Abstract
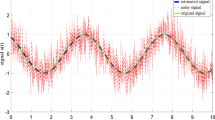
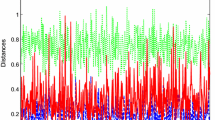
A new algorithm called Structured Nonlinear Total Least Norm (SNTLN) has recently been developed for obtaining an approximate solution to the structured overdetermined nonlinear system. Both theoretical justification and computational testing show that SNTLN is an efficient method for solving structured overdetermined systems. In this paper, we present a method based on SNTLN for estimating the parameters of exponentially damped sinusoidal signals in noise when the model order is unknown. It is compared to two other existing methods to show its robustness in recovering correct values of parameters when the model order is unknown, in spite of some large errors in the measured data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Barkjuijsen, R. De Beer and D. Van Ormondt, Improved algorithm for noniterative time-domain model fitting to exponentially damped magnetic resonance signals, J. Magn. Resonance 73 (1987) 553–557.
H. Chen, S. Van Huffel, D. Ormondt and R. de Beer, Parameter estimation with prior knowledge of known signal poles for the quantification of NMR spectroscopy data in the time domain, J. Magn. Resonance Ser. A 119 (1996) 225–234.
R. De Beer and D. Van Ormondt, Analysis of NMR data using time-domain fitting procedures, in: NMR Basic Principles and Progress Series, Vol. 26 (Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1992) pp. 201–248.
F.B. Hildebrand, Introduction to Numerical Analysis (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1956).
R. Kumaresan, Estimating the parameters of exponentially damped/undamped sinusoidal signals in noise, Ph.D. dissertation, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI (1982).
R. Kumaresan and D.W. Tufts, Accurate parameter estimation of noisy speech-like signals, presented at: IEEE Internat.Conf.on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, Paris, France, 3–5 May 1982.
R. Kumaresan and D.W. Tufts, Estimating the parameters of exponentially damped sinusoids and pole–zero modeling in noise, IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 30(6) (1982) 833–840.
R. Kumaresan, D.W. Tufts and L.L. Scharf, A prony method for noisy data: Choosing the signal components and selecting the order in exponential signal models, Proc. IEEE 72(2) (1984) 230–233.
S.Y. Kung, K.S. Arun and D.V. Bhaskar Rao, State-space and singular value decomposition-based approximation methods for the harmonic retrieval problem, J. Opt. Soc. Amer. 73 (1983) 1799–1811.
A. Macovski and D. Spielman, Magn. Resonance Medicine 3 (1986) 97.
J.P. Norton, An Introduction to Identification (Academic Press, London, 1986).
H. Park, S. Van Huffel and L. Eldén, Fast algorithm for exponential data modeling, in: Proc.of the IEEE Internat.Conf.on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 94), Adelaide, Australia, April 1994, pp. 25–28.
M.B. Priestley, Spectral Analysis and Time Series, Vols. 1 and 2 (Academic Press, London, 1981).
J.B. Rosen, H. Park and J. Glick, Total least norm formulation and solution for structured problems, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 17(1) (1996) 110–128.
J.B. Rosen, H. Park and J. Glick, Total least norm for linear and nonlinear structured problems, in: Recent Advances in Total Least Squares Techniques and Errors-in-Variables Modeling, ed. S. Van Huffel (SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, 1997) pp. 203–214.
J.B. Rosen, H. Park and J. Glick, Structured total least norm for nonlinear problems, SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 20(1) (1999) 14–30.
J.B. Rosen, H. Park and J. Glick, Signal identification using a least L 1 norm algorithm, Optim. Engrg. 1 (2000) 51–65.
J.B. Rosen, H. Park, J. Glick and L. Zhang, Accurate solution to overdetermined linear equations with errors, using L 1 norm minimization, Comput. Optim. Appl. 17 (2000) 329–341.
A. Tarantola, Inverse Problem Theory.Methods for Data Fitting and Model Parameter Estimation (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1987).
A Van den Bos, Estimation of Fourier coefficients, IEEE Trans. Instrument. Measm. 38 (1989) 1005–1007.
S. Van Huffel, L. Aerts, J. Bervoets, J. Vandewalle, C. Decanniere and P. Van Hecke, Improved quantitative time–domain analysis of NMR data by total least squares, in: Signal Processings VI: Theories and Applications, Vol. III, eds. J. Vandewalle, R. Boite, M. Moonen and A. Oosterlinck (Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 1992) pp. 1721–1724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Park, H. & Rosen, J.B. Exponential Modeling with Unknown Model Order Using Structured Nonlinear Total Least Norm. Advances in Computational Mathematics 19, 307–322 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022881907141
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022881907141