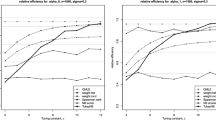
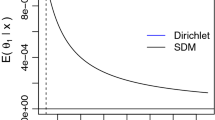
Abstract
We consider computationally-fast methods for estimating parameters in ARMA processes from binary time series data, obtained by thresholding the latent ARMA process. All methods involve matching estimated and expected autocorrelations of the binary series. In particular, we focus on the spectral representation of the likelihood of an ARMA process and derive a restricted form of this likelihood, which uses correlations at only the first few lags. We contrast these methods with an efficient but computationally-intensive Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method. In a simulation study we show that, for a range of ARMA processes, the spectral method is more efficient than variants of least squares and much faster than MCMC. We illustrate by fitting an ARMA(2,1) model to a binary time series of cow feeding data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allcroft D.J. 2001. Statistical models for short-term animal behaviour. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Edinburgh.
Allcroft D.J. and Glasbey C.A. 2000. Estimation of latent Gaussian ARMA models for categorical behaviour data. In: Núñez-Antón V. and Ferreira E. (Eds.), Proceedings of the 15th International Workshop on Statistical Modelling. The University of the Basque Country, Bilbao, pp. 294-299.
Ansley C.F. 1979. An algorithm for the exact likelihood of a mixed autoregressive-moving average process. Biometrika 66: 59-65.
Bartholomew D.J. and Knott M. 1999. Latent Variable Models and Factor Analysis, 2nd Edn. Arnold, London.
Best N.G., Cowles M.K., and Vines S.K. 1995. CODA: Convergence Diagnostics and Output Analysis Software for Gibbs Sampling Output, Version 0.30 MRC Biostatistics Unit, Cambridge, UK.
Box G.E.P., Jenkins G.M., and Reinsel G.C. 1994. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 3rd Edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Brillinger D.R. 1975. Time Series: Data Analysis and Theory. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York.
Brooks S.P. and Roberts G.O. 1998. Convergence assessment techniques for Markov chain Monte Carlo. Statistics and Computing 8: 319-335.
Chatfield C. 1979. Inverse autocorrelations. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society A 142: 363-377.
Cleveland W.S. 1972. The inverse autocorrelations of a time series and their applications. Technometrics 14: 277-293.
Coursol J. and Dacunha-Castelle D. 1983. Remarks on the approxima-tion of the likelihood function of a stationary Gaussian process. Theory of Probability and its Applications 27: 162-167.
Cox D.R. and Miller H.D. 1965. The Theory of Stochastic Processes. Methuen, London.
Cox D.R. and Snell E.J. 1989. Analysis of Binary Data, 2nd Edn. Chapman & Hall, London.
Cressie N. 1985. Fitting variogram models by weighted least squares. Mathematical Geology 17: 563-586.
Glasbey C.A., Nevison I.M., and Hunter A.G.M. 1998. Parameter estimators for Gaussian models with censored time series and spatio-temporal data. In: Payne R. and Green P. (Eds.), COMP-STAT98 Proceedings in Computational Statistics, Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp. 323-328.
Hjort N.L. and Omre H. 1994. Topics in spatial statistics. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 21: 289-357.
Keenan D. 1982. A time series analysis of binary data. Journal of the American Statistical Association 77: 816-821.
Kendall M.G., Stuart A., and Ord J.K. 1983. The Advanced Theory of Statistics, Vol. 3: Design and Analysis, and Time-Series, 4th Edn. Griffin, High Wycombe.
Lütkepohl H. 1991. Introduction to Multiple Time Series Analysis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
MacDonald I.L. and Zucchini W. 1997. Hidden Markov and Other Models for Discrete-valued Time Series. Chapman & Hall, London.
Numerical Algorithms Group. 1993. Library Manual Mark 16. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Phadke M.S. and Kedem G. 1978. Computation of the exact likelihood function of multivariate moving average models. Biometrika 65: 511-519.
Tolkamp B.J., Allcroft D.J., Austin E.J., Nielsen B.L., and Kyriazakis I. 1998. Satiety splits feeding behaviour into bouts. Journal of Theoretical Biology 194: 235-250.
Tong Y.L. 1990. The Multivariate Normal Distribution. Springer, New York.
Whittle P. 1953. The analysis of multiple stationary time series. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B 15: 125-139.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allcroft, D.J., Glasbey, C.A. A Spectral Estimator of Arma Parameters from Thresholded Data. Statistics and Computing 12, 369–376 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020796314300
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020796314300