Abstract
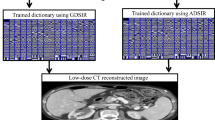
Recently, low-dose computed tomography (CT) has become highly desirable because of the growing concern for the potential risks of excessive radiation. For low-dose CT imaging, it is a significant challenge to guarantee image quality while reducing radiation dosage. Compared with classical filtered backprojection algorithms, compressed sensing-based iterative reconstruction has achieved excellent imaging performance, but its clinical application is hindered due to its computational inefficiency. To promote low-dose CT imaging, we propose a promising reconstruction scheme which combines total-variation minimization and sparse dictionary learning to enhance the reconstruction performance, and properly schedule them with an adaptive iteration stopping strategy to boost the reconstruction speed. Experiments conducted on a digital phantom and a physical phantom demonstrate a superior performance of our method over other methods in terms of image quality and computational efficiency, which validates its potential for low-dose CT imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon, M., Elad, M., Bruckstein, A.M., 2006. The K-SVD: an algorithm for designing of overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 54(11):4311–4322. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2006.881199
Anderson, A.H., Kak, A.C., 1984. Simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique (SART): a superior implementation of the ART algorithm. Ultrason. Imag., 6(1):81–94. https://doi.org/10.1177/016173468400600107
Barzilai, J., Borwein, J., 1988. Two-point step size gradient methods. IMA J. Numer. Anal., 8(1):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/8.1.141
Candes, E.J., Romberg, J., Tao, T., 2006. Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 52(2):489–509. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.2005.862083
Chen, Y., Shi, L.Y., Feng, Q.J., et al., 2014. Artifact suppressed dictionary learning for low-dose CT image processing. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., 33(12):2271–2292. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2336860
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., et al., 2007. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 16(8):2080–2095. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2007.901238
Dong, W.S., Zhang, L., Shi, G.M., et al., 2013. Nonlocally centralized sparse representation for image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 22(4):1620–1630. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2012.2235847
Elad, M., Aharon, M., 2006. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 15(12):3736–3745. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2006.881969
Ginat, D.T., Gupta, R., 2014. Advances in computed tomography imaging technology. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 16:431–453. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-121813-113601
Han, X., Bian, J.G., Ritman, E.L., et al., 2012. Optimizationbased reconstruction of sparse images from few-view projections. Phys. Med. Biol., 57(16):5245–5273. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/57/16/5245
Jia, X., Dong, B., Lou, Y.F., et al., 2011. GPU-based iterative cone-beam CT reconstruction using tight frame regularization. Phys. Med. Biol., 56:3787–3807. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/56/13/004
Liu, J., Chen, Y., Hu, Y., et al., 2016. Low-dose CBCT reconstruction via 3D dictionary learning. IEEE 13th Int. Symp. on Biomedical Imaging, p.735–738. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2016.7493371
Lustig, M., Donoho, D.L., Santos, J.M., et al., 2008. Compressed sensing MRI. IEEE Signal Process. Mag., 25(2):72–82. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2007.914728
Niu, T.Y., Zhu, L., 2012. Accelerated barrier optimization compressed sensing (ABOCS) reconstruction for conebeam CT: phantom studies. Med. Phys., 39(7):4588–4598. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4729837
Niu, T.Y., Ye, X.J., Fruhauf, Q., et al., 2014. Accelerated barrier optimization compressed sensing (ABOCS) for CT reconstruction with improved convergence. Phys. Med. Biol., 59(7):1801–1814. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/59/7/1801
Park, J.C., Song, B.Y., Kim, J.S., et al., 2012. Fast compressed sensing-based CBCT reconstruction using Barzilai-Borwein formulation for application to on-line IGRT. Med. Phys., 39(3):1207–1217. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3679865
Siddon, R.L., 1985. Prism representation: a 3D ray-tracing algorithm for radiotherapy application. Phys. Med. Biol., 30:817–824. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/30/8/005
Sidky, E.Y., Kao, C.M., Pan, X.C., 2008. Image reconstruction in circular cone-beam computed tomogrphy by constrained, total-variation minimization. Phys. Med. Biol., 53:4777–4807. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/53/17/021
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., et al., 2004. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 13(4):600–612. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
Xu, Q., Yu, H.Y., Mou, X.Q., et al., 2012. Low dose X-ray reconstruciton via dictionary learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., 31(9):1682–1697. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2012.2195669
Yan, H., Cervino, L., Jia, X., et al., 2012. A comprehensive study on the relationship between the image quality and imaging dose in low-dose cone beam CT. Phys. Med. Biol., 57(7):2063–2080. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/57/7/2063
Yan, H., Wang, X.Y., Shi, F., et al., 2014. Towards the clinical implementation of iterative low-dose cone-beam CT reconstruction in image-guided radiation therapy: cone/ring artifact correction and multiple GPU implementation. Med. Phys., 41(11):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4898324
Yu, H.Y., Wang, G., 2010. A soft-threshold filtering approach for reconstruction from a limited number of projections. Phys. Med. Biol., 55:3905–3916. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/55/13/022
Yuan, M., Yang, B.X., Ma, Y.D., et al., 2015. Multi-scale UDCT dictionary learning based highly undersampled MR image reconstruction using patch-based constraint splitting augmented Lagrangian shrinkage algorithm. Front. Inform. Technol. Electron. Eng., 16(2):1069–1087. https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National High-Tech R&D Program (863) of China (No. 2015AA016704c) and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (No. LY14F020028)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Hu, T. Efficient scheme of low-dose CT reconstruction using TV minimization with an adaptive stopping strategy and sparse dictionary learning for post-processing. Frontiers Inf Technol Electronic Eng 18, 2001–2008 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1700287
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1700287