Abstract
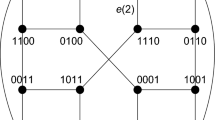
A number of hypercube-variant networks attempt to improve the hypercube by adding extra connections and thus reducing the diameter of the constructed network. We briefly outline a model which describes these variant networks. Further, we show that by restricting this model, we can describe hypercube variants with exactly the same number of edges as the hypercube. We mention several such networks which all have diameter about n/2. We describe a new network within this class that has diameter about 2n/5, thus improving the best known previous bound by a constant factor. We show that within a limited construction paradigm our network is best possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Abraham and K. Padmanabhan, An analysis of the twisted cube topology, in: 1989 International Conference on Parallel Processing (Pennsylvania State Press, 1989) pp. 116-120.
A. Al-Amaway and S. Latifi, Properties and performance of folded hypercubes, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 2(1) (1991) 31-42.
E.R. Berlkamp, R.J. McEliece and H.C.A. Van Tilborg, On the inherent intractibility of certain coding problems, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 24(3) (1978) 384-386.
F.B. Chedid and R.B. Chedid, A new variation on hypercubes with smaller diameter, Information Processing Letters 46(7) (1993) 275-280.
P. Cull and S. Larson, A linear equation model for twisted cube networks, in: International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems 1994, Hinschu, Taiwan (IEEE Computer Soc. Press, 1994) pp. 709-714.
P. Cull and S. Larson, The Möbius cubes, IEEE Transactions on Computers 44(5) (1995) 647-659.
R.K. Das, K. Mukhopadhyaya and B.P. Sinha, A new family of bridged and twisted hypercubes, IEEE Transactions on Computers 40(11) (1991) 1312-1316.
K. Efe, A variation on the hypercube with lower diameter, IEEE Transactions on Computers 40(11) (1991) 1312-1316.
K. Efe, The crossed cube architecture for parallel computation, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 3(5) (1992) 513-524.
A. Estafahanian, L.M. Ni and B. Sagan, The twisted N-cube with application to multiprocessing, IEEE Transactions on Computers 40(1) (1991) 88-93.
P.A.J. Hilbers, R.J.M. Koopman and J.L.A. Van de Snepscheut, The twisted cube, in: PARLE: Parallel Architecture and Languages Europe, eds. J. de Bakker, A. Numan and P. Trelearen (Springer, Berlin, 1987) pp. 152-158.
C. Ho, An observation on the bisectional interconnection networks, IEEE Transactions on Computers 41(7) (1992) 873-877.
S. Larson, A linear equation model for hypercube variant networks, Doctoral thesis, Department of Computer Science, Oregon State University (1995).
M.K. Singhvi and K. Ghose, The MCube: A symmetrical cube based network with twisted links, in: 9th International Parallel Processing Symposium (1995) pp. 11-16.
N. Tzeng and S. Wei, Enhanced hypercubes, IEEE Transactions on Computers 40(3) (1991) 284-294.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cull, P., Larson, S.M. Smaller diameters in hypercube-variant networks. Telecommunication Systems 10, 175–184 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019167000458
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019167000458