Abstract
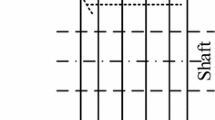
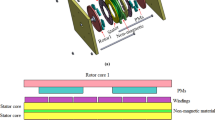
In this study, we investigated the torque characteristics of large low-speed direct-drive permanent magnet synchronous generators with stator radial ventilating air ducts for offshore wind power applications. Magnet shape optimization was used first to improve the torque characteristics using two-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA) in a permanent magnet synchronous generator with a common stator. The rotor step skewing technique was then employed to suppress the impacts of mechanical tolerances and defects, which further improved the torque quality of the machine. Comprehensive three-dimensional FEA was used to evaluate accurately the overall effects of stator radial ventilating air ducts and rotor step skewing on torque features. The influences of the radial ventilating ducts in the stator on torque characteristics, such as torque pulsation and average torque in the machine with and without rotor step skewing techniques, were comprehensively investigated using three-dimensional FEA. The results showed that stator radial ventilating air ducts could not only reduce the average torque but also increase the torque ripple in the machine. Furthermore, the torque ripple of the machine under certain load conditions may even be increased by rotor step skewing despite a reduction in cogging torque.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashabani, M., Mohamed, Y.A.R.I., 2011. Multiobjective shape optimization of segmented pole permanentmagnet synchronous machines with improved torque characteristics. IEEE Trans. Magn., 47(4):795–804. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2010.2104327
Atallah, K., Wang, J., Howe, D., 2003. Torque-ripple minimization in modular permanent-magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 39(6):1689–1695. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2003.818986
Bianchi, N., Bolognani, S., 2002. Design techniques for reducing the cogging torque in surface-mounted PM motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 38(5):1259–1265. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2002.802989
Boukais, B., Zeroug, H., 2010. Magnet segmentation for commutation torque ripple reduction in a brushless DC motor drive. IEEE Trans. Magn., 46(11):3909–3919. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2010.2057439
Chen, H.S., Dorrell, D.G., Tsai, M.C., 2010. Design and operation of interior permanent-magnet motors with two axial segments and high rotor saliency. IEEE Trans. Magn., 46(9):3664–3675. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2010.2048037
Chen, N.N., Ho, S.L., Fu, W.N., 2010. Optimization of permanent magnet surface shapes of electric motors for minimization of cogging torque using FEM. IEEE Trans. Magn., 46(6):2478–2481. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2010.2044764
Chu, W.Q., Zhu, Z.Q., 2013. Reduction of on-load torque ripples in permanent magnet synchronous machines by improved skewing. IEEE Trans. Magn., 49(7):3822–3825. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2013.2247381
Fei, W.Z., Luk, P.C.K., 2009. An improved model for the back-EMF and cogging torque characteristics of a novel axial flux permanent magnet synchronous machine with a segmental laminated stator. IEEE Trans. Magn., 45(10):4609–4612. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2009.2024127
Fei, W.Z., Luk, P.C.K., 2010. A new technique of cogging torque suppression in direct-drive permanent-magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 46(4):1332–1340. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2010.2049551
Fei, W.Z., Luk, P.C.K., 2012. Torque ripple reduction of a direct-drive permanent-magnet synchronous machine by material-efficient axial pole pairing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 59(6):2601–2611. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2011.2158048
Fei, W.Z., Luk, P.C.K., Shen, J.X., 2012. Torque analysis of permanent-magnet flux switching machines with rotor step skewing. IEEE Trans. Magn., 48(10):2664–2673. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2012.2198223
Fei, W.Z., Luk, P.C.K., Wu, D., et al., 2013. Approximate three-dimensional finite element analysis of large permanent magnet synchronous generators with stator radial ventilating ducts. 39th Annual Conf. of IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, p.7313–7318. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2013.6700349
Güemes, J.A., Iraolagoitia, A.A., Del Hoyo, J.I., et al., 2011. Torque analysis in permanent-magnet synchronous motors: a comparative study. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv., 26(1):55–63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2010.2053374
Han, S.H., Jahns, T.M., Soong, W.L., et al., 2010. Torque ripple reduction in interior permanent magnet synchronous machines using stators with odd number of slots per pole pair. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv., 25(1):118–127. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2009.2033196
Islam, M.S., Mir, S., Sebastian, T., et al., 2005. Design consideration of sinusoidally excited permanent-magnet machines for low-torque-ripple applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 41(4):955–962. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2005.851026
Islam, R., Husain, I., Fardoun, A., et al., 2009. Permanentmagnet synchronous motor magnet designs with skewing for torque ripple and cogging torque reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 45(1):152–160. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2008.2009653
Jahns, T.M., Soong, W.L., 1996. Pulsating torque minimization techniques for permanent magnet AC motor drives—a review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 43(2):321–330. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/41.491356
Lateb, R., Takorabet, N., Meibody-Tabar, F., 2006. Effect of magnet segmentation on the cogging torque in surface-mounted permanent-magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Magn., 42(3):442–445. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2005.862756
Li, T., Slemon, G., 1988. Reduction of cogging torque in permanent magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Magn., 24(6):2901–2903. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/20.92282
Pang, Y., Zhu, Z.Q., Howe, D., 2005. Self-shielding magnetized vs. shaped parallel-magnetized PM brushless AC motors. KIEE Int. Trans. Electr. Mach. Energy Conv. Syst., 5-B(1):13–19.
Pyrhonen, J., Ruuskanen, V., Nerg, J., et al., 2010. Permanent-magnet length effects in AC machines. IEEE Trans. Magn., 46(10):3783–3789. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2010.2050002
Ruuskanen, V., Nerg, J., Pyrhonen, J., 2011. Effect of lamination stack ends and radial cooling channels on noload voltage and inductances of permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Magn., 47(11):4643–4649. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2158233
Ruuskanen, V., Nerg, J., Niemelä, M., et al., 2013. Effect of radial cooling ducts on the electromagnetic performance of the permanent magnet synchronous generators with double radial forced air cooling for direct-driven wind turbines. IEEE Trans. Magn., 49(6):2974–2981. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2013.2238679
Sopanen, J., Ruuskanen, V., Nerg, J., et al., 2011. Dynamic torque analysis of a wind turbine drive train including a direct-driven permanent-magnet generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 58(9):3859–3867. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2087301
Tapia, J.A., Pyrhonen, J., Puranen, J., et al., 2013. Optimal design of large permanent magnet synchronous generators. IEEE Trans. Magn., 49(1):642–650. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2012.2207907
Wang, Y., Jin, M.J., Fei, W.Z., et al., 2010. Cogging torque reduction in permanent magnet flux-switching machines by rotor teeth axial pairing. IET Electr. Power Appl., 4(7):500–506. http://dx.doi.org/10.1049/iet-epa.2009.0205
Yang, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, R., et al., 2006. The optimization of pole arc coefficient to reduce cogging torque in surface-mounted permanent magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Magn., 42(4):1135–1138. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2006.871452
Zhu, Z.Q., Howe, D., 2000. Influence of design parameters on cogging torque in permanent magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv., 15(4):407–412. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/60.900501
Zhu, Z.Q., Ruangsinchaiwanich, S., Ishak, D., et al., 2005. Analysis of cogging torque in brushless machines having nonuniformly distributed stator slots and stepped rotor magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn., 41(10):3910–3912. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2005.854968
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51377140) and the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (No. 2013CB035604)
ORCID: He HAO, http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6376-9106
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, H., Fei, Wz., Miao, Dm. et al. Torque characteristics in a large permanent magnet synchronous generator with stator radial ventilating air ducts. Frontiers Inf Technol Electronic Eng 17, 814–824 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1500238
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1500238
Keywords
- Permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG)
- Radial ventilating air duct
- Torque ripple
- Step skewing
- Magnet shape optimization
- Finite element analysis
- Wind power