Abstract
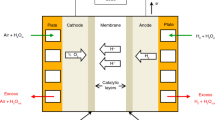
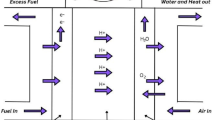
An appropriate mathematical model can help researchers to simulate, evaluate, and control a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) stack system. Because a PEMFC is a nonlinear and strongly coupled system, many assumptions and approximations are considered during modeling. Therefore, some differences are found between model results and the real performance of PEMFCs. To increase the precision of the models so that they can describe better the actual performance, optimization of PEMFC model parameters is essential. In this paper, an artificial bee swarm optimization algorithm, called ABSO, is proposed for optimizing the parameters of a steady-state PEMFC stack model suitable for electrical engineering applications. For studying the usefulness of the proposed algorithm, ABSO-based results are compared with the results from a genetic algorithm (GA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO). The results show that the ABSO algorithm outperforms the other algorithms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari, R., Mohammadi, A., Ziarati, K., 2010. A novel bee swarm optimization algorithm for numerical function optimization. Commun. Nonl. Sci. Numer. Simul., 15(10):3142–3155. [doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2009.11.003]
Bernardi, D.M., Verbrugge, M.W., 1992. A mathematical model of the solid-polymer-electrolyte fuel-cell. J. Electrochem. Soc., 139(9):2477–2491. [doi:10.1149/1.2221251]
Corrêa, J.M., Farret, F.A., Canha, L.N., Simões, M.G., 2004. An electrochemical-based fuel-cell model suitable for electrical engineering automation approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr., 51(5):1103–1112. [doi:10.1109/TIE.2004.834972]
Fuller, T.F., Newman, J., 1993. Water and thermal management in solid-polymer-electrolyte fuel-cells. J. Electrochem. Soc., 140(5):1218–1225. [doi:10.1149/1.2220960]
Jia, J., Li, Q., Wang, Y., Cham, Y.T., Han, M., 2009. Modeling and dynamic characteristic simulation of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv., 24(1):283–291. [doi:10.1109/TEC.2008.2011837]
Karaboga, D., Basturk, B., 2007. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J. Glob. Optim., 39(3):459–471. [doi:10.1007/s10898-007-9149-x]
Mann, R.F., Amphlett, J.C., Hooper, M.A.I., Jensen, H.M., Peppley, B.A., Roberge, P.R., 2000. Development and application of a generalised steady-state electrochemical model for a PEM fuel cell. J. Power Sources, 86(1–2):173–180. [doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(99)00484-X]
Mo, Z.J., Zhu, X.J., Wei, L.Y., Cao, G.Y., 2006. Parameter optimization for a PEMFC model with a hybrid genetic algorithm. Int. J. Energy Res., 30(8):585–597. [doi:10.1002/er.1170]
Nguyen, T.V., White, R.E., 1993. A water and heat management model for proton-exchange-membrane fuel-cells. J. Electrochem. Soc., 140(8):2178–2186. [doi:10.1149/1.2220792]
Ohenoja, M., Leiviska, K., 2010. Validation of genetic algorithm results in a fuel cell model. Int. J. Hydr. Energy, 35(22):12618–12625. [doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.07.129]
Outeiro, M.T., Chibante, R., Carvalho, A.S., de Almeida, A.T., 2008. A parameter optimized model of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell including temperature effects. J. Power Sources, 185(2):952–960. [doi:10.1016/j. jpowsour.2008.08.019]
Outeiro, M.T., Chibante, R., Carvalho, A.S., de Almeida, A.T., 2009. A new parameter extraction method for accurate modeling of PEM fuel cell. Int. J. Energy Res., 33(11):978–988. [doi:10.1002/er.1525]
Springer, T.E., Zawodzinski, T.A., Gottesfeld, S., 1991. Polymer electrolyte fuel-cell model. J. Electrochem. Soc., 138(8):2334–2342. [doi:10.1149/1.2085971]
Yang, X.S., 2005. Engineering optimizations via nature-inspired virtual bee algorithms. LNCS, 3562:317–323. [doi:10.1007/11499305_33]
Ye, M., Wang, X., Xu, Y., 2009. Parameter identification for proton exchange membrane fuel cell model using particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Hydr. Energy, 34(2):981–989. [doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.11.026]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Renewable Energy Organization of Iran (SANA)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Askarzadeh, A., Rezazadeh, A. A new artificial bee swarm algorithm for optimization of proton exchange membrane fuel cell model parameters. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 12, 638–646 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1000355
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1000355
Key words
- Proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack model
- Parameter optimization
- Artificial bee swarm optimization algorithm