (1986) 77-92.
V.R. Karanam, K. Sriram and D.O. Bowker, Performance evaluation of variable bit rate voice in packet networks, AT&T Technology Journal 67(5) (1988) 41-56.
F. Li and L. Merakos, Voice/data channel access integration in TDMA digital cellular networks, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 43(4) (1994) 986-996.
Y.B. Lin, S. Mohan and A. Noerpel, PCS channel assignment strategies for hand-off and initial access, IEEE Personal Communications 1(3) (1994) 47-56.
Y.B. Lin, A. Noerpel and D. Harasty, The subrating channel assignment strategy for PCS hand-offs, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 45(1) (1996) 122-130.
Y.B. Lin, A. Noerpel and D. Harasty, Self-subrating for voice/data in PCS, Telecommunications Systems 5 (1996) 421-429.
S. Redl, M. Weber and M. Oliphant, An Introduction to GSM (Artech House, 1995).
K. Sriram and D.M. Lucantoni, Traffic smoothing effects of bit dropping in a packet voice multiplexer, IEEE Transactions on Communications 37(7) (1989) 703-712.
K. Sriram, R.S. Mckinney and M.H. Sherif, Voice packetization and compression in broadband ATM Networks, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 9(3) (1991) 294-304.
K. Sriram and Y.T. Wang, Voice over ATM using AAL2 and bit dropping: Performance and call admission control, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 17(1) (1999) 18-28.
C.J. Weinstein, Fractional speech loss and talker activity model for TASI and for packet-switched speech, IEEE Transactions on Communications 26(8) (1978) 1253-1257.
R.I. Wilkinson, Theory for toll traffic engineering in the USA, Bell System Technical Journal 35(2) (1956) 421-513.
R.W. Wolff, Poisson arrivals see time averages, Operation Research 30 (1982) 223-231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casares Giner, V. Variable Bit Rate Voice Using Hysteresis Thresholds. Telecommunication Systems 17, 31–62 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016699902484
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016699902484