Abstract
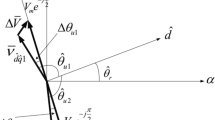
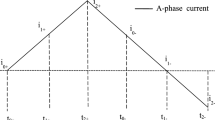
A novel nonlinear model for surface permanent magnet synchronous motors (SPMSMs) is adopted to estimate the initial rotor position for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). Usually, the accuracy of initial rotor position estimation for SPMSMs relies on magnetic saturation. To verify the saturation effect, the transient finite element analysis (FEA) model is presented first. Hybrid injection of a static voltage vector (SVV) superimposed with a high-frequency rotating voltage is proposed. The magnetic polarity is roughly identified with the aid of the saturation evaluation function, based on which an estimation of the position is performed. During this procedure, a special demodulation is suggested to extract signals of iron core saturation and rotor position. A Simulink/MATLAB platform for SPMSMs at standstill is constituted, and the effectiveness of the proposed strategy is verified. The proposed method is also validated by experimental results of an SPMSM drive.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Bolognani, S., Calligaro, S., Petrella, R., 2011. Design issues and estimation errors analysis of back-EMF based position and speed observer for SPM synchronous motors. Symp. on Sensorless Control for Electrical Drives, p.138–145. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/SLED.2011.6051558
El-Serafi, A.M., Wu, J., 1993. Determination of the parameters representing the cross-magnetizing effect in saturated synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv., 8(3):333–342. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/60.257042
Fu, W.N., Ho, S.L., Zhang, Z., 2009. Design of position detection strategy of sensorless permanent magnet motors at standstill using transient finite-element analysis. IEEE Trans. Magn., 45(10):4668–4671. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2009.2022406
Gao, W., Meliopoulos, A.P.S., Solodovnik, E.V., et al., 2005. A nonlinear model for studying synchronous machine dynamic behavior in phase coordinates. IEEE Int. Conf. on Industrial Technology, p.1092–1097. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICIT.2005.1600798
Harke, M.C., de Donato, G., Capponi, F.G., et al., 2008. Implementation issues and performance evaluation of sinusoidal, surface-mounted PM machine drives with Hall-effect position sensors and a vector-tracking observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 44(1):161–173. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2007.912729
Li, Y., Zhu, Z.Q., Howe, D., et al., 2007. Modeling of cross-coupling magnetic saturation in signal-injectionbased sensorless control of permanent-magnet brushless AC motors. IEEE Trans. Magn., 43(6):2552–2554. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2007.892319
Liang, X.D., El-Serafi, A.M., Faried, S.O., 2010. Application of the finite-element method for the determination of the parameters representing the cross-magnetizing in saturated synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv., 25(1):70–79. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2009.2032535
Nakashima, S., Inagaki, Y., Miki, I., 2000. Sensorless initial rotor position estimation of surface permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 36(6):1598–1603. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/28.887211
Seilmeier, M., Piepenbreier, B., 2011. Modeling of PMSM with multiple saliencies using a stator-oriented magnetic circuit approach. IEEE Electric Machines & Drives Conf., p.131–136. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/IEMDC.2011.5994796
Sigmund, D., Lohner, A., Böh, M., et al., 2014. Simulationbased development of an energy-management-system for a drive train of a parallel hybrid electric vehicle. 16th Int. Power Electronics and Motion Control Conf. and Exposition, p.822–827. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/EPEPEMC.2014.6980599
Wang, Y., Zhu, J.G., Guo, Y.G., 2010. A comprehensive analytical mathematic model for permanent-magnet synchronous machines incorporating structural and saturation saliencies. IEEE Trans. Magn., 46(12):4081–4091. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2010.2071392
Wang, Z., Niu, S.X., Ho, S.L., et al., 2012. A position detection strategy for sensorless surface mounted permanent magnet motors at low speed using transient finite-element analysis. IEEE Trans. Magn., 48(2):1003–1006. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2173914
Yan, Y., Zhu, J.G., Guo, Y.G., 2008. Initial rotor position estimation and sensorless direct torque control of surfacemounted permanent magnet synchronous motors considering saturation saliency. IET Electr. Power Appl., 2(1):42–48. http://dx.doi.org/10.1049/iet-epa:20070083
Yang, S.C., 2015. Saliency-based position estimation of permanent-magnet synchronous machines using squarewave voltage injection with a single current sensor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 51(2):1561–1571. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2014.2358796
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51207029 and 51507039), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (No. HIT.NSRIF.2017013), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M591529)
ORCID: Bing TIAN, http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4977-2362
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, B., An, Qt., Sun, L. et al. Initial position estimation strategy for a surface permanent magnet synchronous motor used in hybrid electric vehicles. Frontiers Inf Technol Electronic Eng 17, 803–813 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1500298
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1500298
Keywords
- Surface permanent magnet synchronous motor (SPMSM)
- Initial position estimation
- Nonlinear model
- Hybrid injection
- Position observer