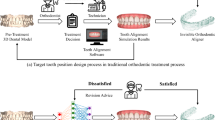
Abstract
A critical step in digital dentistry is to accurately and automatically characterize the orientation and position of individual teeth, which can subsequently be used for treatment planning and simulation in orthodontic tooth alignment. This problem remains challenging because the geometric features of different teeth are complicated and vary significantly, while a reliable large-scale dataset is yet to be constructed. In this paper we propose a novel method for automatic tooth orientation estimation by formulating it as a six-degree-of-freedom (6-DoF) tooth pose estimation task. Regarding each tooth as a three-dimensional (3D) point cloud, we design a deep neural network with a feature extractor backbone and a two-branch estimation head for tooth pose estimation. Our model, trained with a novel loss function on the newly collected large-scale dataset (10 393 patients with 280 611 intraoral tooth scans), achieves an average Euler angle error of only 4.780°–5.979° and a translation L1 error of 0.663 mm on a hold-out set of 2598 patients (77 870 teeth). Comprehensive experiments show that 98.29% of the estimations produce a mean angle error of less than 15°, which is acceptable for many clinical and industrial applications.
摘要
数字牙科的一个关键步骤是准确、自动地表征牙齿的方向和位置, 在此基础上可以辅助制定正畸治疗计划和模拟牙齿排齐. 由于不同牙齿之间的几何特征复杂且差异较大, 且可靠的大规模数据集尚未构建, 表征牙齿的方向和位置仍然具有挑战性. 本文提出一种新的牙齿方位自动估算方法, 将其表述为六方位自由度的牙齿姿态估算任务. 将每个牙齿视为一个三维点云, 设计了一个具有特征提取主干和双支路检测头的深度神经网络模型, 以估算牙齿姿态. 使用新的损失函数训练新收集的大样本数据集(10 393例患者, 280 611颗牙齿的扫描数据), 在2598例患者(77 870颗牙齿)的数据集上, 平均欧拉角误差仅为4.780°–5.979°, 平移L1误差为0.663 mm. 综合实验表明, 98.29%的估算产生的平均角度误差小于15°, 这对于大多数临床和工业应用可以接受.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Cai M, Reid I, 2020. Reconstruct locally, localize globally: a model free method for object pose estimation. Proc IEEE/CVF Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.3150–3160. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00322
Chen QM, Wang YH, Shuai J, 2023. Current status and future prospects of stomatology research. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 24(10):853–867. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200702
Gu CH, Ren XF, 2010. Discriminative mixture-of-templates for viewpoint classification. 11th European Conf on Computer Vision, p.408–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15555-0_30
Herrmann W, 1967. On the completion of Fédération Dentaire Internationale Specifications. Zahn Mitteil, 57(23):1147–1149 (in German).
Hinterstoisser S, Cagniart C, Ilic S, et al., 2012. Gradient response maps for real-time detection of textureless objects. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 34(5):876–888. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2011.206
Kendall A, Grimes M, Cipolla R, 2015. PoseNet: a convolutional network for real-time 6-DOF camera relocalization. Proc IEEE Int Conf on Computer Vision, p.2938–2946. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.336
Li ZG, Wang G, Ji XY, 2019. CDPN: coordinates-based disentangled pose network for real-time RGB-based 6-DoF object pose estimation. Proc IEEE/CVF Int Conf on Computer Vision, p.7677–7686. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00777
Liebelt J, Schmid C, Schertler K, 2008. Viewpoint-independent object class detection using 3D feature maps. IEEE Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587614
Mok V, Ong SH, Foong KWC, et al., 2002. Pose estimation of teeth through crown-shape matching. Proc SPIE 4684, Medical Imaging 2002: Image Processing, p.955–964. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.467048
Newell A, Yang KY, Deng J, 2016. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. 14th European Conf on Computer Vision, p.483–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_29
Oberweger M, Rad M, Lepetit V, 2018. Making deep heatmaps robust to partial occlusions for 3D object pose estimation. Proc 15th European Conf on Computer Vision, p.125–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_8
Park K, Patten T, Vincze M, 2019. Pix2Pose: pixel-wise coordinate regression of objects for 6D pose estimation. Proc IEEE/CVF Int Conf on Computer Vision, p.7667–7676. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00776
Peng SD, Liu Y, Huang QX, et al., 2019. PVNet: pixel-wise voting network for 6DoF pose estimation. Proc IEEE/CVF Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.4556–4565. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00469
Qi CR, Litany O, He KM, et al., 2019. Deep Hough voting for 3D object detection in point clouds. Proc IEEE/CVF Int Conf on Computer Vision, p.9276–9285. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00937
Su H, Qi CR, Li YY, et al., 2015. Render for CNN: viewpoint estimation in images using CNNs trained with rendered 3D model views. Proc IEEE Int Conf on Computer Vision, p.2686–2694. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.308
Sun M, Bradski G, Xu BX, et al., 2010. Depth-encoded Hough voting for joint object detection and shape recovery. 11th European Conf on Computer Vision, p.658–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15555-0_48
Ulrich J, Alsayed A, Arvin F, et al., 2022. Towards fast fiducial marker with full 6 DOF pose estimation. Proc 37th ACM/SIGAPP Symp on Applied Computing, p.723–730. https://doi.org/10.1145/3477314.3507043
Wang C, Xu DF, Zhu YK, et al., 2019. DenseFusion:6D object pose estimation by iterative dense fusion. Proc IEEE/CVF Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.3338–3347. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00346
Wang H, Sridhar S, Huang JW, et al., 2019. Normalized object coordinate space for category-level 6D object pose and size estimation. Proc IEEE/CVF Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.2637–2646. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00275
Wang Y, Sun YB, Liu ZW, et al., 2019. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans Graph, 38(5):146. https://doi.org/10.1145/3326362
Wei GD, Cui MZ, Liu YM, et al., 2020. TANet: towards fully automatic tooth arrangement. 16th European Conf on Computer Vision, p.481–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58555-6_29
Xiang Y, Schmidt T, Narayanan V, et al., 2018. PoseCNN: a convolutional neural network for 6D object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. Proc 14th Robotics: Science and Systems.
Zhou Y, Tuzel O, 2018. VoxelNet: end-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection. Proc IEEE Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.4490–4499. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00472
Zhou Y, Barnes C, Lu JW, et al., 2019. On the continuity of rotation representations in neural networks. Proc IEEE/CVF Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.5738–5746. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00589
Zhu JJ, Yang YX, Wong HM, 2023. Development and accuracy of artificial intelligence-generated prediction of facial changes in orthodontic treatment: a scoping review. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 24(11):974–984. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300244
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wanghui DING, Mengfei YU, and Zuozhu LIU designed and initiated the project. Zuozhu LIU, Jianhua LI, and Wanghui DING designed the model architecture. Kaiwei SUN and Hangzheng LIN conducted validation experiments. Kaiwei SUN, Jianhua LI, and Hangzheng LIN created the dataset. Hangzheng LIN, Kaiwei SUN, and Yang FENG developed the software. Wanghui DING and Kaiwei SUN drafted the paper. Wanghui DING and Zuozhu LIU revised and finalized the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11932012 and 62106222), the Zhejiang University–Angelaling Inc. R&D Center for Intelligent Healthcare, the Zhejiang Provincial Public Welfare Research Program (No. LTGY23H140007), the Clinical Research Project of the Chinese Orthodontic Society (No. COS-C202109), and the Research and Development Project of Stomatology Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine (No. RD2022YFZD01)
List of supplementary materials
Table S1 Tooth axis data statistics
Table S2 Median, minimum, and maximum values of the predicted angle error from Ml
Table S3 Average occlusal angle for teeth pairs
Fig. S1 Visualization of estimated orientation and ground truth for Example 1
Fig. S2 Visualization of estimated orientation and ground truth for Example 2
Supplementary materials for
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, W., Sun, K., Yu, M. et al. Accurate estimation of 6-DoF tooth pose in 3D intraoral scans for dental applications using deep learning. Front Inform Technol Electron Eng 25, 1240–1249 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.2300596
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.2300596