Abstract
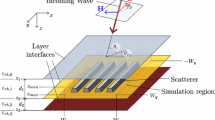
An incident wave source for finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) computation of electromagnetic scattering involving layered dispersive media is described. The method is based on the decomposition of an arbitrary incident wave into its frequency components and computing the corresponding steady-state fields in the FDTD lattice analytically. The wave source can in principle generate an incident wave obeying the dispersion relations and reflection and transmission relations of the FDTD lattice exactly. Numerical results show that, in practical computation, the accuracy of the generated incident wave is limited by FFT aliasing error occurring during waveform synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Higdon, R. L. (1986). Absorbing boundary conditions for difference approximations to the multidimensional wave equation, Math. Comput. 47, 437–459.
Holland, R., and Williams, J. W. (1983). Total-field versus scattered-field finite-difference codes: A comparative assessment, IEEE Trans. Nuclear Sci. NS-30, 4583–4588.
Moharam, M. G., Pommet, D. A., and Grann, E. B. (1995). Stable implementation of the rigorous coupled-wave analysis for surface-relief gratings: Enhanced transmittance matrix approach, J. Opt. Soc. Amer. A12, 1077–1086.
Taflove, A. (1995). Computational Electrodynamics the Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method, Artech House, Boston.
Yee, K. S. (1966). Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell's equations in isotropic media, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. AP-14, 302–307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeung, M.S. Incident Wave Source for Finite-Difference Time-Domain Computation of Electromagnetic Scattering for Objects Embedded in Layered Dispersive Media. Journal of Scientific Computing 14, 121–145 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023278902960
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023278902960