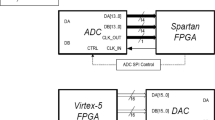
Abstract
Software defined radios (SDR) are highly configurable hardware platforms that provide the technology for realizing the rapidly expanding third (and future) generation digital wireless communication infrastructure. While there are a number of silicon alternatives available for implementing the various functions in a SDR, field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) are an attractive option for many of these tasks for reasons of performance, power consumption and flexibility. Amongst the more complex tasks performed in a high data rate wireless system is synchronization. This paper examines carrier synchronization in SDRs using FPGA based signal processors. We provide a tutorial style overview of carrier recovery techniques for QPSK and QAM modulation schemes and report on the design and FPGA implementation of a carrier recovery loop for a 16-QAM modern. Two design alternatives are presented to highlight the rich design space accessible using configurable logic. The FPGA device utilization and performance for a carrier recovery circuit using a look-up table approach and CORDIC arithmetic are presented. The simulation and FPGA implementation process using a recent system level design tool called System Generator™ for DSP described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Meyr, M. Moeneclaey, and S.A. Fechtal, Digital Communication Receivers. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc., 1998.
Xilinx Inc., Virtex-II Handbook, http://www.xilinx.com/products/virtex/handbook/index.htm Xilinx Inc., Virtex-II Pro™ Platform FPGA Handbook http://www.xilinx.com/publications/products/v2pro/handbook/index.htm
J.E. Volder, “The CORDIC Trigonometric Computing Technique,” IRE Trans. on Electronic Computers, vol. 8, no. 3, 1959, pp. 330-334.
Y.H. Hu, “CORDIC-Based VLSI Architectures for Digital Signal Processing,” IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, July 1992, pp. 16-35.
The Mathworks Inc., Simulink, Dynamic System Simulation for Matlab, Using Simulink. Natick, Massachusetts, USA. 1999.
http://www.xilinx.com/xlnx/xil_prodcat_product.jsp?title=system_generator
The Mathworks Inc., Matlab, Getting Started with Matlab. Natick, Massachusetts, USA, 1999.
R.R. Blahut, Fast Algorithms for Signal Processing. MA: Addison-Wesley, 1985.
C.H. Dick and F.J. Harris, “Direct Digital Synthesis—Some Options for FPGA Implementation,” SPIE International Symposium on Voice Video and Data Communication: Reconfigurable Technology: FPGAs for Computing and Applications Stream. Boston, MA, USA, Sept. 20–21 1999, pp. 2-10.
F.J. Harris and C.H. Dick, “On Structure and Implementation of Algorithms for Carrier and Symbol Synchronization in Software Defined Radios,” EUSIPCO-2000, “Efficient Algorithms for Hardware Implementation of DSP Systems,” Tempere, Finland, 5–8 Sept. 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dick, C., Harris, F. & Rice, M. FPGA Implementation of Carrier Synchronization for QAM Receivers. The Journal of VLSI Signal Processing-Systems for Signal, Image, and Video Technology 36, 57–71 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VLSI.0000008070.30837.e1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VLSI.0000008070.30837.e1