Abstract
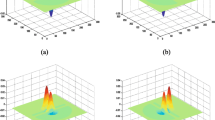
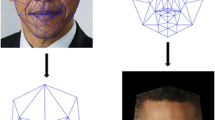
We present a novel approach to face recognition by constructing facial identity structures across views and over time, referred to as identity surfaces, in a Kernel Discriminant Analysis (KDA) feature space. This approach is aimed at addressing three challenging problems in face recognition: modelling faces across multiple views, extracting non-linear discriminatory features, and recognising faces over time. First, a multi-view face model is designed which can be automatically fitted to face images and sequences to extract the normalised facial texture patterns. This model is capable of dealing with faces with large pose variation. Second, KDA is developed to compute the most significant non-linear basis vectors with the intention of maximising the between-class variance and minimising the within-class variance. We applied KDA to the problem of multi-view face recognition, and a significant improvement has been achieved in reliability and accuracy. Third, identity surfaces are constructed in a pose-parameterised discriminatory feature space. Dynamic face recognition is then performed by matching the object trajectory computed from a video input and model trajectories constructed on the identity surfaces. These two types of trajectories encode the spatio-temporal dynamics of moving faces.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Atick, J., Griffin, P., and Redlich, A. 1996. Statistical approach to shape from shading: Reconstruction of 3d face surfaces from single 2d images. Neural Computation, 8(6):1321–1341.
Baudat, G. and Anouar, F. 2000. Generalized discriminant analysis using a kernel approach. Neural Computation, 12:2385–2404.
Bennett, A. and Craw, I. 1991. Finding image features using deformable templates and detailed prior statistical knowledge. In British Machine Vision Conference, Glasgow, UK, pp. 233–239.
Bishop, C.M. 1995. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition. Clarendon Press: Oxford.
Brammer, K. and Siffling, G. 1989. Kalman-Bucy Filters. Artech House: Norwood, USA.
Bruce, V., Burton, A., and Hancock, P. 1998a. Comparisons between human and computer recognition of faces. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, pp. 408–413.
Bruce, V., Hancock, P., and Burton, A. 1998b. Human face perception and identification. In Face Recognition: From Theory to Applications, H. Weschler, J. Philips, V. Bruce, F. Fogelman-Soulie, and T. Huang (Eds.), Springer-Verlag, pp. 51–72.
Brunelli, R. and Poggio, T. 1993. Face recognition: Features vs. templates. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 15(10):1042–1062.
Burges, C.J.C. 1996. Simplified support vector decision rules. In Proceedings, 13th Intl. Conf. on Machine Learning, L. Saitta (Ed.), Morgan Kaufmann: San Mateo, CA, pp. 71–77.
Burges, C.J.C. and Scholkopf, B. 1997. Improving the accuracy and speed of support vector learning machines. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, M. Mozer, M. Jordan, and T. Petsche (Eds.), MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, vol. 9, pp. 375–381.
Choudhury, T., Clarkson, B., Jebara, T., and Pentland, A. 1999. Multimodal person recognition using unconstrained audio and video. In International Conference on Audio-and Video-Based Person Authentication, pp. 176–181.
Cootes, T., Taylor, C., and Lanitis, A. 1994. Active shape models: Evaluation of a multi-resolution method for improving image search. In British Machine Vision Conference, York, England, vol. 1, pp. 327–336.
Cootes, T., Edwards, G., and Taylor, C. 1998. Active appearance models. In European Conference on Computer Vision, Freiburg, Germany, vol. 2, pp. 484–498.
Cootes, T., Taylor, C., Cooper, D., and Graham, J. 1995. Active shape models–Their training and application. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 61(1):38–59.
Cootes, T., Walker, K., and Taylor, C. 2000. View-based active appearance models. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Grenoble, France, pp. 227–232.
Craw, I., Tock, D., and Bennett, A. 1992. Finding face features. In European Conference on Computer Vision, Santa Margherita Ligure, Italy, pp. 92–96.
DeCarlo, D. and Metaxas, D. 2000. Optical flow constraints on deformable models with applications to face tracking. International Journal of Computer Vision, 38(2):99–127.
Edwards, G., Lanitis, A., Taylor, C., and Cootes, T. 1996. Statistical models of face images–Improving specificity. In British Machine Vision Conference, Edinburgh, Scotland, vol. 2, pp. 765–774.
Edwards, G., Lanitis, A., Taylor, C., and Cootes, T. 1998a. Statistical models of face images–Improving specificity. Image and Vision Computing, 16(3):203–211.
Edwards, G., Taylor, C., and Cootes, T. 1998b. Learning to identify and track faces in sequences. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, pp. 260–267.
Edwards, G., Taylor, C., and Cootes, T. 1999. Improving identifi-cation performance by integrating evidence from sequences. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Fort Collins, CO, USA, vol. 1, pp. 486–491.
Ezzat, T. and Poggio, T. 1996. Facial analysis and synthesis using image-based methods. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Vermont, US, pp. 116–121.
Fisher, R.A. 1938. The statistical utilization of multiple measurements. Annals of Eugenics, 8:376–386.
Fukunaga, K. 1972. Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognitiion. Academic Press.
Gong, S., McKenna, S., and Psarrou, A. 2000. Dynamic Vision: From Images to Face Recognition. World Scientific Publishing and Imperial College Press.
Gong, S., Psarrou, A., Katsouli, I., and Palavouzis, P. 1994. Tracking and recognition of face sequences. In European Workshop on Combined Real and Synthetic Image Processing for Broadcast and Video Production, Hamburg, Germany, pp. 96–112.
Howell, A. and Buxton, H. 1996. Towards unconstrained face recognition from image sequences. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Vermont, USA, pp. 224–229.
Jebara, T. and Pentland, A. 1997. Parametrized structure from motion for 3D adaptive feedback tracking of faces. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
Kass, M., Witkin, A., and Terzopoulos, D. 1987. Snakes: Active contour models. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1(4):321–331.
Knight, B. and Johnston, A. 1997. The role of movement in face recognition. Visual Cognition, 4:265–274.
Lades, M., Vorbruggen, J., Buhmann, J., Lange, J., Malsburg, C., Wurtz, R., and Konen, W. 1993. Distortion invariant object recognition in the dynamic link architecture. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 42(3):300–311.
Lanitis, A., Taylor, C., and Cootes, T. 1997. Automatic interpretation and coding of face images using flexible models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 19(7):743–756.
Li, H., Roivainen, P., and Forchheimer, R. 1993. 3-d motion estimation in model-based facial image coding. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 15(6):545–555.
Li, Y., Gong, S., and Liddell, H. 2000a. Recognising the dynamics of faces across multiple views. In British MachineVision Conference, Bristol, UK, pp. 242–251.
Li, Y., Gong, S., and Liddell, H. 2000b. Support vector regression and classification based multi-viewface detection and recognition.In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Grenoble, France, pp. 300–305.
Li, Y., Gong, S., and Liddell, H. 2001. Constructing structures of facial identities using Kernel Discriminant Analysis. In The 2nd International Workshop on Statistical and Computational Theories of Vision, Vancouver, Canada.
McKenna, S. and Gong, S. 1998. Recognising moving faces. In Face Recognition: From Theory to Applications, Wechsler, Philips, Bruce, Fogelman-Soulie, and Huang (Eds.), Springer-Verlag, pp. 578–588.
Mika, S., Ratsch, G., Weston, J., Scholkopf, B., and Muller, K. 1999. Fisher discriminant analysis with kernels. In IEEE Neural Networks for Signal Processing Workshop, pp. 41–48.
Moghaddam, B. and Pentland, A. 1994. Face recognition using viewbased and modular eigenspaces. InAutomatic Systems for the Identification and Inspection of Humans, SPIE, vol. 2277.
Moghaddam, B. and Pentland, A. 1997. Probabilistic visual learning for object representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 19(7):137–143.
Moghaddam, B., Wahid, W., and Pentland, A. 1998. Beyond eigenfaces: Probabilistic matching for face recognition. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, pp. 30–35.
Murase, H. and Nayar, S.K. 1994. Illumination planning for object recognition using parametric eigenspaces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 16(12):1219–1227.
Murase, H. and Nayar, S.K. 1995. Visual learning and recognition of 3-D objects from appearance. International Journal of Computer Vision, 14:5–24.
Okubo, M. and Watanabe, T. 1998. Lip motion capture and its application to 3-D molding. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, pp. 187–192.
Osuna, E., Freund, R., and Girosi, F. 1997a. Support vector machines: Training and applications. Technical report, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. AI Memo 1602.
Osuna, E., Freund, R., and Girosi, F. 1997b. Training support vector machines: An application to face detection. In Proc. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition'97, pp. 130–136.
Romdhani, S., Gong, S., and Psarrou, A. 1999. A multi-view nonlinear active shape model using kernel pca. In British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, UK, pp. 483–492.
Roth, V. and Steinhage, V. 1999. Nonlinear discriminant analysis using kernel functions. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, S. Solla, T. Leen, and K.-R. MÜller (Eds.), MIT Press, vol. 12, pp. 568–574.
Scholkopf, B. 1997. Support Vector Learning.R. OldenbourgVerlag: Munich.
Scholkopf, B., Smola, A., and Muller, K.-R. 1997. Kernel principal component analysis. In Artificial Neural Networks–ICANN'97, W. Gerstner, A. Germond, M. Hasler, and J.-D. Nicoud, (Eds.), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer Berlin, pp. 583–588.
Shakunaga, T., Ogawa, K., and Oki, S. 1998. Integration of eigentemplate and structure matching for automatic facial feature detection. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, pp. 94–99.
Sirovich, L. and Kirby, M. 1987. Low-dimensional procedure for the characterization of human faces. Journal of Optical Society of America, 4:519–524.
Steffens, J., Elagin, E., and Neven, H. 1998. Personspotter–Fast and robust system for human detection, tracking and recognition. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, pp. 516–521.
Sung, K. and Poggio, T. 1994. Example-based learning for viewbased human face detection. Technical report, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. A.I. MEMO 1521.
Swets, D. and Weng, J. 1996. Using discriminant eigenfeatures for image retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 18(8):831–836.
Turk, M. and Pentland, A. 1989. Face processing: Models for recognition. In Intelligent Robots and Computer Vision VIII: Algorithms and Techniques, Philadelphia, PA, USA, pp. 22–32.
Vanderbei, R. 1994. Loqo: An interior point code for quadratic programming. Technical report, Princeton University. Technical Report SOR 94–15.
Vapnik, V. 1995. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. Springer Verlag: New York.
Vetter, T. 1998. Synthesis of novel views from a single face image. International Journal of Computer Vision, 28(2):103–116.
Vetter, T. and Blanz, V. 1998. Generalization to novel views from a single face image. In Face Recognition: From Theory to Applications, Wechsler, Philips, Bruce, Fogelman-Soulie, and Huang (Eds.), Springer-Verlag, pp. 310–326.
Waite, J.B. and Welsh, W.J. 1990. An application of active contour models to head boundary location. In British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 407–412.
Wu, H., Yokoyama, T., Pramadihanto, D., and Yachida, M. 1996. Face and facial feature extraction from color image. In IEEE International Conference onAutomaticFace & Gesture Recognition, Vermont, USA, pp. 345–350.
Yamaguchi, O., Fukui, K., and Maeda, K. 1998. Face recognition using temporal image sequence. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, pp. 318–323.
Yokoyama, T., Yagi, Y., and Yachida, M. 1998. Facial contour extraction model. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, pp. 254–259.
Yuille, A., Hallinan, P., and Cohen, D. 1992. Feature extraction from faces using deformable templates. International Journal of Computer Vision, 8(2):99–111.
Zhao, W. and Chellappa, R. 2000. SFS based view synthesis for robust face recognition. In IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Grenoble, France, pp. 285–292.
Zhao, W., Krishnaswamy, A., Chellappa, R., Swets, D., and Weng, J. 1998. Discriminant analysis of principal components for face recognition. In Face Recognition: From Theory to Applications, Wechsler, Philips, Bruce, Fogelman-Soulie, and Huang (Eds.), Springer-Verlag, pp. 73–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Gong, S. & Liddell, H. Constructing Facial Identity Surfaces for Recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision 53, 71–92 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023083725143
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023083725143