Abstract
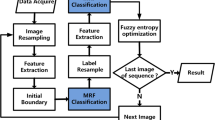
The problem of segmentation of mouse brain images into anatomical structures is an important stage of practically every analytical procedure for these images. The present study suggests a new approach to automated segmentation of anatomical structures in the images of NISSL-stained histological sections of mouse brain. The segmentation algorithm is based on the method of supervised learning using the existing anatomical labeling of the corresponding sections from a specialized mouse brain atlas. A mouse brain section to be segmented into anatomical structures is preliminarily associated with a section from the mouse brain atlas displaying the maximum similarity. The image of this section is then preprocessed in order to enhance its quality and to make it as close to the corresponding atlas image as possible. An efficient algorithm of luminance equalization, an extension of the well-known Retinex algorithm is proposed. A random forest is trained on pixel feature vectors constructed based on the atlas section images and the corresponding class labels associated with anatomical structures extracted from the atlas anatomical labeling. The trained classifier is then applied to classify pixels of an experimental section into anatomical structures. A new combination of features based on superpixels and location priors is suggested. Accuracy of the obtained result is increased by using Markov random field. Procedures of luminance equalization and subsequent segmentation into anatomical structures have been tested on real experimental sections.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Allen Brain Atlas, http://mouse.brain-map.org/atlas/index.html.
Breiman, L., Random Forests, Machine Learning, 2004, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 5–32.
Fulkerson, B., Vedaldi, A., and Soatto, S., Class Segmentation and Object Localization with Superpixel Neighborhoods, IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vision, Kyoto, 2009, pp. 670–677.
Kaynig, V., Fuchs, T., and Buhmann, J.M., Neuron Geometry Extraction by Perceptual Grouping in ssTEM Images, IEEE Conf. Comput. Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, 2010, pp. 2902–2909.
Ng, L., Hawrylycz, M., and Haynor, D., Automated High-Throughput Registration for Localization 3D Mouse Brain Gene Expression Using ITK, Insight J., 2005, vol. 1.
Riklin-Raviv, T., Sochenz, N., Kiryati, N., Ben-Zadok, N., Gefen, S., Bertand, L., and Nissanov, J., Propagating Distributions for Segmentation of Brain Atlas, IEEE Int. Symp. Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Washington, DC, 2007, pp. 1304–1307.
Ali, A., Dale, A., Badea, A., and Johnson, A., Automated Segmentation of Neuroanatomical Structures in Multispectral MR Microscopy of the Mouse Brain, Neuroimage, 2005, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 425–435.
Scheenstra, A., Dijkstraa, J., van de Ven, R., van der Weera, L., and Reiber, J., Automated Segmentation of the Ex Vivo Mouse Brain, Proc. of SPIE, 2007, vol. 6511, p. 651106.
Bae, M., Pan, R., Wu, T., and Badea, A., Automated Segmentation of Mouse Brain Images Using Extended MRF, Neuroimage, 2009, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 717–725.
Rahman, Z., Jobson, D., and Woodell, G.A., Multiscale Retinex for Color Image Enhancement, IEEE Int. Conf. Image Processing, Lausanne, 1996, pp. 1003–1006.
Christoudias, C., Georgescu, B., and Meer, P., Synergism in Low Level Vision, Int. Conf. Pattern Recognition, Quebec, 2002, vol. 4, pp. 150–155.
Paris, S., and Durand, F., Topological Approach to Hierarchical Segmentation Using Mean Shift, IEEE Conf. Comput. Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2007, Minneapolis, Minn., pp. 1–8.
Sudakov, S., Barinova, O., Velizhev, A., and Konushin, A., Semantic Segmentation of Road Images Based on Cascade Classifiers, Proc. of the ISPRS XXI Congr., Beijing, 2008, pp. 601–604.
Boykov, Y., Veksler, O., and Zabih, R., Fast Approximate Energy Minimization Via Graph Cuts, IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2001, vol. 23, no. 11, pp. 1222–1239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.V. Senyukova, A.S. Lukin, D.P. Vetrov, 2011, published in Programmirovanie, 2011, Vol. 37, No. 5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senyukova, O.V., Lukin, A.S. & Vetrov, D.P. Automated atlas-based segmentation of NISSL-stained mouse brain sections using supervised learning. Program Comput Soft 37, 245–251 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0361768811050045
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0361768811050045