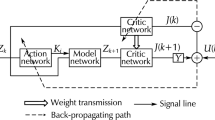
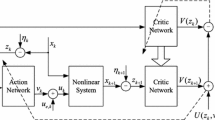
Abstract
We investigate the optimization of linear impulse systems with the reinforcement learning based adaptive dynamic programming (ADP) method. For linear impulse systems, the optimal objective function is shown to be a quadric form of the pre-impulse states. The ADP method provides solutions that iteratively converge to the optimal objective function. If an initial guess of the pre-impulse objective function is selected as a quadratic form of the pre-impulse states, the objective function iteratively converges to the optimal one through ADP. Though direct use of the quadratic objective function of the states within the ADP method is theoretically possible, the numerical singularity problem may occur due to the matrix inversion therein when the system dimensionality increases. A neural network based ADP method can circumvent this problem. A neural network with polynomial activation functions is selected to approximate the pre-impulse objective function and trained iteratively using the ADP method to achieve optimal control. After a successful training, optimal impulse control can be derived. Simulations are presented for illustrative purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, N.U., 2003. Existence of optimal controls for a general class of impulsive systems on Banach spaces. SIAM J. Control Optim., 42(2):669–685. [doi:10.1137/S0363012901391299]
Bainov, D.D., Simeonov, P.S., 1995. Impulsive Differential Equations: Asymptotic Properties of the Solutions. World Scientific, Singapore.
Balakrishnan, S.N., Ding, J., Lewis, F.L., 2008. Issues on stability of ADP feedback controllers for dynamical systems. IEEE Tran. Syst. Man Cybern. B, 38(4):913–917. [doi:10.1109/TSMCB.2008.926599]
Bertsekas, D.P., 2011. Approximate policy iteration: a survey and some new methods. J. Control Theory Appl., 9(3):310–335.
Dierks, T., Jagannathan, S., 2011. Online optimal control of nonlinear discrete-time systems using approximate dynamic programming. J. Control Theory Appl., 9(3):361–369. [doi:10.1007/s11768-011-0178-0]
Fraga, S.L., Pereira, F.L., 2012. Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equation and feedback synthesis for impulsive control. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 57(1):244–249. [doi:10.1109/TAC.2011.2167822]
Jiang, Y., Jiang, Z.P., 2012. Computational adaptive optimal control for continuous-time linear systems with completely unknown dynamics. Automatica, 48(10):2699–2704. [doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2012.06.096]
Jiang, Z.P., Jiang, Y., 2013. Robust adaptive dynamic programming for linear and nonlinear systems: an overview. Eur. J. Control, 19(5):417–425. [doi:10.1016/j.ejcon.2013.05.017]
Kurzhanski, A.B., Daryin, A.N., 2008. Dynamic programming for impulse controls. Ann. Rev. Control, 32(2):213–227. [doi:10.1016/j.arcontrol.2008.08.001]
Lakshmikantham, V., Bainov, D.D., Simeonov, P.S., 1989. Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations. World Scientific, Singapore.
Lewis, F.L., Vrabie, D., 2009. Reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for feedback control. IEEE Circ. Syst. Mag., 9(3):32–50. [doi:10.1109/MCAS.2009.933854]
Liu, B., Teo, K.L., Liu, X.Z., 2008. Optimal control and robust stability of uncertain impulsive dynamical systems. Asian J. Control, 10(3):314–326. [doi:10.1002/asjc.37]
Liu, D.R., Wei, Q.L., 2013. Finite-approximation-errorbased optimal control approach for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 43(2):779–789. [doi:10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2216523]
Liu, X., 1995. Impulsive control and optimization. Appl. Math. Comput., 73(1):77–98. [doi:10.1016/0096-3003(94)00204-H]
Silva, G.N., Vinter, R.B., 1997. Necessary conditions for optimal impulsive control problems. SIAM J. Control Optim., 35(6):1829–1846. [doi:10.1137/S0363012995281857]
Vamvoudakis, K.G., Lewis, F.L., 2010. Online actor-critic algorithm to solve the continuous-time infinite horizon optimal control problem. Automatica, 46(5):878–888. [doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2010.02.018]
Wang, F.Y., Zhang, H.G., Liu, D.R., 2009. Adaptive dynamic programming: an introduction. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag., 4(2):39–47. [doi:10.1109/MCI.2009.932261]
Wang, J.R., Yang, Y.L., 2010. Optimal control of linear impulsive antiperiodic boundary value problem on infinite dimensional spaces. Discr. Dynam. Nat. Soc., Article ID 673013. [doi:10.1155/2010/673013]
Wang, X.H., 2008. Optimal Control of Impulsive Systems Using Adaptive Critic Neural Network. PhD Thesis, Missouri University of Science and Technology, Rolla, Missouri, USA.
Wang, X.H., Balakrishnan, S.N., 2010. Optimal neurocontroller synthesis for impulse-driven systems. Neur. Networks, 23(1):125–134. [doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2009.08.009]
Wang, X.H., Luo, W.Z., Balakrishnan, S.N., 2012. Linear impulsive system optimization using adaptive dynamic programming. 12th Int. Conf. on Control Automation Robotics and Vision, p.725–730. [doi:10.1109/ICARCV.2012.6485247]
Werbos, P.J., 1974. Beyond Regression: New Tools for Prediction and Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences. PhD Thesis, Harvard University, USA.
Werbos, P.J., 2008. Foreword-ADP: the key direction for future research in intelligent control and understanding brain intelligence. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B, 38(4):898–900. [doi:10.1109/TSMCB.2008.924139]
Werbos, P.J., McAvoy, T., Su, T., 1992. Handbook of Intelligent Control. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York.
Wu, Z., Zhang, F., 2011. Stochastic maximum principle for optimal control problems of forward-backward systems involving impulse controls. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 56(6):1401–1406.
Yang, T., 1999. Impulsive control. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 44(5):1081–1083.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61104006, 51175319, and 11202121), the MOE Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 11ZR1412400), and the Shanghai Education Commission (Nos. 12YZ010, 12JC1404100, and 11CH-05), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Xh., Yu, Jj., Huang, Y. et al. Adaptive dynamic programming for linear impulse systems. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 15, 43–50 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300145
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300145