Abstract
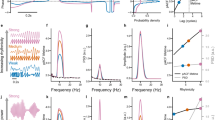
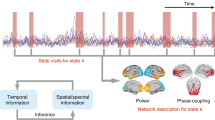
The study of synchronous oscillations in neural systems is a very active area of research. However, cognitive function may depend more crucially upon a dynamic alternation between synchronous and desynchronous activity rather than synchronous behaviour per se. The principle aim of this study is to develop and validate a novel method of quantifying this complex process. The method permits a direct mapping of phase synchronous dynamics and desynchronizing bursts in the spatial and temporal domains. Two data sets are analyzed: Numeric data from a model of a sparsely coupled neural cell assembly and experimental data consisting of scalp-recorded EEG from 40 human subjects. In the numeric data, the approach enables the demonstration of complex relationships between cluster size and temporal duration that cannot be detected with other methods. Dynamic patterns of phase-clustering and desynchronization are also demonstrated in the experimental data. It is further shown that in a significant proportion of the recordings, the pattern of dynamics exhibits nonlinear structure. We argue that this procedure provides a ‘natural partitioning’ of ongoing brain dynamics into topographically distinct synchronous epochs which may be integral to the brain's adaptive function. In particular, the character of transitions between consecutive synchronous epochs may reflect important aspects of information processing and cognitive flexibility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnhold J, Grassberger P, Lehnertz K, Elger C (1999) A robust method for detecting interdependencies: Application to intracranially recorded EEG. Physica D 134: 419-430.
Ashwin P, Covas E, Tavakol R (1999) Transverse instability for nonnormal parameters. Nonlinearity 12: 563-577.
Bak P (1996) How Nature Works: The Science of Self-Organized Criticality. Oxford University Press, New York.
Basar E, Basar-Eroglu C, Karakas S, Schurmann S (2001) Gamma, alpha, delta and theta oscillations govern cognitive processes. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 39: 241-248.
Bertrand O, Tallon-Baudry C (2000) Oscillatory gamma activity in humans: A possible role for object representation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 38: 211-223.
Bullmore ET, Fadili J, Breakspear M, Salvador R, Suckling J, Brammer MJ (2003) Wavelets and statistical analysis of functional magnetic resonance images of the human brain. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 12: 375-399.
Burgess AP, Ali L (2002) Functional connectivity of gamma EEG activity is modulated at low frequency during conscious recollection. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 46: 91-100.
Breakspear M (2002) Nonlinear phase desynchronization in human EEG data. Human Brain Mapping 15: 175-198.
Breakspear M, Terry J (2002a) Nonlinear interdependence in neural systems: Motivation, theory and relevance. Int. J. Neurosci. 112: 1263-1284.
Breakspear M, Terry J (2002b) Detection and description of nonlinear interdependence in normal multichannel human EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 113: 635-753.
Breakspear M, Terry J (2002c) Topographic organisation of nonlinear interdependence in multichannel human EEG. Neuroimage 16: 822-825.
Breakspear M, Terry J, Friston K (2003a) Modulation of excitatory synaptic coupling facilitates synchronization and complex dynamics in a nonlinear model of neuronal dynamics. Network: Comput. Neural Syst. 14: 703-732.
Breakspear M, Terry J, Friston K, Williams L, Brown K, Brennan J, Gordon E (2003b) A disturbance of nonlinear interdependence in scalp EEG of subjects with first episode schizophrenia. NeuroImage 20: 466-478.
Ebeling W (1995) Dynamic entropies and predictability of evolutionary processes. In: Nonlinear Dynamics, Chaotic and Complex Systems, E Infeld, R Zelazny, A Galkowski, eds. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Freeman WJ, Rogers LJ (2002) Fine temporal resolution of analytic phase reveals episodic synchronization by state transitions in gamma EEGs. J. Neurophysiol. 87: 937-945.
Freund J, Rateitschak K (1998) Entropy analysis of noise contaminated sequences. International Journal of Bifurcations and Chaos 8: 933-940.
Friston KJ, Tononi G, Sporns O, Edleman G (1995) Characterising the complexity of neuronal interactions. Human Brain Mapping 3: 302-314.
Friston KJ (1997) Another neural code? NeuroImage 5: 213-220.
Friston KJ (2000) The labile brain. II. Transients, complexity and selection. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 355B: 237-252.
Gatlin L (1972) Information Theory and the Living System. Columbia University Press, New York.
Gratton G, Coles M, Donchin E (1983) A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 55: 468-484.
Haig A, Gordon E (1998) Prestimulus EEG alpha phase synchronicity influences N100 amplitude and reaction time. Psychophysiology 35: 591-595.
Haig A, Gordon E, Wright JJ, Meares R, Bahramali H (2000) Synchronous gamma-band activity in task-relevant cognition. Neuroreport 11: 1-7.
Hebb D (1949) The first stage of perception. Reprinted in: G Shaw, G Palm, eds. Brain Function, World Scientific, Singapore.
Kaneko K (1997) Dominance of Milnor attractors and noise-induced selection in a multiattractor system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78: 2736-2739.
Kelso J, Bressler S, Buchanan S, DeGuzman G, Ding M, Fuchs A, Holroyd T (1992) A phase transition in human brain and behaviour. Physics Letters A 169: 134-144.
Lachaux JP, Rodriguez E, Martinerie J, Varela F (1999) Measuring phase synchrony in brain signals. Human Brain Mapping 8: 194-208.
Larter R, Speelman B (1999) A coupled ordinary differential equation lattice model for the simulation of epileptic seizures. Chaos 9: 795-804.
Le Van Quyen M, Martinerie J, Adam C, Varela F (1999) Nonlinear analyses of interictal EEG map the interdependencies in human focal epilepsy. Physica D 127:250-266.
Lee KH, Williams LM, Breakspear M, Gordon E (2002) Synchronous Gamma activity: A review and contribution to an integrative neuroscience model of schizophrenia. Brain Res. Rev. 41: 57-78.
Maistrenko Y, Maistrenko V, Popovich A, Mosekilde E (1998) Transverse instability and riddled basins in a system of two coupled logistic maps. Physical Review E 57: 2713-2724.
Miltner WHR, Braun C, Arnold M, Witte M, Taub E (1999) Coherence of gamma-band EEG activity as a basis for associative learning. Nature 397: 434-436.
Morris C, Lecar H (1981) Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 35: 193-213.
Netoff TI, Schiff SJ (2002) Decreased neuronal synchronization during experimental seizures. J. Neurosci. 22: 7297-7307.
Nunez PL, Srinivasan R, Westdorp A, Wijesinghe RS, Tucker DM, Silberstein RB, Cadusch PJ (1997) EEG coherency I: Statistics, reference electrode, volume conduction, Laplacians, cortical imaging, and interpretation at multiple scales. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 103: 499-515.
Nunez P, Silberstein R, Shi Z, Carpenter M, Srinivasan R, Tucker D, Doran S, Cadusch P, Wijesinghe R (1999) EEG coherency II: Experimental comparisons of multiple measures. Clin. Neurophysiol. 110: 469-486.
Osborne A, Provencale A (1989) Finite correlation dimension for stochastic systems with power-law spectra. Physica 35D: 357-381.
Pfurtscheller G (1977) Graphical display and statistical evaluation of event-related desynchronization. Electroenceph Clin. Neurophysiol. 43: 757-760.
Pikovsky A, Grassberger P (1991) Symmetry breaking bifurcation for coupled chaotic attractors. J. Phys. A 24: 4587-4597.
Prichard W, Theiler J (1994) Generating surrogate data for time series with several simultaneously measured variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73: 951-954.
Robinson PA, Rennie CJ, Wright JJ, Bahramali H, Gordon E, Rowe DL (2001) Prediction of electroencephalographic spectra from neurophysiology. Phys. Rev. E 63: 021903.
Rodriguez E, George N, Lachaux F, Martinerie J, Renault B, Varela F (1999) Perception's shadow: Long-distance synchronization of human brain activity. Nature 397: 430-433.
Rosenblum M, Pikovsky A, Kurths J (1996) Phase synchronization of chaotic oscillators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76: 1804-1807.
Ruelle D (1990) Deterministic chaos: The science and the fiction. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London 427A: 241-248.
Rulkov N, Sushchik M (1997) Robustness of synchronized chaotic oscillations. Int J Bifurcation and Chaos 7: 625-643.
Schreiber T, Schmitz A (2000) Surrogate time series. Physica 142D: 346-382.
Sergeant J, Geuze R, Van Winsum W (1987) Event-related desynchronization and p300. Psychophysiology 24: 272-277.
Singer W (1995) Putative functions of temporal correlations in neocortical processing. In: C Koch, J Davis, eds. Large-Scale Neuronal Theories of the Brain, MIT Press, London.
Stam CJ, Pijn J, Suffczynski P, Lopes da Silva (1999) Dynamics of the alpha rhythm: evidence for non-linearity? Clin. Neurophysiol. 110: 1801-1813.
Stam CJ, van Dijk BW (2002) Synchronization likelihood: an unbiased measure of generalized synchronization in multivariate data sets. Physica 163D: 236-251.
Stam CJ, van der Made Y, Pijnenburg YAL, Scheltens Ph (2002a) EEG synchronization in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 106: 1-7.
Stam CJ, van Cappellen van Walsum AM, Pijnenburg YAL, Berendse HW, de Munck JC, Scheltens Ph, van Dijk BW (2002b) Generalized synchronization of MEG recordings in Alzheimer's disease: Evidence for involvement of the gamma band. J. Clin. Neurophysiol 19: 562-574.
Stam CJ, van Cappellen van Walsum AM, Micheloyannis S (2002) Variability of EEG synchronization during a working memory task in healthy subjects. Int. J. Psychopysiol. 46: 53-66.
Stam CJ, Breakspear M, van Cappellen van Walsum AM, van Dijk BW (2003) Nonlinear synchronization in EEG and whole-head MEG recordings of healthy subjects. Human Brain Mapping 19: 63-78.
Tallon-Baudry C, Betrand O, Fischer C (2001) Oscillatory synchrony between human extrastriate areas during visual short-term memory maintenance. J. Neurosci. 21: 1-5.
Tass P, Rosenblum M, Weule J, Kurths J, Pikovsky A, Volkmann J, Schnitzler A, Freund H (1998) Detection of n:m phase locking from noisy data: Application to magnetoencephalography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81: 3291-3294.
Tononi G, Sporns O, Edelman GM (1994) A measure for brain complexity: Relating functional segregation and integration in the nervous system. Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 5033-5037.
Van Putten MJAM, Stam CJ (2001) Application of a neural complexity measure to multichannel EEG. Physics Letters A 281: 131-141.
Van Putten MJAM (2002) Proposed links rates in the human brain. Clin. Neurophysiol. 113 (Suppl. 1) S110: 17-01.
Van Winsum W, Sergeant J, Geuze R (1984) The functional significance of event-related desynchronization of alpha rhythm in attentional and activating tasks. Electroenceph Clin. Neurophysiol. 58: 519-524.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breakspear, M., Williams, L.M. & Stam, C.J. A Novel Method for the Topographic Analysis of Neural Activity Reveals Formation and Dissolution of ‘Dynamic Cell Assemblies’. J Comput Neurosci 16, 49–68 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JCNS.0000004841.66897.7d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JCNS.0000004841.66897.7d