Abstract
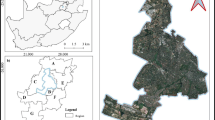
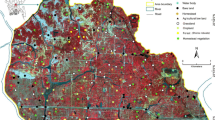
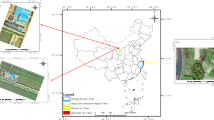
The Chinese ZY-1 02C satellite is one of the most advanced high-resolution earth observation systems designed for terrestrial resource monitoring. Its capability for comprehensive landscape classification, especially in urban areas, has been under constant study. In view of the limited spectral resolution of the ZY-1 02C satellite (three bands), and the complexity and heterogeneity across urban environments, we attempt to test its performance of urban landscape classification by combining a multi-variable model with an object-oriented approach. The multiple variables including spectral reflection, texture, spatial autocorrelation, impervious surface fraction, vegetation, and geometry indexes were first calculated and selected using forward stepwise linear discriminant analysis and applied in the following object-oriented classification process. Comprehensive accuracy assessment which adopts traditional error matrices with stratified random samples and polygon area consistency (PAC) indexes was then conducted to examine the real area agreement between a classified polygon and its references. Results indicated an overall classification accuracy of 92.63% and a kappa statistic of 0.9124. Furthermore, the proposed PAC index showed that more than 82% of all polygons were correctly classified. Misclassification occurred mostly between residential area and barren/farmland. The presented method and the Chinese ZY-1 02C satellite imagery are robust and effective for urban landscape classification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J.B., Sabol, D.E., Kapos, V., et al., 1995. Classification of multispectral images based on fractions of endmembers: application to land-cover change in the Brazilian Amazon. Remote Sens. Environ., 52(2):137–154. [doi:10.1016/0034-4257(94)00098-8]
Aguilar, M.A., Saldaña, M.M., Aguilar, F.J., 2013. GeoEye-1 and WorldView-2 pan-sharpened imagery for object-based classification in urban environments. Int. J. Remote Sens., 34(7):2583–2606. [doi:10.1080/01431161.2012.747018]
Carlson, T.N., Ripley, D.A., 1997. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ., 62(3):241–252. [doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(97)00104-1]
Chen, Y., Shi, P., Fung, T., et al., 2007. Object-oriented classification for urban land cover mapping with ASTER imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens., 28(20):4645–4651. [doi:10.1080/01431160500444731]
Deng, J.S., Wang, K., Deng, Y.H., et al., 2008. PCA-based land-use change detection and analysis using multitemporal and multisensor satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens., 29(16):4823–4838. [doi:10.1080/01431160801950162]
Durieux, L., Lagabrielle, E., Nelson, A., 2008. A method for monitoring building construction in urban sprawl areas using object-based analysis of Spot 5 images and existing GIS data. ISPRS J. Photogr. Remote Sens., 63(4):399–408. [doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2008.01.005]
Han, N., Wang, K., Yu, L., et al., 2012. Integration of texture and landscape features into object-based classification for delineating Torreya using IKONOS imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens., 33(7):2003–2033. [doi:10.1080/01431161.2011.605084]
Hermosilla, T., Ruiz, L.A., Recio, J.A., et al., 2012. Assessing contextual descriptive features for plot-based classification of urban areas. Landscape Urban Plan., 106(1):124–137. [doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2012.02.008]
Hu, S., Wang, L., 2013. Automated urban land-use classification with remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens., 34(3):790–803. [doi:10.1080/01431161.2012.714510]
Jacquin, A., Misakova, L., Gay, M., 2008. A hybrid object-based classification approach for mapping urban sprawl in periurban environment. Landscape Urban Plan., 84(2):152–165. [doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2007.07.006]
Li, G., Weng, Q., 2005. Using Landsat ETM+ imagery to measure population density in Indianapolis, Indiana, USA. Photogr. Eng. Remote Sens., 71(8):947. [doi:10.14358/PERS.71.8.947]
Livingston, F., 2005. Implementation of Breiman’s random forest machine learning algorithm. ECE591Q Machine Learning Journal Paper.
Lu, D., Weng, Q., 2006. Use of impervious surface in urban land-use classification. Remote Sens. Environ., 102(1–2):146–160. [doi:10.1016/j.rse.2006.02.010]
Lu, D., Weng, Q., 2007. A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. Int. J. Remote Sens., 28(5):823–870. [doi:10.1080/01431160600746456]
Mathieu, R., Freeman, C., Aryal, J., 2007. Mapping private gardens in urban areas using object-oriented techniques and very high-resolution satellite imagery. Landscape Urban Plan., 81(3):179–192. [doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2006.11.009]
Novack, T., Esch, T., Kux, H., et al., 2011. Machine learning comparison between WorldView-2 and QuickBird-2-simulated imagery regarding object-based urban land cover classification. Remote Sens., 3(10):2263–2282. [doi:10.3390/rs3102263]
Pacifici, F., Chini, M., Emery, W.J., 2009. A neural network approach using multi-scale textural metrics from very high-resolution panchromatic imagery for urban land-use classification. Remote Sens. Environ., 113(6):1276–1292. [doi:10.1016/j.rse.2009.02.014]
Ridd, M.K., 1995. Exploring a V-I-S (vegetation-impervious surface-soil) model for urban ecosystem analysis through remote sensing: comparative anatomy for cities. Int. J. Remote Sens., 16(12):2165–2185. [doi:10.1080/01431169508954549]
Settle, J.J., Drake, N.A., 1993. Linear mixing and the estimation of ground cover proportions. Int. J. Remote Sens., 14(6):1159–1177. [doi:10.1080/01431169308904402]
Shaban, M.A., Dikshit, O., 2001. Improvement of classification in urban areas by the use of textural features: the case study of Lucknow City, Uttar Pradesh. Int. J. Remote Sens., 22(4):565–593. [doi:10.1080/01431160050505865]
Shahtahmassebi, A., Pan, Y., Lin, L., et al., 2014. Implications of land use policy on impervious surface cover change in Cixi County, Zhejiang Province, China. Cities, 39:21–36. [doi:10.1016/j.cities.2014.02.002]
Shanmugan, K.S., Narayanan, V., Frost, V.S., et al., 1981. Textural features for radar image analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., GE-19(3):153–156. [doi:10.1109/TGRS.1981.350344]
Smith, M.O., Ustin, S.L., Adams, J.B., et al., 1990. Vegetation in deserts: I. A regional measure of abundance from multispectral images. Remote Sens. Environ., 31(1):1–26. [doi:10.1016/0034-4257(90)90074-V]
Trimble Germany GmbH, 2012. eCognition Developer 8.7.1:Reference Book. Documentation, T. Munich, Germany.
Wu, B., Wang, X., Shen, H., et al., 2012. Feature selection based on max-min-associated indices for classification of remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens., 33(17):5492–5512. [doi:10.1080/01431161.2012.663111]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (No. STSN-05-11), Zhejiang Key Scientific and Technological Innovation Team Projects (No. 2010R50030), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31172023)
ORCID: Li-gang MA, http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9377-2189
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Lg., Deng, Js., Yang, H. et al. Urban landscape classification using Chinese advanced high-resolution satellite imagery and an object-oriented multi-variable model. Frontiers Inf Technol Electronic Eng 16, 238–248 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400083
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400083