Abstract
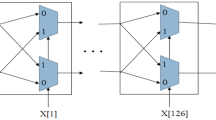
An arbiter physical unclonable function (A-PUF) for solving the identification problem of digital devices is investigated. Conducted experiments by the example of a Xilinx SPARTAN-3E XC3s500e-5FG320 logic integrated circuit on a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuyls, P., Security with Noisy Data, London: Springer-Verlag, 2007.
Ruhmair, U., Solter, J., and Sehn, F., On the foundations of physical unclonable functions, Cryptology, ePrint Archive. http://eprint.iacr.org/2009/277.pdf
Suh, E. and Devadas, S., Physical unclonable functions for device authentication and secret key generation, Proc. 44th Design Automation Conf., San Diego, 2007, pp. 9–14.
Soybali, M., Ors, B., and Saldamli, G., Implementation of a PUF circuit on a FPGA, Proc. Conf. on New Technologies, Mobility and Security (NTMS), 2011.
Ganta, D. and Nazhandali, L., Easy-to-build arbiter physical unclonable function with enhanced challenge/response set, Proc. Quality Electronic Design (ISQED) Int. Symp., Santa Clara, 2013, pp. 733–738.
Yingjie, Lao and Parhi, K.K., Statistical analysis of MUX-based physical unclonable functions, Computer–Aided Design of Integr. Circuits and Systems, 2014, vol. 33, pp. 649–662.
Takanori, M., Yamamoto, D., Iwamoto, M., and Sakiyama, K., A new mode of operation for arbiter PUF to improve uniqueness on FPGA, Proc. Feder. Conf. on Compt. Sci. Inform. Syst., 2014, pp. 871–878.
Yarmolik, V.N. and Vashinko, V.G., Physical unclonable functions, Informatika, 2011, no. 2, pp. 90–100.
ISE WebPACK Design Software (Electronic Resource), Xilinx, http://www.xilinx.com/products/design-tools/ise-design-suite/ise-webpack.html, 2015.
Roth, C.H., Digital System Design using VHDL, Boston: PWS Publ., 1998.
Seung-Seok Choi., Sung-Hyuk Cha., and Tappert, C.C., A survey of binary similarity and distance measures, Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics, 2010, vol. 8, pp. 43–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.P. Klybik, A.A. Ivaniuk, 2015, published in Avtomatika i Vychislitel’naya Tekhnika, 2015, No. 3, pp. 24–34.
About this article
Cite this article
Klybik, V.P., Ivaniuk, A.A. Use of arbiter physical unclonable function to solve identification problem of digital devices. Aut. Control Comp. Sci. 49, 139–147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411615030049
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411615030049