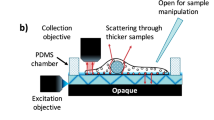
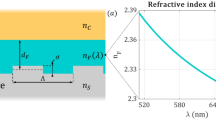
Abstract
In this review, we introduce some chip-based waveguide biosensing and imaging techniques, which significantly reduce the complexity of the entire system. These techniques use a well-confined evanescent field to interact with the surrounding materials and achieve high sensitivity sensing and high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) super-resolution imaging. The fabrication process of these chips is simple and compatible with conventional semiconductor fabrication methods, allowing high-yield production. Combined with recently developed chip-based light sources, these techniques offer the possibility of biosensing and super-resolution imaging based on integrated circuits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbe E, 1873. Beiträge zur theorie des mikroskops und der mikroskopischen wahrnehmung. Arch f Mikrosk Anat, 9(1):413–418 (in German). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02956173
Agnarsson B, Ingthorsson S, Gudjonsson T, et al., 2009. Evanescent-wave fluorescence microscopy using symmetric planar waveguides. Opt Expr, 17(7):5075–5082. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.17.005075
Agnarsson B, Lundgren A, Gunnarsson A, et al., 2015. Evanescent light-scattering microscopy for label-free interfacial imaging: from single sub-100 nm vesicles to live cells. ACS Nano, 9(12):11849–11862. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b04168
Armani AM, Vahala KJ, 2006. Heavy water detection using ultra-high-Q microcavities. Opt Lett, 31(23):1896–1898. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.31.001896
Axelrod D, 2001. Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy in cell biology. Traffic, 2(11):764–774. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0854.2001.21104.x
Axelrod D, Thompson NL, Burghardt TP, 1983. Total internal reflection fluorescent microscopy. J Microsc-Oxford, 129(1):19–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2818.1983.tb04158.x
Bates M, Huang B, Dempsey GT, et al., 2007. Multicolor super-resolution imaging with photo-switchable fluorescent probes. Science, 317(5845):1749–1753. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1146598
Betzig E, Trautman JK, 1992. Near-field optics: microscopy, spectroscopy, and surface modification beyond the diffraction limit. Science, 257(5067):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.257.5067.189
Betzig E, Patterson GH, Sougrat R, et al., 2006. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science, 313(5793):1642–1645. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1127344
Brandenburg A, 1997. Differential refractometry by an integrated-optical Young interferometer. Sens Actuat B Chem, 39(1–3):266–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(97)80216-X
Brandenburg A, Henninger R, 1994. Integrated optical Young interferometer. Appl Opt, 33(25):5941–5947. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.33.005941
Chao CY, Fung W, Guo LJ, 2006. Polymer microring resonators for biochemical sensing applications. IEEE J Sel Top Quant, 12(1):134–142. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2005.862945
Chung JW, Bernhardt R, Pyun JC, 2006. Additive assay of cancer marker CA 19-9 by SPR biosensor. Sens Actuat B Chem, 118(1–2):28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2006.04.015
Coskun AF, Wong J, Khodadadi D, et al., 2013. A personalized food allergen testing platform on a cellphone. Lab Chip, 13(4):636–640. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2LC41152K
Cross GH, Ren YT, Freeman NJ, 1999. Young’s fringes from vertically integrated slab waveguides: applications to humidity sensing. J Appl Phys, 86(11):6483–6488. https://doi.org/10.1063/L371712
Cross GH, Reeves AA, Brand S, et al., 2003. A new quantitative optical biosensor for protein characterisation. Biosens Bioelectron, 19(4):383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-5663(03)00203-3
Cush R, Cronin JM, Stewart WJ, et al., 1993. The resonant mirror: a novel optical biosensor for direct sensing of biomolecular interactions. Part I: principle of operation and associated instrumentation. Biosens Bioelectron, 8(7–8):347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-5663(93)80073-X
Darafsheh A, Walsh GF, Dal Negro L, et al., 2012. Optical super-resolution by high-index liquid-immersed microspheres. Appl Phys Lett, 101(14):141128. https://doi.org/10.1063/L4757600
de Vos K, Bartolozzi I, Schacht E, et al., 2007. Silicon-on-insulator microring resonator for sensitive and label-free biosensing. Opt Expr, 15(12):7610–7615. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.15.007610
Diekmann R, Helle ØI, Øie CI, et al., 2017. Chip-based wide field-of-view nanoscopy. Nat Photon, 11(5):322–328. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2017.55
Fan XD, White IM, Shopova S, et al., 2008. Sensitive optical biosensors for unlabeled targets: a review. Anal Chim Acta, 620(1–2):8–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.05.022
Flueckiger J, Schmidt S, Donzella V, et al., 2016. Subwavelength grating for enhanced ring resonator biosensor. Opt Expr, 24(14):15672–15686. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.015672
Goddard NJ, Pollard-Knight D, Maule CH, 1994. Real-time biomolecular interaction analysis using the resonant mirror sensor. Analyst, 119(4):583–588. https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9941900583
Goddard NJ, Singh K, Hulme JP, et al., 2002. Internally-referenced resonant mirror devices for dispersion compensation in chemical sensing and biosensing applications. Sens Actuat A, 100(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-4247(02)00062-6
Graham CR, Leslie D, Squirrell DJ, 1992. Gene probe assays on a fibre-optic evanescent wave biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron, 7(7):487–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-5663(92)80005-V
Grandin HM, Städler B, Textor M, et al., 2006. Waveguide excitation fluorescence microscopy: a new tool for sensing and imaging the biointerface. Biosens Bioelectron, 21(8):1476–1482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2005.06.011
Guner H, Ozgur E, Kokturk G, et al., 2019. A smartphone based surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRi) platform for on-site biodetection. Sens Actuat B Chem, 239:571–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.061
Gustafsson MGL, 2005. Nonlinear structured-illumination microscopy: wide-field fluorescence imaging with theoretically unlimited resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102(37):13081–13086. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0406877102
Gustafsson MGL, Shao L, Carlton PM, et al., 2008. Three-dimensional resolution doubling in wide-field fluorescence microscopy by structured illumination. Biophys J, 94(12):4957–4970. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.107.120345
Hanumegowda NM, White IM, Oveys H, et al., 2005. Labelfree protease sensors based on optical microsphere resonators. Sens Lett, 3(4):315–319. https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2005.044
Hao X, Kuang CF, Liu X, et al., 2011. Microsphere based microscope with optical super-resolution capability. Appl Phys Lett, 99(20):203102. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3662010
Hao X, Liu X, Kuang CF, et al., 2013. Far-field superresolution imaging using near-field illumination by micro-fiber. Appl Phys Lett, 102(1):013104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4773572
Hassanzadeh A, Nitsche M, Mittler S, et al., 2008. Waveguide evanescent field fluorescence microscopy: thin film fluorescence intensities and its application in cell biology. Appl Phys Lett, 92(23):233503. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2937840
Hastings JT, Guo J, Keathley PD, et al., 2007. Optimal self-referenced sensing using long- and short-range surface plasmons. Opt Expr, 15(26):17661–17672. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.15.017661
Hecht B, Sick B, Wild UP, et al., 2000. Scanning near-field optical microscopy with aperture probes: fundamentals and applications. J Chem Phys, 12(18):7761–7774. https://doi.org/10.1063/T481382
Heideman RG, Kooyman RPH, Greve J, et al., 1991. Simple interferometer for evanescent field refractive index sensing as a feasibility study for an immunosensor. Appl Opt, 30(12):1474–1479. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.30.001474
Heideman RG, Kooyman RPH, Greve J, 1993. Performance of a highly sensitive optical waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometer immunosensor. Sens Actuat B Chem, 10(3): 209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4005(93)87008-D
Hess ST, Girirajan TPK, Mason MD, 2006. Ultra-high resolution imaging by fluorescence photoactivation localization microscopy. Biophys J, 91(11):4258–4272. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.106.091116
Hoa XD, Kirk AG, Tabrizian M, 2007. Towards integrated and sensitive surface plasmon resonance biosensors: a review of recent progress. Biosens Bioelectron, 23(2):151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2007.07.001
Homola J, Yee SS, Gauglitz G, 1999. Surface plasmon resonance sensors. Sens Actuat B Chem, 54(1–2):3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(98)00321-9
Horváth R, Lindvold LR, Larsen NB, 2002. Reversesymmetry waveguides: theory and fabrication. Appl Phys B, 74(4–5):383–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400200823
Horváth R, Pedersen HC, Skivesen N, et al., 2003. Optical waveguide sensor for on-line monitoring of bacteria. Opt Lett, 28(14):1233–1235. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.28.001233
Horváth R, Pedersen HC, Skivesen N, et al., 2005. Monitoring of living cell attachment and spreading using reverse symmetry waveguide sensing. Appl Phys Lett, 86(7): 071101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1862756
Jiménez D, Bartolomé E, Moreno M, et al., 1996. An integrated silicon ARROW Mach-Zehnder interferometer for sensing applications. Opt Commun, 132(5–6):437–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4018(96)00387-2
Kim J, Song KB, 2007. Recent progress of nano-technology with NSOM. Micron, 38(4):409–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2006.06.010
Kim J, Shin Y, Perera AP, et al., 2013. Label-free, PCR-free chip-based detection of telomerase activity in bladder cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron, 45:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.02.001
Klar TA, Engel E, Hell SW, 2001. Breaking Abbe’s diffraction resolution limit in fluorescence microscopy with stimulated emission depletion beams of various shapes. Phys Rev E Stat Nonl Soft Matter Phys, 64(6):066613. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.64.066613
Krioukov E, Greve J, Otto C, 2003. Performance of integrated optical microcavities for refractive index and fluorescence sensing. Sens Actuat B Chem, 90(1–3):58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(03)00022-4
Ksendzov A, Lin Y, 2005. Integrated optics ring-resonator sensors for protein detection. Opt Lett, 30(24):3344–3346. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.30.003344
Lee D, Kim YD, Kim M, et al., 2017. Realization of waferscale hyperlens device for sub-diffractional biomolecular imaging. ACS Photon, 5(7):2549–2554. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01182
Liedberg B, Nylander C, Lunström I, 1983. Surface plasmon resonance for gas detection and biosensing. Sens Actuat, 4(2):299–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/0250-6874(83)85036-7
Lillehoj PB, Huang MC, Truong N, et al., 2013. Rapid electrochemical detection on a mobile phone. Lab Chip, 13(15):2950–2955. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3LC50306B
Lin SY, Crozier KB, 2013. Trapping-assisted sensing of particles and proteins using on-chip optical microcavities. ACS Nano, 7(2):1720–1730. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn305826j
Lin VSY, Motesharei K, Dancil KPS, et al., 1997. A porous silicon-based optical interferometric biosensor. Science, 278(5339):840–843. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.278.5339.840
Liu Q, Tu XG, Woo KK, et al., 2013. Highly sensitive Mach-Zehnder interferometer biosensor based on silicon nitride slot waveguide. Sens Actuat B Chem, 188:681–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.07.053
Liu XW, Kuang CF, Hao X, et al., 2017. Fluorescent nanowire ring illumination for wide-field far-field subdiffraction imaging. Phys Rev Lett, 118(7):076101. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.076101
Liu ZW, Lee H, Xiong Y, et al., 2007. Far-field optical hyperlens magnifying sub-diffraction-limited objects. Science, 315(5819):1686. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1137368
Ma DDD, Lee CS, Au FCK, et al., 2003. Small-diameter silicon nanowire surfaces. Science, 299(5614):1874–1877. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1080313
Millan KM, Saraullo A, Mikkelsen SR, 1994. Voltammetric DNA biosensor for cystic fibrosis based on a modified carbon paste electrode. Anal Chem, 66(18):2943–2948. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00090a023
Moerner WE, 2007. New directions in single-molecule imaging and analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104(31): 12596–12602. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610081104
Nikitin PI, Grigorenko AN, Beloglazov AA, et al., 2000. Surface plasmon resonance interferometry for microarray biosensing. Sens Actuat A, 85(1–3):189–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-4247(00)00386-1
Noto M, Khoshsima M, Keng D, et al., 2005. Molecular weight dependence of a whispering gallery mode biosensor. Appl Phys Lett, 87(22):223901. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2137902
Pang CL, Liu XW, Zhuge MH, et al., 2017. High-contrast wide-field evanescent wave illuminated subdiffraction imaging. Opt Lett, 42(21):4569–4572. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.42.004569
Pang CL, Li JX, Tang MW, et al., 2019. On-chip super-resolution imaging with fluorescent polymer films. Adv Funct Mat, 29(27):1900126. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201900126
Prakash PA, Yogeswaran U, Chen SM, 2009. A review on direct electrochemistry of catalase for electrochemical sensors. Sensors, 9(3):1821–1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90301821
Prieto F, Sepúlveda B, Calle A, et al., 2003. Integrated Mach-Zehnder interferometer based on ARROW structures for biosensor applications. Sens Actuat B Chem, 92(1–2):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(03)00257-0
Ramachandran S, Cohen DA, Quist AP, et al., 2013. High performance, LED powered, waveguide based total internal reflection microscopy. Sci Rep, 3:2133. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02133
Rho J, Ye ZL, Xiong Y, et al., 2010. Spherical hyperlens for two-dimensional sub-diffractional imaging at visible frequencies. Nat Commun, 1:143. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1148
Roda A, Michelini E, Zangheri M, et al., 2016. Smartphone-based biosensors: a critical review and perspectives. Trends Anal Chem, 79:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.10.019
Rotenberg N, Kuipers L, 2014. Mapping nanoscale light fields. Nat Photon, 8(12):919–926. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.285
Schermelleh L, Heintzmann R, Leonhardt H, 2010. A guide to super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol, 190(2):165–175. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201002018
Schipper EF, Brugman AM, Dominguez C, et al., 1997. The realization of an integrated Mach-Zehnder waveguide immunosensor in silicon technology. Sens Actuat B Chem, 40(2–3):147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(97)80254-7
Schneider BH, Edwards JG, Hartman NF, 1997. Hartman interferometer: versatile integrated optic sensor for label-free, real-time quantification of nucleic acids, proteins, and pathogens. Clin Chem, 43(9):1757–1763.
Schneider BH, Dickinson EL, Vach MD, et al., 2000. Highly sensitive optical chip immunoassays in human serum. Biosens Bioelectron, 15(1–2):13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-5663(00)00056-7
Schweinsberg A, Hocdé S, Lepeshkin N, et al., 2007. An environmental sensor based on an integrated optical whispering gallery mode disk resonator. Sens Actuat B Chem, 123(2):727–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2006.10.007
Serpengüzel A, Arnold S, Griffel G, 1995. Excitation of resonances of microspheres on an optical fiber. Opt Lett, 20(7):654–656. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.20.000654
Skivesen N, Horvath R, Pedersen HC, 2003. Multimode reverse-symmetry waveguide sensor for broad-range refractometry. Opt Lett, 28(24):2473–2475. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.28.002473
Skivesen N, Horvath R, Pedersen HC, 2005. Optimization of metal-clad waveguide sensors. Sens Actuat B Chem, 106(2):668–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.09.014
Skivesen N, Horvath R, Thinggaard S, et al., 2007. Deep-probe metal-clad waveguide biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron, 22(7):1282–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2006.05.025
Su H, Kallury KMR, Thompson M, et al., 1994. Interfacial nucleic acid hybridization studied by random primer 32P labeling and liquid-phase acoustic network analysis. Anal Chem, 66(6):769–777. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00078a002
Sun JB, Shalaev MI, Litchinitser NM, 2015. Experimental demonstration of a non-resonant hyperlens in the visible spectral range. Nat Commun, 6:7201. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8201
Sundram V, Nanda JS, Rajagopal K, et al., 1993. Domain truncation studies reveal that the streptokinase-plasmin activator complex utilizes long range protein-protein interactions with macromolecular substrate to maximize catalytic turnover. JBiol Chem, 278(33):30569–30577. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M303799200
Suter JD, White IM, Zhu HY, et al., 2007. Thermal characterization of liquid core optical ring resonator sensors. Appl Opt, 46(3):386–389. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.46.000389
Taniguchi T, Hirowatari A, Ikeda T, et al., 2016. Detection of antibody-antigen reaction by silicon nitride slot-ring biosensors using protein G. Opt Commun, 365:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2015.11.068
Teraoka I, Arnold S, 2006. Theory of resonance shifts in TE and TM whispering gallery modes by nonradial perturbations for sensing applications. J Opt Soc Am B, 23(7): 1381–1389. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.23.001381
Tian BZ, Cohen-Karni T, Qing Q, et al., 2010. Three-dimensional, flexible nanoscale field-effect transistors as localized bioprobes. Science, 329(5993):830–834. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1192033
Tiefenthaler K, Lukosz W, 1989. Sensitivity of grating couplers as integrated-optical chemical sensors. J Opt Soc Am B, 6(2):209–220. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.6.000209
Tong L, Gattass RR, Ashcom JB, et al., 2003. Subwavelength-diameter silica wires for low-loss optical wave guiding. Nature, 426(6968):816–819. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02193
Wang ZB, Guo W, Li L, et al., 2011. Optical virtual imaging at 50 nm lateral resolution with a white-light nanoscope. Nat Commun, 2:218. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1211
Watts HJ, Lowe CR, Pollard-Knight DV, 1994. Optical biosensor for monitoring microbial cells. Anal Chem, 66(15):2465–2470. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00087a010
Watts HJ, Yeung D, Partees H, 1995. Real-time detection and quantification of DNA hybridization by an optical biosensor. Anal Chem, 67(23):4283–4289. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00119a013
Weisser M, Tovar G, Mittler-Neher S, et al., 1999. Specific bio-recognition reactions observed with an integrated Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Biosens Bioelectron, 14(4):405–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-5663(98)00124-9
White IM, Fan XD, 2008. On the performance quantification of resonant refractive index sensors. Opt Expr, 16(2): 1020–1028. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.16.001020
White IM, Gohring J, Fan XD, 2007. SERS-based detection in an optofluidic ring resonator platform. Opt Expr, 15(25): 17433–17442. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.15.017433
Willig KI, Rizzoli SO, Westphal V, et al., 2006. STED microscopy reveals that synaptotagmin remains clustered after synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Nature, 440(7086): 935–939. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04592
Yahiatène I, Hennig S, Müller M, et al., 2015. Entropy-based super-resolution imaging (ESI): from disorder to fine detail. ACS Photon, 2(8):1049–1056. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00307
Yalcin A, Popat KC, Aldridge JC, et al., 2006. Optical sensing of biomolecules using microring resonators. IEEE J Sel Top Quant, 12(1):148–155. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2005.863003
Yang Q, Wang WH, Xu S, et al., 2011. Enhancing light emission of ZnO microwire-based diodes by piezophototronic effect. Nano Lett, 11(9):4012–4017. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl202619d
Ymeti A, Kanger JS, Greve J, et al., 2003. Realization of a multichannel integrated Young interferometer chemical sensor. Appl Opt, 42(28):5649–5660. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.42.005649
Yu L, Shi ZZ, Fang C, et al., 2015. Disposable lateral flow-through strip for smartphone-camera to quantitatively detect alkaline phosphatase activity in milk. Biosens Bioelectron, 69:307–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.02.035
Zenhausern F, Martin Y, Wickramasinghe HK, 1995. Scanning interferometric apertureless microscopy: optical imaging at 10 angstrom resolution. Science, 269(5227): 1083–1085. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.269.5227.1083
Zhang JJ, Li GX, 2004. Third-generation biosensors based on the direct electron transfer of proteins. Anal Sci, 20(4):603–609. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.20.603
Zhang JL, Khan I, Zhang QW, et al., 2018. Lipopolysaccharides detection on a grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance smartphone biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron, 99:312–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.048
Zhu HY, Suter JD, White I, et al., 2006. Aptamer based microsphere biosensor for thrombin detection. Sensors, 6(8):785–795. https://doi.org/10.3390/s6080785
Zourob M, Goddard NJ, 2005. Metal clad leaky waveguides for chemical and biosensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron, 20(9):1718–1727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2004.06.031
Zourob M, Mohr S, Brown BJ, et al., 2003a. The development of a metal clad leaky waveguide sensor for the detection of particles. Sens Actuat B Chem, 90:296–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(03)00052-2
Zourob M, Mohr S, Fielden PR, et al., 2003b. Small-volume refractive index and fluorescence sensor for micro total analytical system (μ-TAS) applications. Sens Actuat B Chem, 94:304–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(03)00460-X
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61735017, 61822510, and 51672245), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. R17F050003), the National Key Basic Research Program of China (No. 2015CB352003), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China, the Program for Zhejiang Leading Team of S&T Innovation, the Cao Guangbiao Advanced Technology Program, and the First-Class Universities and Academic Programs
Contributors
Chen-lei PANG designed the research and drafted the manuscript. Qing YANG helped organize the manuscript. Xu LIU and Wei CHEN revised the manuscript. Chen-lei PANG and Qing YANG finalized the paper.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Chen-lei PANG, Xu LIU, Wei CHEN, and Qing YANG declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Chen-lei PANG, first author of this invited paper, received his PhD degree in Optical Engineering in 2019 from Zhejiang University. He was awarded a scholarship under the State Scholarship Fund to study at California Institute of Technology as a joint PhD student from March 2018 to March 2019. He currently works at Zhejiang Lab, and his research interests focus on chip-based super-resolution imaging and defect inspection.
Qing YANG, corresponding author of this invited paper, received her BS and PhD degrees in College of Materials Science and Engineering from Zhejiang University in 2001 and 2006, respectively. She was a visiting scholar at Georgia Tech from 2009 to 2012, and a visiting scientist at University of Cambridge in 2018. She is currently a professor at the State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Zhejiang University, and an associate editor of Science Bulletin. Her research interests focus on smart and high-resolution sensing and imaging based on micro/nanophotonics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, Cl., Liu, X., Chen, W. et al. Chip-based waveguides for high-sensitivity biosensing and super-resolution imaging. Front Inform Technol Electron Eng 21, 1134–1149 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1900211
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1900211
Key words
- Waveguide-based sensing
- Waveguide-based imaging
- Evanescent illumination
- Frequency shifting and stitching