Abstract
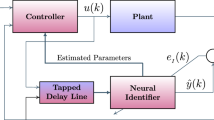
This paper deals with the design and implementation of a neural network-based self-tuning controller. The structure of the controller is based on using a neural network, or a set of them, as a self-tuner for a controller. The intention of this approach is to take advantage of the ability to learn of the neural networks and to use them in place of an identifier in the conventional self-tuner scheme. The work is divided into two main parts. The first one is dedicated to the design of the self-controller. And the second is an application of the algorithm on a nonlinear system: an overhead crane. Some simulations were carried out to verify the efficiency of the self-tuner and then a real-time implementation on a scale prototype was performed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Cheng and C. Chen, “Controllerdesign for an overhead crane system with uncertainty”, Control Engineering Practice, Vol. 4, No. 5, pp. 645–653, 1996.
D. Clarke, Introduction to self-tuning controllers, in C.J. Harris and S.A. Billings (eds), Selftuning and Adaptive Control: Theory and Applications, London: Peter Peregrinus LTD.
T. Fukuda and T. Shibata, Theory and applications of Neural Networks for industrial control systems, IEEE Trans. on Industrial Electronics, Vol. 39, No. 6, pp. 472–489, 1992.
T. Gustaffson,On the design and implementation of a rotary crane controller, European Journal of Control, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 166–175, 1996.
K. Hara, T. Yamamoto, A. Kobayashi and M. Okamoto, Jib crane control to suppress load swing, International Journal of Systems Science, Vol. 20, pp. 715–731.
C.S.G. Lee and M.J. Chung, An adaptive control strategy for mechanical manipulators, IEEE Trans. on Automatic Control, Vol. 29, No. 9, pp. 837–840, 1984.
W. Miller, III, R. Sutton and P. Werbos (eds), Neural Networks for Control. The MIT Press: Cambridge, 1990.
D.R. Strip, Swing-free transport of suspend objects: a general treatment, IEEE Trans. on Robotics and Automation, Vol. 5, pp. 234–236, 1988.
J. Tanomaru and S. Omatu, Process control by on-line trainedNeural Networks, IEEE Trans. on Industrial Electronics, Vol. 39, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acosta, L., Méndez, J., Torres, S. et al. On the Design and Implementation of a Neuromorphic Self-Tuning Controller. Neural Processing Letters 9, 229–242 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018635403382
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018635403382