Abstract
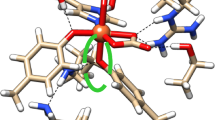
Various molecular docking software packages are available for modeling interactions between small molecules and proteins. However, there have been few reports of modeling the interactions between metal ions and metalloproteins. In this study, the AutoDock package was employed to example docking into a di-iron binding protein, bacterioferritin. Each binding site of this protein was tested for docking with iron ions. Blind docking experiments showed that all docking conformations converged into two clusters, one for internal iron binding in sites within the metalloprotein and the other for external iron binding on the protein surface. Local docking experiments showed that there were significant differences between two internal iron binding sites. Docking at one site gave a reasonable root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) distribution with relatively low binding energy. Analysis of the binding mode quality for this site revealed that more than half of the docking conformations were categorized as having good binding geometry, while no good conformations were found for the other site. Further investigations indicated that coordinating water molecules contributed to the stability of binding geometries. This study provides an empirical approach towards the study of molecular docking in metalloproteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananthanarayanan, V.S., Kerman, A., 2006. Role of metal ions in ligand receptor interaction: insights from structural studies. Mol. Cell. Endocr., 246(1–2):53–59. [doi:10. 1016/j.mce.2005.11.023]
Bissantz, C., Folkers, G., Rognan, D., 2000. Protein-based virtual screening of chemical databases. I. Evaluation of different docking/scoring combinations. J. Med. Chem., 43(25):4759–4767. [doi:10.1021/jm001044l]
Böhm, H.J., 1998. Prediction of binding constants of protein ligands: a fast method for the prioritization of hits obtained from de novo design or 3D database search programs. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des., 12(4):309–323. [doi:10.1023/A:1007999920146]
Chen, D., Menche, G., Power, T.D., Sower, L., Peterson, J.W., Schein, C.H., 2007. Accounting for ligand-bound metal ions in docking small molecules on adenylyl cyclase toxins. Proteins, 67(3):593–605. [doi:10.1002/prot.21249]
Ferrara, P., Gohlke, H., Price, D.J., Klebe, G., Brooks, C.L.I., 2004. Assessing scoring functions for protein-ligand interactions. J. Med. Chem., 47(12):3032–3047. [doi:10. 1021/jm030489h]
Friesner, R.A., Banks, J.L., Murphy, R.B., Halgren, T.A., Klicic, J.J., Mainz, D.T., Repasky, M.P., Knoll, E.H., Shelley, M., Perry, J.K., et al., 2004. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. I. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem., 47(7):1739–1749. [doi:10.1021/jm0306430]
Halgren, T.A., Murphy, R.B., Friesner, R.A., Beard, H.S., Frye, L.L., Pollard, W.T., Banks, J.L., 2004. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. Part 2: Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem., 47(7):1750–1759. [doi:10.1021/jm030644s]
Halperin, I., Ma, B.Y., Wolfson, H., Nussinov, R., 2002. Principles of docking: an overview of search algorithms and a guide to scoring functions. Proteins, 47(4):409–443. [doi:10.1002/prot.10115]
Hu, X., Shelver, W.H., 2003. Docking studies of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: zinc parameter optimization to improve the binding free energy prediction. J. Mol. Graph. Model., 22(2):115–126. [doi:10.1016/S1093-3263(03)00 153-0]
Huey, R., Morris, G.M., Olson, A.J., Goodsell, D.S., 2007. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J. Comput. Chem., 28(6):1145–1152. [doi:10. 1002/jcc.20634]
Jones, G., Willett, P., Glen, R.C., Leach, A.R., Taylor, R., 1997. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol., 267(3):727–748. [doi:10. 1006/jmbi.1996.0897]
Khandelwal, A., Lukacova, V., Comez, D., Kroll, D., Raha, S., Balaz, S., 2005. A combination of docking, QM/MM methods, and MD simulation for binding affinity estimation of metalloprotein ligands. J. Med. Chem., 48(17): 5437–5447. [doi:10.1021/jm049050v]
Kramer, B., Rarey, M., Lengauer, T., 1999. Evaluation of the FLEXX incremental construction algorithm for protein-ligand docking. Proteins, 37(2):228–241. [doi:10.1002/ (SICI)1097-0134(19991101)37:2〈228::AID-PROT8〉3.0.C O;2-8]
Kurtz, D.M.Jr., 1997. Structural similarity and functional diversity in diiron-oxo proteins. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2(2):159–167. [doi:10.1007/s007750050120]
Morris, G.M., Goodsell, D.S., Huey, R., Olson, A.J., 1996. Distributed automated docking of flexible ligands to proteins: parallel applications of AutoDock 2.4. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des., 10(4):293–304. [doi:10.1007/BF00124499]
Morris, G.M., Goodsell, D.S., Halliday, R.S., Huey, R., Hart, W.E., Belew, R.K., Olson, A.J., 1998. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem., 19(14): 1639–1662. [doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19981115)19: 14〈1639::AID-JCC10〉3.0.CO;2-B]
Spyrakis, F., Amadasi, A., Fornabaio, M., Abraham, D.J., Mozzarelli, A., Kellogg, G.E., Cozzini, P., 2007. The consequences of scoring docked ligand conformations using free energy correlations. Eur. J. Med. Chem., 42(7):921–933. [doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2006.12.037]
Venkatachalam, C.M., Jiang, X., Oldfield, T., Waldman, M., 2003. LigandFit: a novel method for the shape-directed rapid docking of ligands to protein active sites. J. Mol. Graph. Model., 21(4):289–307. [doi:10.1016/S1093-3263 (02)00164-X]
Warren, G.L., Andrews, C.W., Capelli, A.M., Clarke, B., LaLonde, J., Lambert, M.H., Lindvall, M., Nevins, N., Semus, S.F., Senger, S., et al., 2006. A critical assessment of docking programs and scoring functions. J. Med. Chem., 49(20):5912–5931. [doi:10.1021/jm050362n]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 2011-II-010) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Liu, P. & Xie, H. An empirical molecular docking study of a di-iron binding protein with iron ions. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 14, 118–124 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1200072
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1200072