Abstract
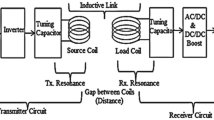
The efficiency of inductive power links driven by Class-E amplifiers may deteriorate due to variation in the coupling coefficient when the relative position of the radio frequency (RF) coils changes. To solve this problem, a new design methodology of power links is presented in this paper. The aim of the new design is to use the feedback signal, which is a phase difference between the driving signal and the output current of the Class-E amplifier, to adjust the duty cycle and angular frequency of the driving signal to maintain the optimum state of the inductive power link, and to adjust the supply voltage to keep the output power constant when the coupling coefficient of the RF coils changes. The parameter adjustments with respect to the coupling coefficient and the feedback signal are derived from the design equation of the inductive power link. To validate the feedback control rules, a prototype of the inductive power link was constructed, and its performance validated with the coupling coefficient set at 0.2 and a duty cycle of 0.5. The experimental results showed that, by adjusting the duty cycle, the angular frequency, and the supply voltage, the power link can be kept in optimal operation with a constant output power when the coupling coefficient changes from 0.2 to 0.1 to 0.25.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, M.W., Rahul, S., 2007. Feedback analysis and design of RF power links for low-power bionic systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circ. Syst., 1(1):28–38. [doi:10.1109/TBCAS.2007.893180]
Donaldson, N.N., Perkins, T.A., 1983. Analysis of resonant coupled coils in the design of radio frequency transcutaneous links. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., 21(5): 612–627. [doi:10.1007/BF02442388]
Kazimierczuk, M.K., Czarkowski, D., 1995. Resonant Power Converters. Wiley, New York.
Kendir, G.A., Liu, W., Wang, G., Sivaprakasam, M., Bashirullash, R., Humayun, M.S., Weiland, J.D., 2005. An optimal design methodology for inductive power link with Class-E amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst.-I, 52(5):857–868. [doi:10.1109/TCSI.2005.846208]
Kessler, D.J., Kazimierczuk, M.K., 2004. Power losses and efficiency of Class-E power amplifier at any duty ratio. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst.-I, 51(9):1675–1689. [doi:10.1109/TCSI.2004.834505]
Ko, W.H., Liang, S.P., Fung, C.D.F., 1977. Design of radio-frequency powered coils for implant instruments. Med. Biol. Eng., 15(6):634–640. [doi:10.1007/BF02457921]
Lenaerts, B., Puers, R., 2007. An inductive power link for a wireless endoscope. Biosens. & Bioelectron., 22(7):1390–1395. [doi:10.1016/j.bios.2006.06.015]
Lenaerts, B., Puers, R., 2008. Automatic inductance compensation for Class-E driven flexible coils. Sens. & Actuat. A, 145–146:154–160. [doi:10.1016/j.sna.2007.11.011]
Mury, T., Fusco, V.F., 2006. Analysis and synthesis of pHEMT class-E amplifiers with shunt inductor including ON-state active-device resistance effects. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst.-I, 53(7):1556–1564. [doi:10.1109/TCSI.2006.876416]
Raab, F.H., 1977. Idealized operation of the Class-E tuned power amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst., 24(12):725–735. [doi:10.1109/TCS.1977.1084296]
Sarpeshkar, R., Salthouse, C., Sit, J.J., Baker, M.W., Zhak, S.M., Lu, T.K.T., Turicchia, L., Balster, S., 2005. An ultra-low-power programmable analog bionic ear processor. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 52(4):711–727. [doi:10.1109/TBME.2005.844043]
Sokal, N.O., Sokal, A.D., 1975. Class E: a new class of high-efficiency tuned single-ended switching power amplifiers. IEEE J. Sol.-State Circ., 10(3):168–176. [doi:10.1109/JSSC.1975.1050582]
Wang, G., Liu, W., Sivaprakasam, M., Kendir, G.A., 2005. Design and analysis of an adaptive transcutaneous power telemetry for biomedical implants. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst.-I, 52(10):2109–2117. [doi:10.1109/TCSI.2005.852923]
Yang, T.L., Zhao, C.Y., Zhang, J.Y., Chen, D.Y., 2009. Power Loss and Efficiency of Transcutaneous Energy Transmission System with Class-E Power Amplifier at Any Duty Ratio. Int. Symp. on Signals, Circuits and Systems, p.425–428. [doi:10.1109/ISSCS.2009.5206221]
Zan, P., Yan, G., Liu, H., Luo, N., Zhao, Y., 2007. Adaptive transcutaneous power delivery for an artificial anal sphincter system. J. Med. Eng. Technol., 33(2):136–141. [doi:10.1080/03091900801943205]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 60271031) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Tl., Zhao, Cy. & Chen, Dy. Feedback analysis and design of inductive power links driven by Class-E amplifiers with variable coupling coefficients. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 11, 629–636 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C0910607
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C0910607