Abstract
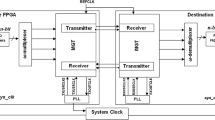
High-speed, fixed-latency serial links find application in distributed data acquisition and control systems, such as the timing trigger and control (TTC) system for high energy physics experiments. However, most high-speed serial transceivers do not keep the same chip latency after each power-up or reset, as there is no deterministic phase relationship between the transmitted and received clocks after each power-up. In this paper, we propose a fixed-latency serial link based on high-speed transceivers embedded in Xilinx field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). First, we modify the configuration and clock distribution of the transceiver to eliminate the phase difference between the clock domains in the transmitter/receiver. Second, we use the internal alignment circuit of the transceiver and a digital clock manager (DCM)/phase-locked loop (PLL) based clock generator to eliminate the phase difference between the clock domains in the transmitter and receiver. The test results of the link latency are shown. Compared with existing solutions, our design not only implements fixed chip latency, but also reduces the average system lock time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliaga, R.J., Monzo, J.M., Spaggiari, M., et al., 2011. PET system synchronization and timing resolution using highspeed data links. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 58(4):1596–1605. [doi:10.1109/TNS.2011.2140130]
Aloisio, A., Cevenini, F., Giordano, R., et al., 2009. Highspeed, fixed-latency serial links with FPGAs for synchronous transfers. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 56(5):2864–2873. [doi:10.1109/TNS.2009.2027236]
Aloisio, A., Cevenini, F., Giordano, R., et al., 2010. Emulating the GLink chip set with FPGA serial transceivers in the ATLAS Level-1 Muon trigger. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 57(2):467–471. [doi:10.1109/TNS.2009.2036175]
Aloisio, A., Ameli, F., Bocci, V., et al., 2013. Design, implementation and test of the timing trigger and control receiver for the LHC. J. Instrum., 8(2):T02003. [doi:10. 1088/1748-0221/8/02/T02003]
Giordano, R., Aloisio, A., 2011. Fixed-latency, multi-gigabit serial links with Xilinx FPGAs. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 58(1):194–201. [doi:10.1109/TNS.2010.2101083]
Giordano, R., Aloisio, A., 2012. Protocol-independent, fixedlatency links with FPGA-embedded SerDeses. J. Instrum., 7(5):P05004. [doi:10.1088/1748-0221/7/05/P05004]
Lemke, F., Slogsnat, D., Burkhardt, N., et al., 2010. A unified DAQ interconnection network with precise time synchronization. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 57(2):412–418. [doi:10.1109/TNS.2010.2042176]
Le-Provost, H., Moudden, Y., Anvar, S., et al., 2011. A readout system-on-chip for a cubic kilometer submarine neutrino telescope. J. Instrum., 6(12):C12044. [doi:10.1088/1748-0221/6/12/C12044]
Moreira, P., Marchioro, A., Kloukinas, K., 2007. The GBT: a proposed architecture for multi-Gb/s data transmission in high energy physics. Proc. Topical Workshop on Electronics for Particle Physics, p.332–336.
Taylor, B.G., 1998. TTC distribution for LHC detectors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 45(3):821–828. [doi:10.1109/23.682644]
Texas Instruments (TI), 2013. SCAN25100 2457.6, 1228.8, and 614.4 Mbps CPRI SerDes with Auto RE Sync and Precision Delay Calibration Measurement. Available from http://www.ti.com.cn/cn/lit/ds/symlink/scan25100.pdf
Widmer, A.X., Franaszek, P.A., 1983. A DC-balanced, partitioned-block, 8b/10b transmission code. IBM J. Res. Devel., 27(5):440–451. [doi:10.1147/rd.275.0440]
Xilinx, 2009a. UG196 Virtex-5 FPGA RocketIO GTP Transceiver User Guide v2.1. Available from http://www.xilinx. com/support/documentation/user_guides/ug196.pdf
Xilinx, 2009b. UG198 Virtex-5 FPGA RocketIO GTX Transceiver User Guide v3.0. Available from http://www.xilinx. com/support/documentation/user_guides/ug198.pdf
Xilinx, 2011. UG347 ML505/ML506/ML507 Evaluation Platform User Guide v3.1.2. Available from http://www.xilinx. com/support/documentation/boards_and_kits/ug347.pdf
Xilinx, 2012. UG190 Virtex-5 FPGA User Guide v5.4. Available from http://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/user_ guides/ug190.pdf
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Science and Technology Support Program of China (No. 2012BAK24B01), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (No. N100204001), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, China (No. 20110042110021), and the National Science Foundation for Post-doctoral Scientists of China (No. 2013M541243)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Deng, Qx., Hou, Bn. et al. High-speed, fixed-latency serial links with Xilinx FPGAs. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 15, 153–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300249
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300249