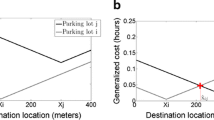
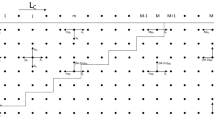
Abstract
In this paper we consider the problem of designing parking facilities for park'n ride trips. We present a new continuous equilibrium network design problem to decide the capacity and fare of these parking lots at a tactical level. We assume that the parking facilities have already been located and other topological decisions have already been taken.
The modeling approach proposed is mathematical programming with equilibrium constraints. In the outer optimization problem, a central Authority evaluates the performance of the transport network for each network design decision. In the inner problem a multimodal traffic assignment with combined modes, formulated as a variational inequality problem, generates the share demand for modes of transportation, and for parking facilities as a function of the design variables of the parking lots. The objective is to make optimal parking investment and pricing decisions in order to minimize the total travel cost in a subnetwork of the multimodal transportation system.
We present a new development in model formulation based on the use of generalized parking link cost as a design variable.
The bilevel model is solved by a simulated annealing algorithm applied to the continuous and non-negative design decision variables. Numerical tests are reported in order to illustrate the use of the model, and the ability of the approach to solve applications of moderate size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abdulaal and L.J. LeBlanc, Continuous equilibrium network design models, Transportation Research B 13 (1979) 19-32.
M.S. Bazaraa, H.D. Sherali and C.M. Shetty, Nonlinear Programming: Theory and Algorithms, 2nd ed. (Wiley, New York, 1993).
D.P. Bertsekas and E.M. Gafni, Projection methods for variational inequalities with application to the traffic assignment problem, Math. Prog. Study 17 (1982) 139-159.
S. Carrese, S. Gori and T. Picano, Relationship between parking location and traffic flows in urban areas, in: Advanced Methods in Transportation Analysis, eds. L. Bianco and P. Toth (Springer, Berlin, 1996) pp. 183-214.
M. Coffin and M.F. Saltzman, Statistical analysis of computational tests of algorithms and heuristics, INFORMS Journal on Computing 12 (2000) 24-44.
E. Fernández, J. De Cea, M. Florian and E. Cabrera, Network equilibrium models with combined modes, Transportation Science 28 (1994) 182-192.
P. Ferrari, A model of urban transport management, Transportation Research B 33 (1999) 43-61.
M. Florian, Private communication (1990).
T.L. Friesz, H.-J. Cho, N. Tobin and G. Anandalingam, A Simulated annealing approach to the network design problem with variational inequality constraints, Transportation Science 26 (1992) 18-26.
T.L. Friesz, N. Tobin, S. Shah, M. Mehta and G. Anandalingam, The multiobjective equilibrium network design problem revisited: a simulated annealing approach, European Journal of Operations Research 65 (1993) 44-57.
R. García and A. Marín, Urban multimodal interchange design methodology, in: Mathematical Methods on Optimization in Transportation Systems, eds.M. Pursula and J. Niittymaki (Kluwer, Dordrecht, 2001) pp. 49-79.
R. García and A. Marín, Network equilibrium models with combined modes: Models and solution algorithms, Report, Departamento de Matemática Aplicada y Estadística, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, España (2000).
R. García, A. Marín and M. Patriksson, A class of column generation/simplicial decomposition algorithms in convex differentiable optimization, I: Convergence analysis, II: Numerical experiments, Reports, Departamento de Matemática Aplicada y Estadística, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, España (1999).
R. García, Metodología para el Diseño de Redes de Transporte y para la elaboración de algoritmos en Programación Matemática Convexa y Diferenciable, Ph.D. dissertation, Departamento de Matemática Aplicada y Estadística, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, España (2001).
A. Geoffrion, Elements of large-scale mathematical programming, Management Science 16 (1970).
T. Larsson, M. Patriksson and C. Rydergren, Applications of simplicial decomposition with nonlinear column generation to nonlinear network flows, in: Network Optimization, eds. P.M. Pardalos, W.W. Hager and D.W. Hearn (Springer, Berlin, 1997) pp. 346-373.
Z. Luo, J. Pang and D. Ralph, Mathematical Programs with Equilibrium Constraints (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1996).
P. Marcotte, Network optimization with continuous control parameters, Transportation Science 17 (1983) 181-197.
Q. Meng, H. Yang and M.G.H. Bell, An equivalent continously differentiable model and a locally convergent algorithm for the continuous network design problem, Transportation Research 35 (2001) 83-105.
S. Nguyen and C. Dupuis, An efficient method for computing traffic equilibria in networks with asymmetric transportation costs, Transportation Science 18 (1984) 185-202.
J. Nocedal and J. Wright, Numerical Optimization (Springer, New York, 1999).
J. de D. OrtÚzar and L.G.Willumsen, Modelling Transport (Wiley, New York, 1994).
M. Patriksson, The Traffic Assignment Problem.Models and Methods (VSP, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1994).
Y. Sheffi, Urban Transportation Networks (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1985).
C. Suwansirikul, T. Friesz and R.L. Tobin, Equilibrium decomposed optimization: A heuristic for the continuous equilibrium network design problem, Transportation Science 4 (1987) 254-263.
H.N. Tan, S.S. Gershwin and M. Athans, Hybrid optimization in urban traffic networks, Technical report, N DOT-TSC-RSPA-79-7, National Technical Information Service, Springfield, III (1979).
H. Yang and M.G.H. Bell, Models algorithms for road network design: a review and some new developments, Transportation Reviews 18 (1998) 257-278.
D. Vanderbilt and S.G. Louie, A Monte Carlo simulated annealing approach to optimization over continuous variables, Journal of Computational Physics 56 (1984) 259-271.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García, R., Marín, A. Parking Capacity and Pricing in Park'n Ride Trips: A Continuous Equilibrium Network Design Problem. Annals of Operations Research 116, 153–178 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021332414941
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021332414941