Abstract
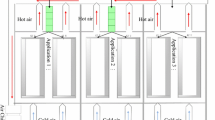
Rise in inlet air temperature increases the corresponding outlet air temperature from the server. As an added effect of rise in inlet air temperature, some active servers may start exhaling intensely hot air to form a hotspot. Increase in hot air temperature and occasional hotspots are an added burden on the cooling mechanism and result in energy wastage in data centers. The increase in inlet air temperature may also result in failure of server hardware. Identifying and comparing the thermal sensitivity to inlet air temperature for various servers helps in the thermal-aware arrangement and location switching of servers to minimize the cooling energy wastage. The peak outlet temperature among the relocated servers can be lowered and even be homogenized to reduce the cooling load and chances of hotspots. Based upon mutual comparison of inlet temperature sensitivity of heterogeneous servers, this paper presents a proactive approach for thermal-aware relocation of data center servers. The experimental results show that each relocation operation has a cooling energy saving of as much as 2.1 kW·h and lowers the chances of hotspots by over 77%. Thus, the thermal-aware relocation of servers helps in the establishment of green data centers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABB, 2013. Efficient DC Power Supply for Data Centers. Available from http://www.electricalreview.co.uk/features/9475-efficient-dc-power-supply-for-data-centres
Ahuja, N., 2012. Datacenter power savings through high ambient datacenter operation: CFD modeling study. Proc. 28th Annual IEEE Semiconductor Thermal Measurement and Management Symp., p.104–107. [doi:10.1109/STHERM.2012.6188833]
Ahuja, N., Rego, C., Ahuja, S., et al., 2011. Data center efficiency with higher ambient temperatures and optimized cooling control. Proc. 27th Annual IEEE Semiconductor Thermal Measurement and Management Symp., p.105–109. [doi:10.1109/STHERM.2011.5767186]
ASHRAE, 2011. 2011 Thermal Guidelines for Data Processing Environments—Expanded Data Center Classes and Usage Guidance. Available from http://ecoinfo.cnrs.fr/IMG/pdf/ashrae_2011_thermal_guidelines_data_center.pdf
Banerjee, A., Mukherjee, T., Varsamopoulos, G., et al., 2010. Cooling-aware and thermal-aware workload placement for green HPC data centers. Int. Green Computing Conf., p.245–256. [doi:10.1109/GREENCOMP.2010.5598306]
Banerjee, A., Mukherjee, T., Varsamopoulos, G., et al., 2011. Integrating cooling awareness with thermal aware workload placement for HPC data centers. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst., 1(2):134–150. [doi:10.1016/j.suscom.2011. 02.003]
BBC, 2014. Energy Transfer and Storage. Available from http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/energy_electricity_forces/energy_transfer_storage/revision/1/
Corradi, A., Fanelli, M., Foschini, L., 2011. Increasing cloud power efficiency through consolidation techniques. Proc. IEEE Symp. on Computers and Communications, p.129–134. [doi:10.1109/ISCC.2011.5984005]
Huck, S., 2011. Measuring Processor Power TDP vs. ACP. Available from http://www.intel.com/content/dam/doc/white-paper/resources-xeon-measuring-processor-power-paper.pdf
Jonas, M., Varsamopoulos, G., Gupta, S.K.S., 2007. On developing a fast, cost-effective and non-invasive method to derive data center thermal maps. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Cluster Computing, p.474–475. [doi:10.1109/CLUSTR.2007.4629269]
Jonas, M., Varsamopoulos, G., Gupta, S.K.S., 2010. Noninvasive thermal modeling techniques using ambient sensors for greening data centers. Proc. 39th Int. Conf. on Parallel Processing Workshops, p.453–460. [doi:10.1109/ICPPW.2010.67]
Koomey, J., 2011. Growth in Data Center Electricity Use 2005 to 2010. Analytics Press, Oakland, CA.
Kusic, D., Kephart, J.O., Hanson, J.E., et al., 2009. Power and performance management of virtualized computing environments via lookahead control. Cluster Comput., 12(1):1–15. [doi:10.1007/s10586-008-0070-y]
LD Didactic Gmbh. Converting Electrical Energy into Heat Energy—Measuring with the Joule and Wattmeter. LD DIDACTIC GmbH, Germany.
Lee, E.K., Kulkarni, I., Pompili, D., et al., 2012. Proactive thermal management in green datacenters. J. Supercomput., 60(2):165–195. [doi:10.1007/s11227-010-0453-8]
Liu, Z., Chen, Y., Bash, C., et al., 2012. Renewable and cooling aware workload management for sustainable data centers. ACM SIGMETRICS Perform. Eval. Rev., 40(1): 175–186. [doi:10.1145/2318857.2254779]
Masiero, M., 2012. CPU Charts 2012: 86 Processors from AMD and Intel, Tested. Tom’s Hardware.
Mersenne Research, Inc., 2012. Great Internet Mersenne Prime Search (GIMPS). Available from http://www.mersenne.org/freesoft/
Moore, J., Chase, J., Ranganathan, P., et al., 2005. Making scheduling “cool”: temperature-aware workload placement in data centers. Proc. USENIX Annual Technical Conf., p.61–75.
Mukherjee, T., Banerjee, A., Varsamopoulos, G., et al., 2009. Spatio-temporal thermal-aware job scheduling to minimize energy consumption in virtualized heterogeneous data centers. Comput. Netw., 53(17):2888–2904. [doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2009.06.008]
Rodero, I., Lee, E.K., Pompili, D., et al., 2010. Towards energy-efficient reactive thermal management in instrumented datacenters. Proc. 11th IEEE/ACM Int. Conf. on Grid Computing, p.321–328. [doi:10.1109/GRID.2010.5698002]
Rodero, I., Viswanathan, H., Lee, E.K., et al., 2012. Energyefficient thermal-aware autonomic management of virtualized HPC cloud infrastructure. J. Grid Comput., 10(3): 447–473. [doi:10.1007/s10723-012-9219-2]
Sansottera, A., Cremonesi, P., 2011. Cooling-aware workload placement with performance constraints. Perform. Eval., 68(11):1232–1246. [doi:10.1016/j.peva.2011.07.018]
Tang, Q., Mukherjee, T., Gupta, S.K.S., et al., 2006. Sensorbased fast thermal evaluation model for energy efficient high-performance datacenters. Proc. 4th Int. Conf. on Intelligent Sensing and Information Processing, p.203–208. [doi:10.1109/ICISIP.2006.4286097]
Tang, Q., Gupta, S.K.S., Varsamopoulos, G., 2007. Thermalaware task scheduling for data centers through minimizing heat recirculation. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Cluster Computing, p.129–138. [doi:10.1109/CLUSTR.2007.462 9225]
Tu, C.Y., Kuo, W.C., Teng, W.H., et al., 2010. A poweraware cloud architecture with smart metering. Proc. 39th Int. Conf. on Parallel Processing Workshops, p.497–503. [doi:10.1109/ICPPW.2010.73]
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2007. Report to Congress on Server and Data Center Energy Efficiency Public Law 109-431. Available from http://www.energystar.gov/ia/partners/prod_development/downloads/EPA_Datacenter_Report_Congress_Final1.pdf?6133-414f
VMware Inc., 2009. VMware vSphere Basics ESXi 5.0 vCenter Server 5.0 (in Chinese). Available from http://pubs.vmware.com/vsphere-50/topic/com.vmware.ICbase/PDF/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-50-basics-guide.pdf
Wang, L., von Laszewski, G., Dayal, J., et al., 2009a. Thermal aware workload scheduling with backfilling for green data centers. Proc. IEEE 28th Int. Performance Computing and Communications Conf., p.289–296. [doi:10.1109/PCCC.2009.5403821]
Wang, L., von Laszewski, G., Dayal, J., et al., 2009b. Towards thermal aware workload scheduling in a data center. Proc. 10th Int. Symp. on Pervasive Systems, Algorithms, and Networks, p.116–122. [doi:10.1109/I-SPAN.2009.22]
Wang, L., Khan, S.U., Dayal, J., 2012. Thermal aware workload placement with task-temperature profiles in a data center. J. Supercomput., 61(3):780–803. [doi:10.1007/s11227-011-0635-z]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ORCID: Muhammad Tayyab CHAUDHRY, http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9485-0054
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhry, M.T., Ling, T.C., Hussain, S.A. et al. Thermal-aware relocation of servers in green data centers. Frontiers Inf Technol Electronic Eng 16, 119–134 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400174
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400174