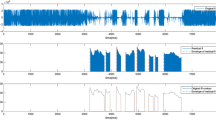
Abstract
A method based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) is proposed for accurately detecting the time varying pitch of speech in tonal languages. Unlike frame-, event-, or subspace-based pitch detectors, the time varying information of pitch within the short duration, which is of crucial importance in speech processing of tonal languages, can be accurately extracted. The Chinese Linguistic Data Consortium (CLDC) database for Mandarin Chinese was employed as standard speech data for the evaluation of the effectiveness of the method. It is shown that the proposed method provides more accurate and reliable results, particularly in estimating the tones of non-monotonically varying pitches like the third one in Mandarin Chinese. Also, it is shown that the new method has strong resistance to noise disturbance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananthapadmanabha, T., Yegnanarayana, B., 1975. Epoch extraction of voiced speech. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process., 23(6):562–570. [doi:10.1109/TASSP.1975.1162745]
Bekara, M., Baan, M.V.D., 2009. Random and coherent noise attenuation by empirical mode decomposition. Geophysics, 74(5):89–98. [doi:10.1190/1.3157244]
Boersma, P., 2002. Praat, a system for doing phonetics by computer. Glot Int., 5:341–345.
Chan, K.W., So, H.C., 2004. Accurate frequency estimation for real harmonic sinusoids. IEEE Signal Process. Lett., 11(7):609–612. [doi:10.1109/LSP.2004.830115]
Chang, E., Zhou, J., Di, S., Huang, C., Lee, K., 2000. Large Vocabulary Mandarin Speech Recognition with Different Approaches in Modeling Tones. Proc. Int. Conf. on Spoken Language Processing, p.983–986.
Cheng, Y.M., O’shaughnessy, D., 1989. Automatic and reliable estimation of glottal closure instant and period. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process., 37(12):1805–1815. [doi:10.1109/29.45529]
Christensen, M.G., Jakobsson, A., Jensen, S.H., 2007. Joint high-resolution fundamental frequency and order estimation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process., 15(5):1635–1644. [doi:10.1109/TASL.2007.899267]
Christensen, M.G., Stoica, P., Jakobsson, A., Jensen, S.H., 2008. Multi-pitch estimation. Signal Process., 88(4):972–983. [doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2007.10.014]
de Cheveigne, A., Kawahara, H., 2002. YIN, a fundamental frequency estimator for speech and music. J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 111(4):1917–1930. [doi:10.1121/1.1458024]
Deller, J., Proakis, J., Hanson, J., 1993. Discrete-Time Processing of Speech Signals. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA.
Goska, A., Krawiecki, A., 2006. Analysis of phase synchronization of coupled chaotic oscillators with empirical mode decomposition. Phys. Rev. E, 74(4):046217. [doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.74.046217]
Hong, H., Wang, X.L., Tao, Z.Y., 2009. Local integral mean-based sifting for empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett., 16(10):841–844. [doi:10.1109/LSP.2009.2025925]
Huang, H., Pan, J., 2006. Speech pitch determination based on Hilbert-Huang transform. Signal Process., 86(4):792–803. [doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2005.06.011]
Huang, N.E., Wu, Z., 2007. An adaptive data analysis method for nonlinear and nonstationary time series: the empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis. Wavel. Anal. Appl., 1(4):363–376. [doi:10.1007/978-3-7643-7778-6_25]
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R., Wu, M.C., Shih, H.H., Zheng, Q., Yen, N.C., Tung, C.C., Liu, H.H., 1998. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A, 454:903–995. [doi:10.1098/rspa.1998.0193]
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S., 1999. A new view of nonlinear water waves: the Hilbert spectrum. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech., 31(1):417–459. [doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.31.1.417]
Huang, N.E., Chern, C.C., Huang, K., Salvino, L.W., Long, S.R., Fan, K.L., 2001. A new spectral representation of earthquake data: Hilbert spectral analysis of Station TCU129, Chi-Chi, Taiwan, 21 September 1999. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am., 91(5):1310–1338. [doi:10.1785/0120000735]
Jánosi, I.M., Müller, R., 2005. Empirical mode decomposition and correlation properties of long daily ozone records. Phys. Rev. E, 71(5):056126. [doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.71.056126]
Kadambe, S., Boudreaux-Bartels, G.F., 1992. Application of the wavelet transform for pitch detection of speech signals. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, 38(2):917–924. [doi:10.1109/18.119752]
Lei, Y.G., He, Z.J., Zi, Y.Y., 2009. Application of the EEMD method to rotor fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Mech. Syst. Signal Process., 23(4):1327–1338. [doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2008.11.005]
Li, H.B., Stoica, P., Li, J., 2000. Computationally efficient parameter estimation for harmonic sinusoidal signals. Signal Process., 80(9):1937–1944. [doi:10.1016/S0165-1684(00)00103-1]
Liang, H., Lin, Z., McCallum, R.W., 2000. Artifact reduction in electrogastrograms based on the empirical mode decomposition. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., 38(1):35–41. [doi:10.1007/BF02344686]
Lin, S.L., Tung, P.C., Huang, N.E., 2009. Data analysis using a combination of independent component analysis and empirical mode decomposition. Phys. Rev. E, 79(6):066705. [doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.79.066705]
Noll, A.M., 1967. Cepstrum pitch determination. J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 41(2):293–309. [doi:10.1121/1.1910339]
Pai, P.F., Palazotto, A.N., 2008. Detection and identification of nonlinearities by amplitude and frequency modulation analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process., 22(5):1107–1132. [doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2007.11.006]
Qi, K., He, Z.J., Zi, Y.Y., 2007. Cosine window-based boundary processing method for EMD and its application in rubbing fault diagnosis application in rubbing fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process., 21(7):2750–2760. [doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2007.04.007]
Resch, B., Nilsson, M., Ekman, A., Kleijn, W.B., 2007. Estimation of the instantaneous pitch of speech. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process., 15(3):813–822. [doi:10.1109/TASL.2006.885242]
Schlurmann, T., Dose, T., Schimmels, S., 2001. Characteristic Modes of the ‘Adreanov Tsunami’ Based on the Hilbert-Huang Transformation. Proc. 4th Int. Symp. on Ocean Wave Measurement and Analysis, 2:1525–1534. [doi:10.1061/40604(273)154]
Talkin, D., 1995. A robust algorithm for pitch tracking (RAPT). Speech Cod. Synth., 14:495–518.
Wang, C., Seneff, S., 1998. A Study of Tones and Tempo in Continuous Mandarin Digit Strings and Their Application in Telephone Quality Speech Recognition. Proc. Int. Conf. on Spoken Language Processing, p.635–638.
Wu, Z., Huang, N.E., 2009. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal., 1(1):1–41. [doi:10.1142/S1793536909000047]
Xu, G.L., Wang, X.T., Xu, X.G., 2009. Time-varying frequency-shifting signal-assisted empirical mode decomposition method for AM-FM signals. Mech. Syst. Signal Process., 23(8):2458–2469. [doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2009.06.006]
Zhang, J.X., Christensen, M.G., Jensen, S.H., Moonen, M., 2010. A robust and computationally efficient subspace-based fundamental frequency estimator. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process., 18(3):487–497. [doi:10.1109/TASL.2010.2040786]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 10574070) and the State Key Laboratory Foundation of China (No. 9140C240207060C24)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, H., Zhu, Xh., Su, Wm. et al. Detection of time varying pitch in tonal languages: an approach based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 13, 139–145 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1100092
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1100092