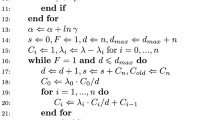Abstract
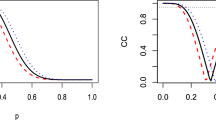
Kolassa and Tanner (J. Am. Stat. Assoc. (1994) 89, 697–702) present the Gibbs-Skovgaard algorithm for approximate conditional inference. Kolassa (Ann Statist. (1999), 27, 129–142) gives conditions under which their Markov chain is known to converge. This paper calculates explicity bounds on convergence rates in terms calculable directly from chain transition operators. These results are useful in cases like those considered by Kolassa (1999).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kolassa J.E. and Tanner M.A. 1994. Approximate conditional inference in exponential families via the Gibbs sampler. Journal of the American Statistical Association 89: 697-702.
Kolassa J.E. 1999. Convergence and accuracy of Gibbs sampling for conditional distributions in generalized linear models. Ann. Statist., 27: 129-142.
Kolassa J.E. 2000. Explicit bounds for geometric convergence of Markov chains. Journal of Applied Probability, In press.
Meyn S.P. and Tweedie R.L. 1994. Computable bounds for geometric convergence rates of Markov chains. Advances in Applied Probability 4: 981-1011.
Nummelin E. 1984. General Irreducible Markov Chains and Non-Negative Operators. Cambridge University Press, New York.
Rosenthal J.S. 1995a. Rates of convergence for Gibbs sampling for variance components models. Annals of Statistics 23: 740-761.
Rosenthal J.S. 1995b. Minorization conditions and convergence rates for Markov chain Monte Carlo. Journal of the American Statistical Association 90: 558-566.
Roberts G.O. and Polson N.G. 1994. On the geometric convergence of the Gibbs sampler. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B 56: 377-384.
Schervish M.J. and Carlin B.P. 1992. On the convergence of successive substitution sampling.Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 1: 111-127.
Tanner M.A. 1996. Tools for Statistical Inference. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg.
Tierney L. 1994. Markov Chains for exploring posterior distributions. Annals of Statistics 22: 1701-1762.
Wolfram Research. 1996. Mathematica 3.0. Wolfram Research, Champaign, IL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolassa, J.E. Bounding convergence rates for Markov chains: An example of the use of computer algebra. Statistics and Computing 11, 83–87 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026566101230
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026566101230