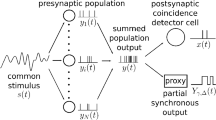
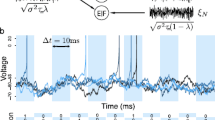
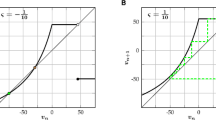
Abstract
We demonstrate that a realistic neuron model expressed by the Hodgkin-Huxley equations shows a stochastic resonance phenomenon, by computing cross-correlation between input and output spike timing when the neuron receives both aperiodic signal input of spike packets and background random noise of both excitatory and inhibitory spikes. We consider that such a signal detection is realized because the neuron with active properties is sensitive to fluctuation caused by a sharp increase just after a sudden dip of excitatory noise spikes and a gradual decrease of inhibitory noise spikes. We also show that the model generates highly irregular firing of output spikes on the basis of the modulation detecting property.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Jung, P.: Periodically driven stochastic systems, Phys. Rep., 234 (1993), 175-295.
Moss, F., Pierson, D. and O'Gorman, D.: Stochastic resonance: Tutorial and update, Int. J. Bifurc. and Chaos, 4(6) (1994), 1383-1397.
Wiesenfeld, K. and Moss, F.: Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: fromice ages to crayfish and SQUIDs, Nature, 373 (1995), 33-36.
Douglass, J., Wilkens, L., Pantazelou, E. and Moss, F.: Noise enhancement of the information transfer in crayfish mechanoreceptors by stochastic resonance, Nature, 365 (1993), 337-340.
Longtin, A.: Stochastic resonance in neuron models, J. Stat. Phys., 70 (1993), 309-327.
Collins, J. J., Chow, C. C. and Imhoff, T. T.: Stochastic resonance without tuning, Nature, 376 (1995), 236-238.
Bulsara, A. R., Elton, T. C., Doering, C. R., Lowen, S. B. and Lindenberg, K.: Cooperative behavior in periodically driven noisy integrate-fire models of neuronal dynamics, Phys. Rev. E, 53(4) (1996), 3958-3969.
Gluckman, B. J., Netoff, T. I., Neel, E. J., Ditto, W. L., Spano, M. L. and Schiff, S. J.: Stochastic resonance in a neuronal network from mammalian brain, Phys. Rev. Lett., 77(19) (1996), 4098-4101.
Chapeau-Blondeau, F., Godivier, X. and Chambet, N.: Stochastic resonance in a neuron model that transmits spike trains, Phys. Rev. E, 53 (1996), 1273-1275.
Fakir, R.: Nonstationary stochastic resonance in a single neuronlike system, Phys. Rev. E, 58 (1998), 5175-5178.
Calvin, W. H. and Stevens, C. F.: Synaptic noise and other sources of randomness in motoneuron interspike intervals, J. Neurophysiol., 31 (1968), 574-587.
Softky, W. R. and Koch, C.: The highly irregular firing of cortical cells is inconsistent with temporal integration of random EPSPs, J. Neuroscience, 13(1) (1993), 334-350.
Abeles, M.: Role of the cortical neuron: integrator or coincidence detector? Israel J. Med. Sci., 18 (1982), 83-92.
Mainen, Z. F. and Sejnowski, T. J.: Reliability of spike timing in neocortical neurons, Science, 268 (1995), 1503-1506.
Markram, H., Lübke, J., Frotscher, M. and Sakmann, B.: Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs, Science, 275 (1997), 213-215.
van Steveninck, R. R. D., Lewen, G. D., Strong, S. P., Koberle, R. and Bialek, W.: Reproducibility and variability in neural spike trains, Science, 275 (1997), 1805-1808.
Azouz, R. and Gray, C. M.: Dynamic spike threshold reveals a mechanism for synaptic coincidence detection in cortical neurons in vivo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97 (2000), 8110-8115.
Robinson, H. P. C. and Kawai, N.: Injection of digitally synthesized synaptic conductance transients to measure the integrative properties of neurons, J. Neurosci. Methods, 49 (1993), 157-165.
Robinson, H. P. C.: Analog circuits for injecting time-varying linear and nonlinear (NMDA-type) conductances into neurons, J. Physiol., 518P (1999), 9-10.
Hodgkin, A. L. and Huxley, A. F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve, J. Physiol., 117 (1952), 500-544.
Rall, W.: Distinguishing theoretical synaptic potentials computed for different somadendritic distributions of synaptic inputs, J. Neurophysiol., 30 (1967), 1138-1168.
Jack, J. J. B., Noble, D. and Tsein, R. W.: Electrical Current Flow in Excitable Cells, Oxford, Claredon Press, second edition, 1975.
Diesmann, M., Gewaltig, M. and Aertsen, A.: Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural network, Nature, 402 (1999), 529-533.
Palm, G., Aertsen, A. and Gerstein, G. L.: On the significance of correlations among neuronal spike trains, Biol. Cybern., 59 (1988), 1-11.
Aertsen, A., Gerstein, G. L., Habib, M. K. and Palm, G.: Dynamics of neuronal firing correlation: Modulation of 'effective connectivity', J. Neurophysiol., 61(5) (1989), 900-917.
Softky, W. R.: Simple codes versus efficient codes, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 5 (1995), 239-247.
Fujii, H., Ito, H., Aihara, K., Ichinose, N. and Tsukada, M.: Dynamical cell assembly hypothesis-theoretical possibility of spatio-temporal coding in the cortex, Neural Networks, 9(8) (1996), 1303-1350.
Watanabe, M. and Aihara, K.: Chaos in neural networks composed of coincidence detector neurons, Neural Networks, 10(8) (1997), 1353-1359.
Watanabe, M., Aihara, K. and Kondo, S.: A dynamic neural network with temporal coding and functional connectivity, Biol. Cybern., 78 (1998), 87-93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakumura, Y., Aihara, K. Stochastic Resonance and Coincidence Detection in Single Neurons. Neural Processing Letters 16, 235–242 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021786719535
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021786719535