Abstract
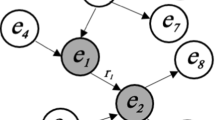
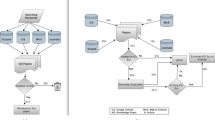
Linked data is a decentralized space of interlinked Resource Description Framework (RDF) graphs that are published, accessed, and manipulated by a multitude of Web agents. Here, we present a multi-agent framework for mining hypothetical semantic relations from linked data, in which the discovery, management, and validation of relations can be carried out independently by different agents. These agents collaborate in relation mining by publishing and exchanging inter-dependent knowledge elements, e.g., hypotheses, evidence, and proofs, giving rise to an evidentiary network that connects and ranks diverse knowledge elements. Simulation results show that the framework is scalable in a multi-agent environment. Real-world applications show that the framework is suitable for interdisciplinary and collaborative relation discovery tasks in social domains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleman-Meza, B., 2005. Ranking complex relationships on the Semantic Web. IEEE Internet Comput., 9(3):37–44. [doi:10.1109/MIC.2005.63]
Aleman-Meza, B., Nagarajan, M., Ramakrishnan, C., Ding, L., Kolari, P., Sheth, A.P., Arpinar, I.B., Joshi, A., Finin, T., 2006. Semantic Analytics on Social Networks: Experiences in Addressing the Problem of Conflict of Interest Detection. Proc. 15th Int. Conf. on World Wide Web, p.407–416. [doi:10.1145/1135777.1135838]
Anyanwu, K., 2007. Supporting Link Analysis Using Advanced Querying Methods on Semantic Web Datasets. PhD Thesis, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia.
Anyanwu, K., Sheth, A., 2003. ρ-Queries: Enabling Querying for Semantic Associations on the Semantic Web. Proc. 12th Int. Conf. on World Wide Web, p.690–699.
Anyanwu, K., Maduko, A., Sheth, A., 2007. SPARQ2L: Towards Support for Subgraph Extraction Queries in RDF Databases. Proc. 16th Int. Conf. on World Wide Web, p.797–806. [doi:10.1145/1242572.1242680]
Ayers, D., 2008. Graph farming. IEEE Internet Comput., 12(1):80–83. [doi:10.1109/MIC.2008.13]
Berners-Lee, T., 2006. Linked Data—Design Issues. Available from http://www.w3.org/DesignIssues/Linked-Data.html [Accessed on Feb. 19, 2012].
Berners-Lee, T., Fielding, R.T., Masinter, L., 1998. Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI): Generic Syntax. IETF RFP 3986 (Standards Track). Available from www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3986.txt
Berners-Lee, T., Hendler, J., Lassilia, O., 2001. The Semantic Web. Sci. Am., 284(5):34–44. [doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0501-34]
Berners-Lee, T., Hall, W., Hendler, J.A., O’Hara, K., Shadbolt, N., Weitzner, D.J., 2006. A framework for Web science. Found. Trends Web Sci., 1(1):1–130. [doi:10.1561/1800000001]
Berners-Lee, T., Hollenbach, J., Lu, K., Presbrey, J., Prud’ommeaux, E., Schraefel, M., 2008. Tabulator Redux: Browsing and Writing Linked Data. Proc. www Workshops: Linked Data on the Web.
Bizer, C., 2006. State of the LOD Cloud. Available from http://www4.wiwiss.fu-berlin.de/lodcloud/state/ [Accessed on Feb. 19, 2012].
Bizer, C., Heath, T., Berners-Lee, T., 2009. Linked data—the story so far. Int. J. Semant. Web Inf. Syst., 5(3):1–22. [doi:10.4018/jswis.2009081901]
Carroll, J.J., Bizer, C., Hayes, P., Stickler, P., 2005. Named Graphs, Provenance and Trust. Proc. 14th Int. Conf. on World Wide Web, p.613–622. [doi:10.1145/1060745.1060835]
Deerwester, S., Dumais, S.T., Landauer, T.K., Furnas, G.W., Harshman, R.A., 1990. Indexing by latent semantic analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inform. Sci., 41(6):391–407. [doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4571(199009)41:6<391::AIDASI1>3.0.CO;2-9]
de Raedt, L., Kimmig, A., Toivonen, H., 2007. Problog: a Probabilistic Prolog and Its Application in Link Discovery. Proc. 20th Int. Joint Conf. on Artifical Intelligence, p.2468–2473.
Feigenbaum, L., Herman, I., Hongsermeier, T., Neuman, E., Stephens, S., 2007. The Semantic Web in action. Sci. Am., 297(6):90–97. [doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1207-90]
Heath, T., Bizer, C., 2011. Linked Data: Evolving the Web into a Global Data Space (1st Ed.). In: Jantsch, E., Waddington, C. (Eds.), Synthesis Lectures on the Semantic Web: Theory and Technology. Morgan & Claypool, California, p.1–136. [doi:10.2200/S00334ED1V01Y201102WBE001]
Hendler, J., 2001. Agents and the Semantic Web. IEEE Intell. Syst., 16(2):30–37. [doi:10.1109/5254.920597]
Hendler, J., 2007. Where are all the intelligent agents? IEEE Intell. Syst., 22(3):2–3. [doi:10.1109/MIS.2007.62]
Mika, P., 2005. Flink: Semantic Web technology for the extraction and analysis of social networks. Web Semant., 3(2–3):211–223. [doi:10.1016/j.websem.2005.05.006]
Mukherjea, S., 2005. Information retrieval and knowledge discovery utilising a biomedical Semantic Web. Brief. Bioinform., 6(3):252–262. [doi:10.1093/bib/6.3.252]
Mukherjea, S., Bamba, B., Kankar, P., 2005. Information retrieval and knowledge discovery utilizing a biomedical patent Semantic Web. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., 17(8):1099–1110. [doi:10.1109/TKDE.2005.130]
Ruttenberg, A., Rees, J.A., Samwald, M., Marshall, M.S., 2009. Life sciences on the Semantic Web: the neurocommons and beyond. Brief Bioinform., 10(2):193–204. [doi:10.1093/bib/bbp004]
Sabou, M., d’Aquin, M., Motta, E., 2008. SCARLET: SemantiC relAtion discoveRy by harvesting onLinE on-Tologies. LNCS, 5021:854–858. [doi:10.1007/978-3-540-68234-9_72]
Semantic Web Deployment Working Group, 2009. Simple Knowledge Organization System (SKOS). Available from http://www.w3.org/2001/sw/wiki/SKOS [Accessed on Feb. 19, 2012].
Stephens, S., Morales, A., Quinlan, M., 2006. Applying Semantic Web technologies to drug safety determination. IEEE Intell. Syst., 21(1):82–86. [doi:10.1109/MIS.2006.2]
Tarjan, R.E., 1981. Fast algorithms for solving path problems. J. ACM, 28(3):594–614. [doi:10.1145/322261.322273]
Thomas, L.T., Valluri, S.R., Karlapalem, K., 2006. Margin: Maximal Frequent Subgraph Mining. Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on Data Mining, p.1097–1101.
Volz, J., Bizer, C., Gaedke, M., Kobilarov, G., 2009. Discovering and Maintaining Links on the Web of Data. Int. Semantic Web Conf., p.1–16.
W3C OWL Working Group, 2009. OWL 2 Web Ontology Language Overview. Available from http://www.w3.org/TR/owl2-overview/ [Accessed on Feb. 19, 2012].
W3C RDF Working Group, 2004. Resource Description Framework (RDF). Available from http://www.w3.org/2001/sw/wiki/RDF [Accessed on Feb. 19, 2012].
W3C SPARQL Working Group, 2008. SPARQL Query Language for RDF. Available from http://www.w3.org/2001/sw/wiki/SPARQL [Accessed on Feb. 19, 2012].
Recommended reading
Aleman-Meza, B., 2005. Ranking complex relationships on the Semantic Web. IEEE Internet Comput., 9(3):37–44. [doi:10.1109/MIC.2005.63]
Aleman-Meza, B., Nagarajan, M., Ramakrishnan, C., Ding, L., Kolari, P., Sheth, A.P., Arpinar, I.B., Joshi, A., Finin, T., 2006. Semantic Analytics on Social Networks: Experiences in Addressing the Problem of Conflict of Interest Detection. Proc. 15th Int. Conf. on World Wide Web, p.407–416. [doi:10.1145/1135777.1135838]
Anyanwu, K., Maduko, A., Sheth, A., 2007. SPARQ2L: Towards Support for Subgraph Extraction Queries in RDF Databases. Proc. 16th Int. Conf. on World Wide Web, p.797–806. [doi:10.1145/1242572.1242680]
Mukherjea, S., 2005. Information retrieval and knowledge discovery utilising a biomedical Semantic Web. Brief. Bioinform., 6(3):252–262.[doi:10.1093/bib/6.3.252]
Mukherjea, S., Bamba, B., Kankar, P., 2005. Information retrieval and knowledge discovery utilizing a biomedical patent Semantic Web. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., 17(8):1099–1110. [doi:10.1109/TKDE.2005.130]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61070156 and 61100183) and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (No. Y1110477)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Hj., Yu, T., Zheng, Qz. et al. A multi-agent framework for mining semantic relations from linked data. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 13, 295–307 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1101010
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1101010