Abstract
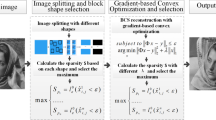
We present a novel image fusion scheme based on gradient and scrambled block Hadamard ensemble (SBHE) sampling for compressive sensing imaging. First, source images are compressed by compressive sensing, to facilitate the transmission of the sensor. In the fusion phase, the image gradient is calculated to reflect the abundance of its contour information. By compositing the gradient of each image, gradient-based weights are obtained, with which compressive sensing coefficients are achieved. Finally, inverse transformation is applied to the coefficients derived from fusion, and the fused image is obtained. Information entropy (IE), Xydeas’s and Piella’s metrics are applied as non-reference objective metrics to evaluate the fusion quality in line with different fusion schemes. In addition, different image fusion application scenarios are applied to explore the scenario adaptability of the proposed scheme. Simulation results demonstrate that the gradient-based scheme has the best performance, in terms of both subjective judgment and objective metrics. Furthermore, the gradient-based fusion scheme proposed in this paper can be applied in different fusion scenarios.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amolins, K., Zhang, Y., Dare, P., 2007. Wavelet based image fusion techniques—an introduction, review and comparison. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens., 62(4): 249–263. [doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2007.05.009]
Byeungwoo, J., Landgrebe, D.A., 1999. Decision fusion approach for multitemporal classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 37(3):1227–1233. [doi:10.1109/36.763278]
Candès, E.J., Romberg, J., 2005. l 1-Magic: Recovery of Sparse Signals via Convex Programming. Available from http://www.acm.caltech.edu/l1magic/
Candès, E.J., Tao, T., 2006. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 52(12):5406–5425. [doi:10.1109/TIT.2006.885507]
Candès, E.J., Wakin, M.B., 2008. An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag., 25(2):21–30. [doi:10.1109/MSP.2007.914731]
Chen, R.Y., Li, S., Yang, R., et al., 2008. Multi-focus images fusion based on data assimilation and genetic algorithm. Proc. Int. Conf. on Computer Science and Software Engineering, p.249–252. [doi:10.1109/CSSE.2008.525]
Chen, S.S., Donoho, D.L., Saunders, M.A., 1998. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 20(1):33–61. [doi:10.1137/S1064827596304010]
Ding, M., Wei, L., Wang, B.F., 2013. Research on fusion method for infrared and visible images via compressive sensing. Infrared Phys. Technol., 57:56–67. [doi:10.1016/j.infrared.2012.12.014]
Do, T.T., Lu, G., Nguyen, N.H., et al., 2012. Fast and efficient compressive sensing using structurally random matrices. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 60(1):139–154. [doi:10.1109/TSP.2011.2170977]
Donoho, D.L., 2006. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 52(4):1289–1306. [doi:10.1109/TIT.2006.871582]
Duarte, M.F., Davenpot, M.A., Takhar, D., et al., 2008. Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag., 25(2):83–91. [doi:10.1109/MSP.2007.914730]
Figueiredo, M.A.T., Nowak, R.D., Wright, S.J., 2007. Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process., 1(4):586–597. [doi:10.1109/JSTSP.2007.910281]
Han, J.J., Loffeld, O., Hartmann, K., et al., 2010. Multi image fusion based on compressive sensing. Proc. Int. Conf. on Audio Language and Image Processing, p.1463–1469. [doi:10.1109/ICALIP.2010.5684502]
Jolliffe, I.T., 1986. Principal Component Analysis. Springer.
Kang, B., Zhu, W.P., Yan, J., 2013. Fusion framework for multi-focus images based on compressed sensing. IET Image Process., 7(4):290–299. [doi:10.1049/iet-ipr.2012.0543]
Li, S.T., Yang, B., 2008. Multifocus image fusion by combining curvelet and wavelet transform. Patt. Recog. Lett., 29(9):1295–1301. [doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2008.02.002]
Li, S.T., Kwok, J.T.Y., Tsang, I.W., et al., 2004. Fusing images with different focuses using support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neur. Netw., 15(6):1555–1561. [doi:10.1109/TNN.2004.837780]
Li, X., Qin, S.Y., 2011. Efficient fusion for infrared and visible images based on compressive sensing principle. IET Image Process., 5(2):141–147. [doi:10.1049/iet-ipr.2010.0084]
Liu, Z., Tsukada, K., Hanasaki, K., et al., 2001. Image fusion by using steerable pyramid. Patt. Recog. Lett., 22(9): 929–939. [doi:10.1016/S0167-8655(01)00047-2]
Luo, X.Y., Zhang, J., Yang, J.Y., et al., 2009. Image fusion in compressed sensing. Proc. 16th IEEE Int. Conf. on Image Processing, p.2205–2208. [doi:10.1109/ICIP.2009.5413866]
Pajares, G., de la Cruz, J.M., 2004. A wavelet-based image fusion tutorial. Patt. Recog., 37(9):1855–1872. [doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2004.03.010]
Petrović, V.S., Xydeas, C.S., 2004. Gradient-based multiresolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 13(2):228–237. [doi:10.1109/TIP.2004.823821]
Piella, G., Heijmans, H., 2003. A new quality metric for image fusion. Proc. Int. Conf. on Image Processing, p.173–176. [doi:10.1109/ICIP.2003.1247209]
Qu, G.H., Zhang, D.L., Yan, P.F., 2002. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett., 38(7):313–315. [doi:10.1049/el:20020212]
Romberg, J., 2008. Imaging via compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag., 25(2):14–20. [doi:10.1109/MSP.2007.914729]
Ross, A.A., Govindarajan, R., 2005. Feature level fusion of hand and face biometrics. Proc. SPIE, p.196–204. [doi:10.1117/12.606093]
Shi, W.Z., Zhu, C.Q., Tian, Y., et al., 2005. Wavelet-based image fusion and quality assessment. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform., 6(3–4):241–251. [doi:10.1016/j.jag.2004.10.010]
Smith, L.I., 2002. A Tutorial on Principal Components Analysis. Available from www.cs.otago.ac.nz/cosc453/student_tutorials/principal_components.pdf.
Tropp, J., Gilbert, A.C., 2007. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 53(12):4655–4666. [doi:10.1109/TIT.2007.909108]
Wan, T., Qin, Z.C., 2011. An application of compressive sensing for image fusion. Int. J. Comput. Math., 88(18): 3–9. [doi:10.1080/00207160.2011.598229]
Wang, R., Du, L.F., 2014. Infrared and visible image fusion based on random projection and sparse representation. Int. J. Remote Sens., 35(5):1640–1652. [doi:10.1080/01431161.2014.880819]
Wang, Y., Yang, J.F., Yin, W., et al., 2008. A new alternating minimization algorithm for total variation image reconstruction. SIAM J. Image Sci., 1(3):248–272. [doi:10.1137/080724265]
Xydeas, C.S., Petrović, V., 2000. Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron. Lett., 36(4):308–309. [doi:10.1049/el:20000267]
Yang, X.H., Jin, H.Y., Jiao, L.C., 2007. Adaptive image fusion algorithm for infrared and visible light images based on DT-CWT. J. Infrared Millim. Waves, 26(6):419–424 (in Chinese).
Yang, Y., Han, C.Z., Kang, X., et al., 2007. An overview on pixel-level image fusion in remote sensing. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Automation and Logistics, p.2339–2344. [doi:10.1109/ICAL.2007.4338968]
Zheng, Y.Z., Qin, Z., 2009. Region-based image fusion method using bidimensional empirical mode decomposition. J. Electron. Imag., 18(1):013008. [doi:10.1117/1.3099703]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National S&T Major Program (No. 9140A1550212 JW01047) and the ‘Twelfth Five’ Preliminary Research Project of PLA (No. 402040202)
ORCID: Yang CHEN, http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0927-000X
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Qin, Z. Gradient-based compressive image fusion. Frontiers Inf Technol Electronic Eng 16, 227–237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400217
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400217