Abstract
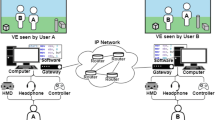
This paper analyzes the impact of the communication system on distributed virtual environments. We present a platform model that express the communication requirements of this kind of applications and evaluate it via simulation. Performance measurements varied the number of participants, the partition of the virtual environment, a participant's speed, and the size of the virtual world. Results show that the division of the environment improves the delay both to enter and to exchange groups, and reduces the number of messages exchanged. This partition allows both a participant's speed and the number of participants to increase, thereby ensuring a good interactivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Bajaj et al., “Improving simulation for network research,” Technical Report 99-702, University of Southern California, March 1999.
J.W. Barrus, R.C. Waters, and D.B. Anderson, “Locales: Supporting large multiuser virtual environments,” IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, Vol. 16, No. 6, pp. 50–57, 1996.
S. Deering, Host Extensions for IP Multicasting. RFC-1112, Aug. 1989.
M. Diaz, “Modeling and analysis of communication and cooperation protocols using Petri Net based models,” Computer Networks and ISDN Systems, Vol. 6, No. 6, pp. 419–441, 1982.
K. Fall and K. Varadhan, “NS notes and documentation,” Technical Report, The VINT Project, November 1997.
S. Floyd, V. Jacobson, C.-G. Liu, S. McCanne, and L. Zhang, “A reliable multicast framework for light-weight sessions and application level framing,” IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, Vol. 5, No. 6, pp. 784–803, 1997.
C. Greenhalgh and S. Benford, “MASSIVE: A collaborative virtual environment for teleconferencing,” ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 239–261, 1995.
C. Greenhalgh and S. Benford, “MASSIVE: A distributed virtual reality system incorporating spatial trading,” in Proceedings IEEE DCS'95, Vancouver, Canada, 1995.
O. Hagsand, “Interactive multiuser VEs in the DIVE system,” IEEE Multimedia, Vol. 3, No.1, pp. 30–39, 1996.
Institute for Defense Analysis, SIMNET, May 1990.
M.R. Macedonia, “A network software architecture for large scale virtual environments,” Ph.D. Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California, June 1995.
M.R. Macedonia and M.J. Zyda, “A taxonomy for networked virtual environment,” IEEE Multimedia, Vol. 4, No. 1, 1997.
M.R. Macedonia, M.J. Zyda, D.R. Pratt, P.T. Barham, and S. Zeswitz, “NPSNET: A network software architecture for large scale virtual environments,” Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 265–287, 1994.
M.R. Macedonia, M.J. Zyda, D.R. Pratt, D.P. Brutzman, and P.T. Barham, “Exploiting reality with multicast groups,” IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, pp. 38–50, 1995.
K. Pimentel and B. Blau, “Teaching your system to share,” IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, Vol. 14, No. 1, 1994.
S. Pingali, D. Towsley, and J. Kurose, “A comparison of sender-initiated and receiver-iniciated reliable multicast protocols,” IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 398–406, 1997.
Standard Commitee on Interactive Simulation, IEEE Computer Society. IEEE Standard for Distributed Interactive Simulation. IEEE Std 1278.1-1995, 1995.
M.R. Stytz, “Distributed virtual environments,” IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, Vol. 16, No. 3, pp. 19–31, 1996.
E.W. Zegura, K. Calvert, and S. Bhattacharjee, “A quantitative comparision of graph-based models for internet topology,” IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, Vol. 5, No. 6, pp. 770–783, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, R.C., Duarte, O.C.M. Evaluating the Impact of the Communication System on Distributed Virtual Environments. Multimedia Tools and Applications 19, 259–278 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023277330439
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023277330439