Abstract
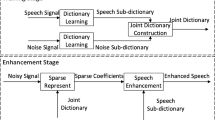
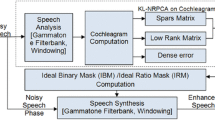
Speech communication is often influenced by various types of interfering signals. To improve the quality of the desired signal, a generalized sidelobe canceller (GSC), which uses a reference signal to estimate the interfering signal, is attracting attention of researchers. However, the interference suppression of GSC is limited since a little residual desired signal leaks into the reference signal. To overcome this problem, we use sparse coding to suppress the residual desired signal while preserving the reference signal. Sparse coding with the learned dictionary is usually used to reconstruct the desired signal. As the training samples of a desired signal for dictionary learning are not observable in the real environment, the reconstructed desired signal may contain a lot of residual interfering signal. In contrast, the training samples of the interfering signal during the absence of the desired signal for interferer dictionary learning can be achieved through voice activity detection (VAD). Since the reference signal of an interfering signal is coherent to the interferer dictionary, it can be well restructured by sparse coding, while the residual desired signal will be removed. The performance of GSC will be improved since the estimate of the interfering signal with the proposed reference signal is more accurate than ever. Simulation and experiments on a real acoustic environment show that our proposed method is effective in suppressing interfering signals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon, A.M., Elad, M., 2006. K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 54(11):4311–4322. [doi:10.1109/TSP.2006.881199]
Avargel, Y., Cohen, I., 2008. Adaptive system identification in the short-time fourier transform domain using cross-multiplicative transfer function approximation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process., 16(1):162–173. [doi:10.1109/TASL.2007.910789]
Elad, M., Aharon, M., 2006. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 15(12):3736–3745. [doi:10.1109/TIP.2006.881969]
Engan, K., Skretting, K., Husøy, J.H., 2007. Family of iterative LS-based dictionary learning algorithms, ILSDLA, for sparse signal representation. Dig. Signal Process., 17(1):32–49. [doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2006.02.002]
Eshaghi, M., Karami Mollaei, M., 2010. Voice activity detection based on using wavelet packet. Dig. Signal Process., 20(4):1102–1115. [doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2009.11.008]
Gannot, S., Burshtein, D., Weinstein, E., 2001. Signal enhancement using beamforming and nonstationarity with applications to speech. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 49(8):1614–1626. [doi:10.1109/78.934132]
Gemmeke, J.F., Cranen, B., 2009. Sparse imputation for noise robust speech recognition using soft masks. IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, p.4645–4648. [doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2009.4960666]
Gribonval, R., Schnass, K., 2008. Some recovery conditions for basis learning by ℓ 1-minimization. IEEE 3rd Int. Symp. on Communications, Control and Signal Processing, p.768–773. [doi:10.1109/ISCCSP.2008.4537326]
Griffiths, L., Jim, C., 1982. An alternative approach to linearly constrained adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 30(1):27–34. [doi:10.1109/TAP.1982.1142739]
Habets, E.A.P., 2010. Room Impulse Response Generator for MATLAB. Univeristy of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Bavaria, Germany.
He, Y., Han, J., Deng, S., et al., 2012. A solution to residual noise in speech denoising with sparse representation. IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, p.4653–4656. [doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2012.6288956]
Herbordt, W., Kellermann, W., 2001. Efficient frequencydomain realization of robust generalized sidelobe cancellers. IEEE 4th Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, p.377–382. [doi:10.1109/MMSP.2001.962763]
Hoshuyama, O., Sugiyama, A., Hirano, A., 1999. A robust adaptive beamformer for microphone arrays with a blocking matrix using constrained adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 47(10):2677–2684. [doi:10.1109/78.790650]
ITU, 2007. Wideband Extension to Rec. P.862 for the Assessment of Wideband Telephone Networks and Speech Codecs, P.862.2. International Telecommunication Union, Geneva.
Kowalski, M., Torrésani, B., 2008. Random models for sparse signals expansion on unions of bases with application to audio signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 56(8):3468–3481. [doi:10.1109/TSP.2008.920144]
Krueger, A., Warsitz, E., Haeb-Umbach, R., 2011. Speech enhancement with a GSC-like structure employing eigenvector-based transfer function ratios estimation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process., 19(1):206–219. [doi:10.1109/TASL.2010.2047324]
Mairal, J., Bach, F., Ponce, J., et al., 2010. Online learning for matrix factorization and sparse coding. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 11:19–60.
Martin, R., 2001. Noise power spectral density estimation based on optimal smoothing and minimum statistics. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process., 9(5):504–512. [doi:10.1109/89.928915]
Martin, R., 2006. Bias compensation methods for minimum statistics noise power spectral density estimation. Signal Process., 86(6):1215–1229. [doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2005.07.037]
Plumbley, M.D., Blumensath, T., Daudet, L., et al., 2010. Sparse representations in audio and music: from coding to source separation. Proc. IEEE, 98(6):995–1005. [doi:10.1109/JPROC.2009.2030345]
Rauhut, H., Schnass, K., Vandergheynst, P., 2008. Compressed sensing and redundant dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 54(5):2210–2219. [doi:10.1109/TIT.2008.920190]
Rebollo-Neira, L., 2004. Dictionary redundancy elimination. IEEE Proc.-Vis. Image Signal Process., 151(1):31–34. [doi:10.1049/ip-vis:20040294]
Sigg, C.D., Dikk, T., Buhmann, J.M., 2012. Speech enhancement using generative dictionary learning. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process., 20(6):1698–1712. [doi:10.1109/TASL.2012.2187194]
Skretting, K., Engan, K., 2010. Recursive least squares dictionary learning algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 58(4):2121–2130. [doi:10.1109/TSP.2010.2040671]
Sohn, J., Kim, N.S., Sung, W., 1999. A statistical modelbased voice activity detection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett., 6(1):1–3. [doi:10.1109/97.736233]
Talmon, R., Cohen, I., Gannot, S., 2009. Convolutive transfer function generalized sidelobe canceler. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process., 17(7):1420–1434. [doi:10.1109/TASL.2009.2020891]
Tanyer, S.G., Ozer, H., 2000. Voice activity detection in nonstationary noise. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process., 8(4):478–482. [doi:10.1109/89.848229]
Wright, S.J., Nowak, R.D., Figueiredo, M.A.T., 2009. Sparse reconstruction by separable approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 57(7):2479–2493. [doi:10.1109/TSP.2009.2016892]92]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (No. 2012CB316400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61171151)
ORCID: Li-chun YANG, http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1651-798X; Yun-tao QIAN, http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7418-5891
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Lc., Qian, Yt. Speech enhancement with a GSC-like structure employing sparse coding. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 15, 1154–1163 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1400085
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1400085
Key words
- Generalized sidelobe canceller
- Speech enhancement
- Voice activity detection
- Dictionary learning
- Sparse coding